Welcome to our comprehensive guide on flexors and extensors – two essential muscle groups that play a crucial role in our everyday movements. Have you ever wondered what flexors and extensors are, or how they differ from each other? In this article, we will explore the functions, anatomy, and importance of flexors and extensors, helping you gain a deeper understanding of these remarkable muscles.
Key Takeaways:
- Flexors decrease the angle between bones, while extensors increase it.
- Flexors are involved in bending movements, like flexing the elbow and knee.
- Extensors enable straightening movements, such as extending the fingers and standing up.
- Flexors and extensors work together in antagonistic pairs to maintain balance and stability.
- Proper care and strengthening of these muscles are essential for daily activities and injury prevention.
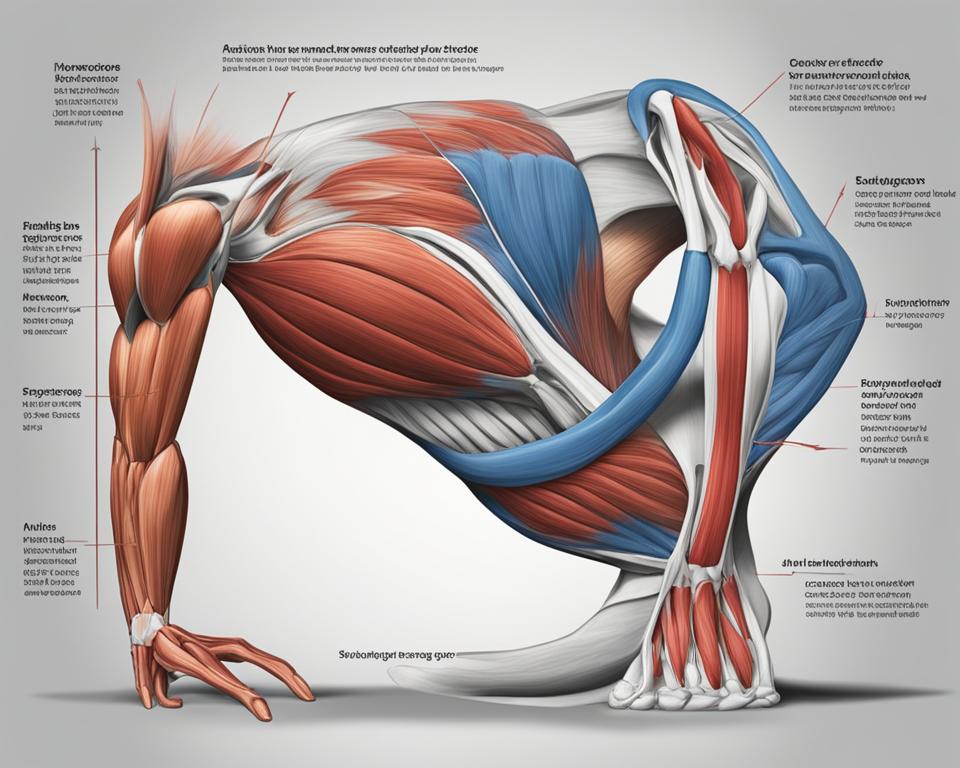
Anatomy of Flexors and Extensors
Flexors and extensors are composed of multiple muscles located throughout the body. In the hand, flexor muscles include flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and flexor digitorum profundus. Extensor muscles in the hand include extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis longus, and extensor digitorum. In the foot, flexor muscles include flexor digitorum brevis and flexor digitorum longus, while extensor muscles include extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis longus. The specific arrangement and interaction of these muscles allow for precise movements and coordination.
To better understand the anatomy of flexors and extensors, it is helpful to visualize their arrangement in a table:
| Muscle Group | Muscles |
|---|---|
| Hand Flexors | Flexor carpi radialis |
| Flexor carpi ulnaris | |
| Flexor digitorum profundus | |
| Hand Extensors | Extensor carpi ulnaris |
| Extensor carpi radialis longus | |
| Extensor digitorum | |
| Foot Flexors | Flexor digitorum brevis |
| Flexor digitorum longus | |
| Foot Extensors | Extensor digitorum brevis |
| Extensor hallucis longus |
As shown in the table, flexor and extensor muscles are organized into specific groups based on their location and function. Understanding this arrangement can provide valuable insights into the complexity of the body’s musculoskeletal system.
