Welcome to our informative article on the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Understanding these two types of strokes is crucial for recognizing the signs and symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and receiving the appropriate treatment.
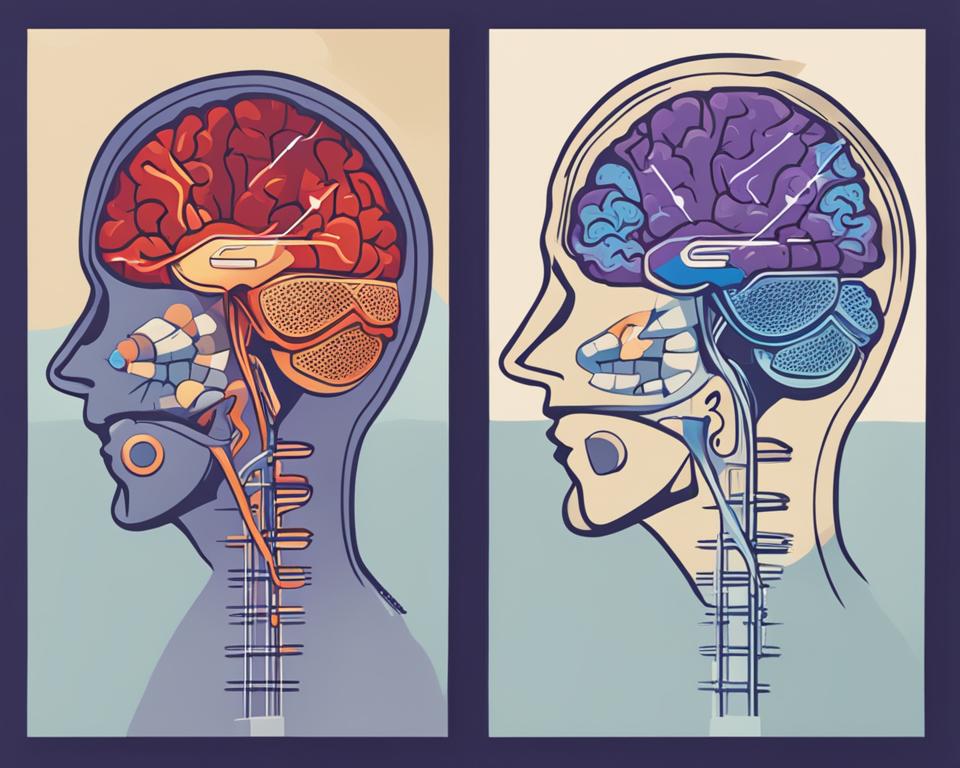
Ischemic stroke occurs when there is a lack of blood supply to the brain due to a clot or blockage in an artery. It accounts for 87% of all strokes and can result in brain death in the affected area. On the other hand, hemorrhagic stroke is caused by bleeding into the brain tissue due to a ruptured blood vessel. It accounts for 13% of all strokes and can present with sudden, severe symptoms such as headache, vomiting, and rapid deterioration in neurological function.
Both types of stroke require immediate medical attention. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, treatment options, risk factors, and preventive measures for each type of stroke, providing you with valuable insights to help you better understand this medical condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Ischemic stroke is caused by a lack of blood supply to the brain, while hemorrhagic stroke is caused by bleeding into the brain tissue.
- Ischemic stroke accounts for 87% of all strokes, while hemorrhagic stroke accounts for 13%.
- Both types of stroke require immediate medical attention.
- Symptoms of ischemic stroke may include numbness or weakness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, and visual disturbances.
- Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke may include sudden, severe headache, vomiting, seizure, and loss of consciousness.
Causes and Symptoms of Ischemic Stroke
An ischemic stroke occurs when there is a lack of blood supply to the brain due to a clot or blockage in an artery. Understanding the causes and recognizing the symptoms of ischemic stroke is crucial for prompt medical intervention.
The most common cause of ischemic stroke is atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque can rupture or become lodged in a blood vessel, leading to reduced blood flow to the brain. Other causes include high blood pressure and heart disease, which can contribute to the formation of blood clots that disrupt blood flow in the brain.
