Welcome to our informative article where we will explore the key differences between pacemakers and defibrillators. If you’ve ever wondered about the variances and similarities between these two medical devices, you’ve come to the right place. Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
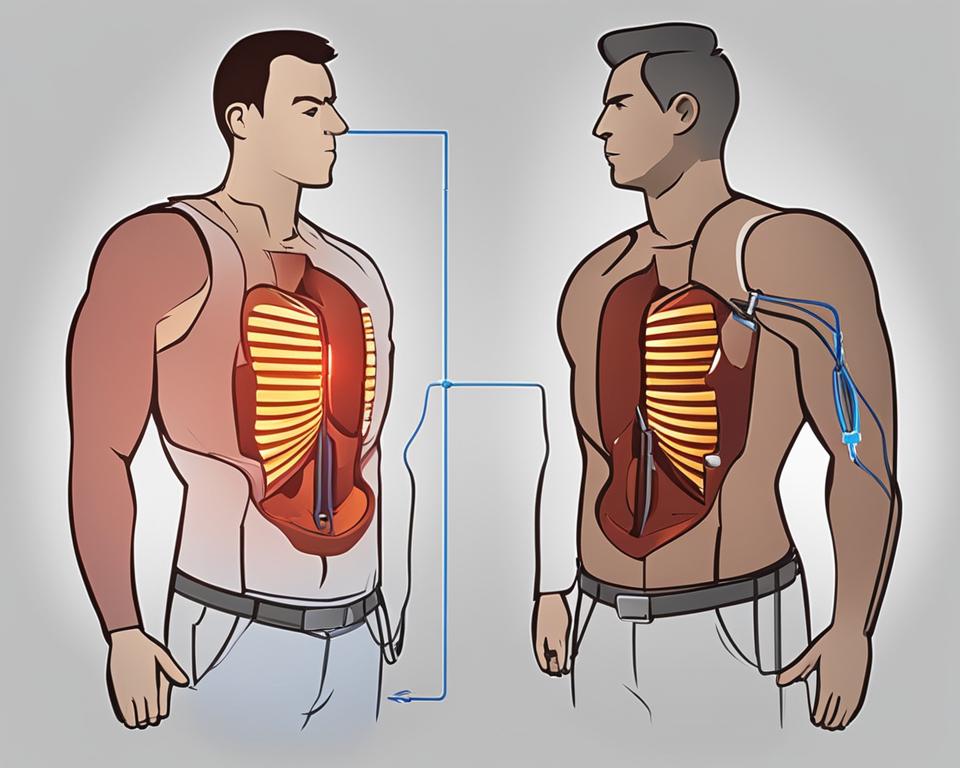
- A pacemaker provides ongoing regulation of the heartbeat, while a defibrillator delivers a shock when the heart’s function is dangerously abnormal.
- Pacemakers are used to restore a normal heart rate and rhythm when the heart beats too slowly or erratically, while defibrillators are used for life-threatening situations and for patients at risk of sudden cardiac death.
- In some cases, a patient may need both a pacemaker and a defibrillator implant if they have a heart condition that requires regular monitoring and modification of the heart’s function, as well as a higher risk of heart attacks.
- A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device that helps regulate the heart’s rhythm, while a defibrillator delivers an electric shock to restore abnormal heart function.
- Consulting with a doctor is crucial in determining the best treatment option for individual needs.
When is a Pacemaker Used?
A pacemaker is a small device implanted under the skin in the upper chest. It is used to regulate the heart’s rhythm and is typically recommended for patients with a slow heartbeat or irregular heart rhythm. When the heart beats too slowly, a pacemaker sends electrical impulses to stimulate the heart and maintain a normal heart rate and rhythm.
One common indication for a pacemaker is a condition called bradycardia, which is characterized by a heart rate that is too slow. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and fainting. A pacemaker helps alleviate these symptoms by ensuring that the heart beats at a healthy pace.