By examining the detailed anatomy of flexors and extensors, it becomes evident that these muscle groups are essential for a wide range of movements, ensuring optimal function and coordination.
Functions of Flexors and Extensors
Flexor muscles and extensor muscles in the body have distinct functions that are essential for movement and coordination. While flexors decrease the angle between bones, extensors increase the angle between bones, allowing for a wide range of motions.
Flexor muscles play a crucial role in bending movements. They are responsible for bringing body parts closer together and decreasing the angle between bones. For example, when you bend your elbow or flex your knee, the flexor muscles in those areas are activated. Flexors are also involved in actions like curling the fingers and toes. Without flexor muscles, these bending motions would be impossible.
On the other hand, extensor muscles facilitate extension movements, which involve straightening or lengthening body parts. They increase the angle between bones and are involved in actions like standing up and straightening the elbow. For instance, when you extend your fingers or push an object away from you, the extensor muscles in your hand and arm are engaged. Extensors are crucial for maintaining posture and performing tasks that require pushing or extending movements.
Flexors and extensors work together in antagonistic pairs to allow for smooth and controlled movements. When you bend a joint, the flexor muscles contract while the extensor muscles relax. Conversely, when you straighten the joint, the extensor muscles contract while the flexor muscles relax. This coordinated effort between flexors and extensors ensures proper balance, stability, and range of motion in the body.
Anatomy of Flexors and Extensors
In order to better understand the functions of flexors and extensors, it is important to have a basic understanding of their anatomy. Flexor muscles and extensor muscles are composed of multiple muscles located throughout the body.
| Body Part | Flexor Muscles | Extensor Muscles |
|---|---|---|
| Hand | Flexor carpi radialis Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum profundus |
Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor digitorum |
| Foot | Flexor digitorum brevis Flexor digitorum longus |
Extensor digitorum brevis Extensor hallucis longus |
These are just a few examples of flexor and extensor muscles in the hand and foot. Throughout the body, there are numerous other flexor and extensor muscles that enable specific movements.
The arrangement and interaction of these muscles allow for precise movements and coordination. They work together to provide the necessary force and control for actions like grasping, walking, and performing intricate fine motor skills.
Importance of Flexors and Extensors in Daily Motions
Flexors and extensors play a vital role in our daily activities, enabling us to perform a wide range of motions with ease and precision. These muscle groups are involved in various actions that we often take for granted, such as gripping objects, typing on a keyboard, and walking. Without the proper function of flexors and extensors, these seemingly simple tasks would be challenging or impossible to perform.
Flexors are responsible for bending movements, bringing body parts closer together, and decreasing the angle between bones. They allow us to flex our elbows, knees, and fingers. Extensors, on the other hand, facilitate extension movements, which involve straightening or lengthening body parts. They are involved in actions like extending our fingers, wrists, and legs.
The balance between flexors and extensors is crucial for maintaining stability and coordination in our movements. These muscle groups work together in antagonistic pairs, enabling us to perform tasks that require both bending and straightening motions. For example, when we pick up an object, our flexors contract to grip it, while our extensors stabilize our wrist and fingers to maintain a firm hold.
The Role of Flexors and Extensors in Daily Activities
The importance of flexors and extensors extends beyond basic movements. These muscle groups also play a crucial role in fine motor skills, such as writing, playing musical instruments, and using tools. The coordinated action of flexors and extensors allows us to perform precise and delicate tasks with dexterity and control.
Furthermore, flexors and extensors contribute to our overall posture and balance. The proper functioning of these muscles helps us maintain an upright position and stabilize our body during activities like standing, walking, and running. They provide the necessary support and control to keep us steady and prevent falls.
| Activities | Flexor Involvement | Extensor Involvement |
|---|---|---|
| Writing | Flexing fingers to hold the pen or pencil | Stabilizing wrist and fingers to maintain control |
| Walking | Bending the knees and ankles | Straightening the legs and propelling forward |
| Gripping Objects | Bending the fingers to hold objects securely | Stabilizing the wrist and fingers for a firm grip |
As we can see, flexors and extensors are involved in a wide range of activities that are essential for our daily functioning. Taking care of these muscle groups through regular exercise, proper ergonomics, and avoiding overuse or repetitive motions can help prevent injuries and maintain their health. Incorporating exercises that target flexors and extensors into our fitness routines can contribute to improved strength, flexibility, and overall well-being.