Recognizing the symptoms of ischemic stroke is essential for seeking immediate medical attention. Common symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the body or face, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, confusion, and visual disturbances. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, it is important to call emergency services right away.
| Common Causes of Ischemic Stroke | Symptoms of Ischemic Stroke |
|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis | Numbness or weakness on one side of the body or face |
| High blood pressure | Difficulty speaking or understanding speech |
| Heart disease | Confusion |
| Visual disturbances |
Immediate medical intervention is crucial in the case of an ischemic stroke. Thrombolytic medication such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) can be administered to dissolve the clot causing the stroke. Mechanical thrombectomy may also be performed to remove the clot. Timely treatment can minimize brain damage and improve the chances of recovery.
Causes and Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a ruptured blood vessel in the brain, leading to bleeding into the brain tissue. This type of stroke accounts for 13% of all strokes and can have severe and sudden symptoms. Understanding the causes and recognizing the symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke is crucial for prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment.
Causes
There are several common causes of hemorrhagic stroke. One of the main causes is weakened blood vessels, which can be a result of conditions such as high blood pressure or arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Aneurysms, which are weakened and bulging areas in the blood vessels, can also lead to hemorrhagic stroke. Other less common causes include head trauma, blood-thinning medications, and certain medical conditions such as liver disease or blood disorders.
Symptoms
Hemorrhagic stroke can present with sudden, severe symptoms that require immediate medical attention. Common symptoms include a sudden and severe headache, often described as the worst headache of one’s life. Other symptoms may include vomiting, seizures, loss of consciousness, confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, weakness or numbness on one side of the body, and vision changes. It is important to note that the symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke can vary depending on the location and extent of the bleeding.
| Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Sudden, severe headache | Described as the worst headache of one’s life |
| Vomiting | Often accompanied by the severe headache |
| Seizures | Can occur due to the bleeding in the brain |
| Loss of consciousness | May occur as a result of the brain’s response to the bleeding |
| Confusion | Difficulty thinking clearly or understanding information |
| Difficulty speaking or understanding speech | May be accompanied by slurred speech or language difficulties |
| Weakness or numbness on one side of the body | Can affect the face, arm, or leg on one side |
| Vision changes | Blurry vision, double vision, or complete loss of vision in one or both eyes |
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Calling emergency services is essential to ensure prompt evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment, which can help prevent further brain damage and improve outcomes.
Treatment Options for Ischemic Stroke
When it comes to the treatment of ischemic stroke, the main goal is to restore blood flow to the brain as quickly as possible. The gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke is the administration of thrombolytic medication, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). This medication helps to dissolve the clot that is causing the blockage. Studies have shown that when tPA is given within the first few hours of the onset of symptoms, it can significantly improve the chances of a good recovery.
In addition to thrombolytic medication, mechanical thrombectomy is another effective treatment option for ischemic stroke. This procedure involves physically removing the clot from the blocked blood vessel in the brain. It is typically performed on patients with large-vessel occlusion strokes. Mechanical thrombectomy has shown to be highly successful in restoring blood flow and reducing disability in these cases.
It is important to note that the success of these treatments depends on the timeliness of their administration. Time is of the essence when it comes to ischemic stroke, as every minute without treatment can result in the death of millions of brain cells. That is why it is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms of a stroke, such as sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or visual disturbances, to seek immediate medical attention by calling 911.
Table: Comparison of Ischemic Stroke Treatments
| Treatment Option | Description | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Thrombolytic Medication (tPA) | Administered intravenously to dissolve the clot causing the stroke. | High success rate when given within the first few hours of symptoms. |
| Mechanical Thrombectomy | Involves physically removing the clot from the blocked blood vessel in the brain. | High success rate for large-vessel occlusion strokes. |
In conclusion, early intervention is crucial in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Thrombolytic medication and mechanical thrombectomy are effective options for restoring blood flow to the brain and improving outcomes. However, it is important to remember that time is of the essence, and seeking immediate medical attention is paramount. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of a stroke and acting quickly, individuals can increase their chances of a successful recovery.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment. The specific treatment options depend on the type and severity of the bleeding. In cases of intracerebral hemorrhage, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the blood clot and stop the bleeding. This can involve procedures such as craniotomy or minimally invasive techniques like stereotactic aspiration. For subarachnoid hemorrhage, which occurs in the space surrounding the brain, treatments such as surgical clipping or coiling may be performed to address the underlying cause and prevent future bleeding episodes.