In addition to bradycardia, a pacemaker may be used after certain heart procedures, such as an ablation or heart valve surgery. These procedures can disrupt the heart’s electrical system, causing an irregular heartbeat. A pacemaker can help restore a stable heart rhythm and prevent further complications.
Pacemaker vs Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)
It’s important to note that a pacemaker is different from an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). While both devices are implanted under the skin and help manage heart conditions, they serve different purposes. A pacemaker regulates the heart’s rhythm and ensures a normal heartbeat, while an ICD is designed to deliver a shock when the heart’s function becomes dangerously abnormal.
In contrast to a pacemaker, an ICD is typically used in patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death due to abnormalities in heart function or a history of heart attacks. The ICD constantly monitors the heart’s activity and delivers a shock when necessary to restore a stable heartbeat.
Overall, a pacemaker is used when the heart beats too slowly or erratically, while an ICD is used for life-threatening situations and for patients at risk of sudden cardiac death. The specific device recommended depends on the individual’s heart condition and risks, and it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Pacemaker vs Defibrillator: Understanding Their Functions and Benefits
When it comes to managing heart conditions, pacemakers and defibrillators play vital roles, each serving distinct purposes. To better understand their functions and benefits, let’s take a closer look at how these devices are used.
Pacemaker
A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device that helps regulate the heart’s rhythm. It is primarily used for patients with a slow heartbeat or irregular heart rhythms. By delivering electrical impulses to the heart, a pacemaker ensures that the heart beats at a steady and appropriate pace.
In addition to maintaining a normal heart rate, a pacemaker can help alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath. It can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with certain heart conditions, allowing them to engage in daily activities without limitations.
Defibrillator
A defibrillator, specifically an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), is employed in more critical situations. This device is designed to detect highly unstable heart rhythms and deliver an electric shock to restore normal heart function. Defibrillators are used for patients at risk of sudden cardiac death, especially those with abnormal heart conditions or a history of heart attacks.
Unlike pacemakers, defibrillators are typically reserved for life-threatening scenarios. They are programmed to deliver a shock when the heart’s beating becomes dangerously abnormal. This prompt intervention can potentially save lives and prevent severe cardiac complications.
| Pacemaker | Defibrillator |
|---|---|
| Regulates heart rhythm | Delivers shock to restore normal heart function |
| Used for slow heart rates or irregular heart rhythms | Used for life-threatening situations and high-risk patients |
| Improves quality of life for individuals with specific heart conditions | Prevents sudden cardiac death and severe cardiac complications |
It’s important to note that while pacemakers and defibrillators have distinct functions, some newer devices can incorporate both features. These advanced devices act as pacemakers and ICDs, providing combined benefits for patients who require ongoing heart rate regulation as well as protection against life-threatening cardiac events.
In conclusion, pacemakers and defibrillators are essential tools in managing heart conditions, with each device offering unique benefits. Understanding their functions and uses is crucial in determining the most appropriate treatment option for individual patients. If you or a loved one are experiencing heart-related concerns, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized recommendations.
Pacemaker and Defibrillator Similarities
In some cases, a patient may require both a pacemaker and a defibrillator implant to manage their heart condition effectively. While these devices serve different purposes, there are some similarities between them. One notable similarity is that both a pacemaker and a defibrillator are implanted under the skin in the upper chest. They consist of a small generator and leads that deliver electrical impulses to the heart.
Another similarity is that both devices monitor heart activity. A pacemaker continuously detects the heart’s rhythm and delivers electrical impulses when the heartbeat is too slow or irregular. Similarly, a defibrillator, specifically an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), constantly monitors heart function and delivers a shock when the heartbeat becomes highly unstable or dangerous.
Furthermore, technological advancements have led to the development of devices that combine the functions of both a pacemaker and a defibrillator. These devices, known as cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillators (CRT-D), are designed to regulate heart rhythm while also providing the capability to deliver shocks when needed. This innovative approach benefits patients who require both treatments, reducing the need for multiple implants.