Strengthening Flexors and Extensors
To maintain the health and functionality of flexor and extensor muscles, it’s important to incorporate exercises that specifically target these muscle groups. By regularly engaging in exercises that strengthen flexors and extensors, you can improve muscle strength, endurance, and overall movement capabilities.
Exercises for Flexors
Wrist Curls: This exercise targets the flexor muscles in your forearms and wrists. Hold a dumbbell in your hand, palm facing upward. Rest your forearm on a bench or your thigh, allowing your hand and wrist to hang over the edge. Slowly curl your wrist upward, bringing the dumbbell towards your forearm. Lower the weight back down and repeat for several repetitions.
Finger Curls: This exercise focuses on strengthening the flexor muscles in your fingers. Place a rubber band around your fingers and thumb, holding it tightly. Spread your fingers apart against the resistance of the band, then slowly squeeze your fingers together, tightening the band. Repeat this movement for several repetitions.
Bicep Curls: While primarily targeting the biceps, this exercise also engages the flexor muscles in your forearms. Hold a dumbbell or a barbell with an underhand grip, palms facing upward. Bend your elbows and curl the weight upward towards your shoulders, then slowly lower it back down. Repeat for several repetitions.
Exercises for Extensors
Wrist Extensions: This exercise focuses on the extensor muscles in your forearms and wrists. Hold a dumbbell in your hand, palm facing downward. Rest your forearm on a bench or your thigh, allowing your hand and wrist to hang over the edge. Slowly extend your wrist upward, bringing the back of your hand towards your forearm. Lower the weight back down and repeat for several repetitions.
Reverse Curls: This exercise targets both the extensor muscles in your forearms and the brachialis muscles in your upper arms. Hold a barbell with an overhand grip, palms facing downward. Bend your elbows and curl the weight upward towards your shoulders, keeping your palms facing downward throughout the movement. Slowly lower the weight back down and repeat for several repetitions.
Tricep Dips: While primarily targeting the triceps, this exercise also engages the extensor muscles in your forearms. Position yourself on parallel bars or the edge of a stable chair or bench. Extend your legs forward and lower your body downward, bending your elbows to a 90-degree angle. Push yourself back up to the starting position and repeat for several repetitions.
Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase as you build strength. Perform these exercises two to three times a week, allowing for at least a day of rest in between sessions. Listen to your body, and if you experience any pain or discomfort, consult with a healthcare professional.
Summary:
To strengthen flexor and extensor muscles, incorporate exercises such as wrist curls, finger curls, bicep curls, wrist extensions, reverse curls, and tricep dips into your fitness routine. These exercises target the muscles responsible for bending and straightening movements, helping to improve strength, endurance, and overall muscle health. Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase as you build strength. Take rest days between sessions and listen to your body to avoid overexertion. Consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any pain or discomfort during these exercises.
Common Injuries in Flexors and Extensors
Injuries can occur in both flexor and extensor muscles, particularly when they are overused or subjected to repetitive motions. These injuries can range from strains and tendonitis to more severe conditions like tears and sprains. It is important to understand the common injuries associated with flexors and extensors to ensure proper prevention and treatment.
Flexor injuries commonly include strains, which are stretched or torn muscles or tendons. Tendonitis, an inflammation of the tendons, is also prevalent in flexor muscles. Additionally, sprains, which are stretched or torn ligaments, can occur in the flexor muscles of the hand and foot.
Extensor injuries often involve strains, which can result from overstretching or tearing of the muscles or tendons. Tendonitis is another common injury in extensor muscles, causing inflammation and pain. In some cases, tears can occur in the extensor muscles due to excessive force or repetitive stress.