There are various goals of treatment for hemorrhagic stroke, including stopping the bleeding, relieving pressure on the brain, and preventing further damage. In some cases, medications may be used to control blood pressure and reduce the risk of further bleeding. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke occur, as early intervention can improve outcomes and minimize the long-term effects of the stroke.
| Treatment Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgical Intervention | Includes procedures such as craniotomy, stereotactic aspiration, surgical clipping, or coiling to remove the blood clot or address the underlying cause of bleeding. |
| Medication | May be used to control blood pressure, prevent further bleeding, and manage other symptoms. |
| Monitoring and Supportive Care | Patient monitoring, including frequent neurological assessments, to ensure adequate oxygenation and prevent complications. Supportive care may include managing symptoms, providing physical therapy, and facilitating rehabilitation. |
| Preventive Measures | Addressing underlying risk factors such as hypertension, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of future strokes. |
“Immediate medical attention is critical in cases of hemorrhagic stroke. Early intervention can help stop the bleeding, relieve pressure on the brain, and improve overall outcomes.”
Risk Factors and Prevention of Stroke
Stroke is a serious medical condition that can have devastating consequences. Understanding the risk factors associated with stroke and taking preventive measures is crucial for maintaining good health. By identifying and addressing these risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of experiencing a stroke.
Risk Factors
There are several common risk factors that increase the likelihood of having a stroke. These include:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Sedentary lifestyle
These risk factors can contribute to the development of conditions such as atherosclerosis, which can lead to a stroke. It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take proactive steps to manage them.
Prevention
Preventing stroke involves making positive lifestyle changes and managing underlying health conditions. Here are some preventive measures that can be taken:
- Quit smoking
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Engage in regular exercise
- Manage hypertension and diabetes
- Control cholesterol levels
- Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
These preventive measures not only reduce the risk of stroke but also promote overall well-being. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for guidance and support in implementing these lifestyle changes.
| Risk Factors | Prevention Measures |
|---|---|
| High blood pressure | Monitor blood pressure regularly and take prescribed medications |
| Smoking | Quit smoking and seek support if needed |
| Obesity | Maintain a healthy weight through proper diet and regular exercise |
| Diabetes | Manage blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and exercise |
| Sedentary lifestyle | Engage in regular physical activity and reduce sedentary behaviors |
By taking proactive steps to address risk factors and make positive lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of stroke. Prevention is key when it comes to stroke, and every effort made towards maintaining a healthy lifestyle can have a significant impact on overall well-being.
The Importance of Early Intervention
People need to recognize the symptoms of stroke and take immediate action to seek medical attention. Stroke is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to minimize the damage to the brain. Remember the acronym “BE FAST” to identify potential stroke symptoms: Balance loss, Eye vision changes, Facial drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, and Time to call 911.
By calling emergency services, individuals enable early intervention and ensure timely administration of stroke treatments. This significantly increases the chances of recovery and minimizes long-term effects. Remember, time is of the essence when dealing with strokes. Quick action can save lives and help preserve brain function.
If you or someone around you experiences any of the symptoms associated with stroke, do not wait or try to self-diagnose. Instead, immediately call 911 or your local emergency number. Emergency medical professionals are equipped to provide the necessary care and transport you to a stroke center where specialized treatment can be administered.