Table: Pacemaker vs. Defibrillator Similarities
| Pacemaker | Defibrillator (ICD) |
|---|---|
| Implanted under the skin | Implanted under the skin |
| Monitors heart rhythm | Monitors heart function |
| Delivers electrical impulses | Delivers shocks |
| Regulates heartbeat | Restores abnormal heart function |
| Can be combined with a defibrillator | Can be combined with a pacemaker |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sNy3EWkBcDM
What is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device that helps regulate the heart’s rhythm. It is used for patients with a slow heartbeat and can be permanent or temporary. The pacemaker consists of a generator and leads that deliver electrical impulses to the heart, allowing it to beat at a normal rate.
The function of a pacemaker is to monitor the heart’s activity and detect any irregularities. When the pacemaker senses a slow or abnormal heartbeat, it sends electrical signals to the heart muscles, stimulating them to contract and maintain a steady rhythm. This ensures that the heart is able to pump blood effectively throughout the body.
One important similarity between a pacemaker and a defibrillator is their role in managing heart conditions. While a pacemaker focuses on regulating the heart’s rhythm, a defibrillator is designed to respond to life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances by delivering a shock to restore normal function. Both devices are implanted under the skin and are used to improve the quality of life for patients with cardiac conditions.
Overall, a pacemaker is a vital device for individuals who have a slow or irregular heartbeat. By providing the necessary electrical impulses, it helps maintain a normal heart rate and rhythm, allowing patients to live healthy and active lives.
The Function of a Pacemaker:
- Regulates the heart’s rhythm
- Monitors heart activity
- Delivers electrical impulses to stimulate heart muscles
In summary, a pacemaker is a small device that plays a crucial role in managing heart conditions. By ensuring the heart beats at a normal rate, it helps maintain proper blood circulation and improves the overall health of patients.
Conclusion
Pacemakers and defibrillators are both vital devices in managing heart conditions, but they have distinct differences. A pacemaker is designed to regulate the heartbeat, ensuring it maintains a normal rhythm. On the other hand, a defibrillator is used when the heart’s function becomes dangerously abnormal, delivering a shock to restore its normal activity.
While a pacemaker focuses on ongoing regulation, a defibrillator is primarily used in life-threatening situations, especially for patients at risk of sudden cardiac death. It is particularly beneficial for those with abnormal heart conditions or a history of heart attacks.
In some cases, patients may require both a pacemaker and a defibrillator implant. This is typically necessary for individuals with a heart condition that requires constant monitoring and modification of heart function, along with a higher risk of heart attacks. Advances in medical technology have led to the development of devices that serve as both a pacemaker and an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
Ultimately, the choice between a pacemaker and a defibrillator depends on an individual’s specific needs and the recommendation of their healthcare provider. Consulting with a doctor is crucial in determining the most suitable treatment option. Whether it’s ongoing regulation or restoring abnormal heart function, these devices play a critical role in managing heart conditions and improving the quality of life for many patients.
FAQ
What is the difference between a pacemaker and a defibrillator?
A pacemaker provides ongoing regulation of the heartbeat, while a defibrillator delivers a shock when the heart’s function is dangerously abnormal.
When is a pacemaker used?
A pacemaker is used when the heart beats too slowly or erratically, or after certain heart procedures like an ablation.
When is a defibrillator used?
A defibrillator is used for life-threatening situations and for patients at risk of sudden cardiac death, especially those with abnormal heart conditions or a history of heart attacks.
Should I get both a pacemaker and a defibrillator implant?
In some cases, a patient may need both a pacemaker and a defibrillator implant if they have a heart condition that requires regular monitoring and modification of the heart’s function, as well as a higher risk of heart attacks. Some newer devices can act as both a pacemaker and an ICD.
What is a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device that helps regulate the heart’s rhythm. It consists of a generator and leads that deliver electrical impulses to the heart.