Stroke symptoms can be sudden and severe, so it is vital to stay vigilant and act promptly. Time lost can lead to irreversible damage and long-term disability. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of stroke and calling 911 without delay, you can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
| Stroke Symptoms | Importance of Early Intervention |
|---|---|
| Numbness or weakness on one side of the body | Immediate medical attention can prevent further damage and enable timely treatment options. |
| Difficulty speaking or understanding speech | Early intervention increases the likelihood of a better recovery and minimizes long-term speech-related issues. |
| Sudden severe headache | Calling 911 allows for quick assessment and appropriate management to prevent further complications. |
| Loss of balance or coordination | Paramedics can provide on-site care and facilitate transportation to a stroke center for specialized treatment. |
Remember, stroke is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Don’t hesitate to call 911 if you suspect that you or someone around you may be experiencing a stroke. Quick action can make a significant difference in the outcome and quality of life after a stroke.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types, causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods for stroke is vital in promoting prompt medical intervention and reducing the risk of long-term complications. Ischemic stroke occurs when there is a blockage or clot in an artery, leading to a lack of blood supply to the brain. On the other hand, hemorrhagic stroke is caused by bleeding into the brain tissue due to a ruptured blood vessel. Both types of stroke require immediate medical attention to prevent further damage and improve outcomes.
By recognizing the common risk factors for stroke, such as high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent stroke. Making lifestyle modifications, like quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and managing chronic conditions, can significantly reduce the risk. Additionally, controlling cholesterol levels and following a balanced diet can also contribute to stroke prevention.
Recognizing the symptoms of stroke and acting promptly is crucial. Remember the acronym “BE FAST” to identify potential stroke symptoms: Balance loss, Eye vision changes, Facial drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, and Time to call 911. Seeking immediate medical attention by calling emergency services allows for early intervention and proper administration of stroke treatments, increasing the chances of recovery and minimizing long-term effects.
In conclusion, being knowledgeable about stroke types, causes, symptoms, treatment options, prevention methods, and risk factors empowers individuals to take control of their health and reduce the risk of experiencing a stroke. By promoting awareness and taking proactive measures, we can work together to prevent stroke and its potentially devastating impact on individuals and their families.
FAQ
What is the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke?
Ischemic stroke occurs when there is a lack of blood supply to the brain due to a clot or blockage in an artery, while hemorrhagic stroke is caused by bleeding into the brain tissue due to a ruptured blood vessel.
What are the causes and symptoms of ischemic stroke?
Ischemic stroke is usually caused by a clot, narrowing, or blockage in a brain or neck artery. Common causes include atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Symptoms can include numbness or weakness on one side of the body or face, difficulty speaking, and visual disturbances.
What are the causes and symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke?
Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a ruptured blood vessel in the brain, leading to bleeding into the brain tissue. Common causes include weakened blood vessels, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations. Symptoms can include sudden, severe headache, vomiting, seizure, and loss of consciousness.
What are the treatment options for ischemic stroke?
The gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke is thrombolytic medication, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which helps dissolve the clot causing the stroke. Mechanical thrombectomy, which involves removing the clot from the brain circulation, is also an effective treatment for large-vessel occlusion strokes.
What are the treatment options for hemorrhagic stroke?
The treatment options for hemorrhagic stroke depend on the type and severity of the bleeding. In cases of intracerebral hemorrhage, surgical intervention may be needed to remove the blood clot and stop the bleeding. For subarachnoid hemorrhage, treatments such as surgical clipping or coiling may be performed to address the underlying cause and prevent future bleeding episodes.
What are the risk factors and how can stroke be prevented?
Risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle. To reduce the risk of stroke, individuals should make lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and managing chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes. Additionally, controlling cholesterol levels and consuming a balanced diet can help prevent stroke.
Why is early intervention important in stroke cases?
Recognizing the symptoms of stroke and seeking immediate medical attention is crucial for optimal outcomes. The acronym “BE FAST” can help identify potential stroke symptoms: Balance loss, Eye vision changes, Facial drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, and Time to call 911. Calling emergency services allows for early intervention and timely administration of stroke treatments, increasing the chances of recovery and minimizing long-term effects.
What is the conclusion about stroke types, causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention, and risk factors?
Understanding the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke is essential for recognizing the signs and symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and receiving appropriate treatment. Risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle. By recognizing stroke risk factors and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing a stroke and its potentially devastating effects.