Common Injuries in Flexors:
| Injury | Description |
|---|---|
| Strains | Stretched or torn muscles or tendons |
| Tendonitis | Inflammation of the tendons |
| Sprains | Stretched or torn ligaments |
Common Injuries in Extensors:
| Injury | Description |
|---|---|
| Strains | Overstretching or tearing of the muscles or tendons |
| Tendonitis | Inflammation of the tendons |
| Tears | Excessive force or repetitive stress causing muscle tears |
Preventing injuries in flexors and extensors involves proper warm-up, stretching exercises, and using correct techniques during physical activity. It is also important to listen to your body and avoid overexertion or excessive force. If injuries do occur, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help reduce swelling and promote healing. Seeking medical attention and rehabilitation exercises may be necessary for more severe injuries.
Tips for Maintaining Flexors and Extensors Health
Maintaining the health and functionality of your flexor and extensor muscles is crucial for overall well-being and preventing injuries. Here are some tips to help you take care of these vital muscle groups:
- Regular stretching: Incorporate stretching exercises into your daily routine to improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness. Focus on both flexor and extensor muscles to maintain a balanced approach.
- Proper warm-up: Before engaging in physical activity or exercise, make sure to warm up adequately. This helps prepare your muscles for movement, reduces the risk of strains or sprains, and optimizes performance.
- Vary your movements: Avoid repetitive motions without rest breaks to prevent overuse injuries in flexors and extensors. Alternate between different activities and exercises to minimize strain on specific muscle groups.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain in your flexor and extensor muscles. If you experience persistent pain or unusual symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.
- Proper nutrition and hydration: Ensure you have a well-balanced diet that provides essential nutrients for muscle health. Stay hydrated to support optimal muscle function and recovery.
By following these tips, you can improve the health and functionality of your flexor and extensor muscles, enabling you to perform daily activities with ease and reduce the risk of injuries.
Conclusion
Flexors and extensors are essential muscle groups that contribute to the wide range of movements in our bodies. Flexor muscles, such as the flexor carpi radialis and flexor digitorum profundus, decrease the angle between bones, enabling bending motions. On the other hand, extensor muscles, like the extensor carpi ulnaris and extensor digitorum, increase the angle between bones, facilitating extension movements.
These muscle groups work together in antagonistic pairs to provide balance and stability. Flexors and extensors play a crucial role in daily activities, from grasping objects and bending fingers to extending wrists and pushing objects away. Imagine trying to perform these tasks without the proper function of flexors and extensors – it would be challenging, if not impossible!
To ensure overall muscle health and prevent injuries, it is important to strengthen and care for flexors and extensors. Regular stretching, flexibility exercises, and proper warm-up before physical activity can help maintain their health. It is also crucial to avoid overexertion and repetitive motions without rest breaks. By understanding the functions and anatomy of flexors and extensors, we can better appreciate the importance of these muscle groups and take steps to keep them in good shape.
FAQ
What are flexor muscles?
Flexor muscles are responsible for decreasing the angle between bones in a joint, allowing for bending movements. Examples of flexor muscles include flexor carpi radialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor hallucis longus.
What are extensor muscles?
Extensor muscles increase the angle between bones in a joint and are responsible for straightening movements. Examples of extensor muscles include extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digitorum, and extensor hallucis longus.
How do flexors and extensors work together?
Flexors and extensors work as antagonistic pairs, balancing each other to allow for a wide range of movements. Flexors are responsible for bending movements, while extensors facilitate extension movements.
What is the role of flexor and extensor muscles in daily activities?
Flexor muscles enable actions like grasping objects, bending the fingers, and flexing the wrist. Extensor muscles are involved in movements like extending the fingers, extending the wrist, and pushing objects away.
How can I strengthen my flexor and extensor muscles?
Some exercises that can help strengthen flexor muscles include wrist curls, finger curls, and bicep curls. For extensor muscles, wrist extensions, reverse curls, and tricep dips are effective exercises.
What are common injuries in flexors and extensors?
Common injuries in flexors and extensors can include strains, tendonitis, sprains, and tears. Overuse injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome and tennis elbow can also affect these muscle groups.
How can I maintain the health of my flexor and extensor muscles?
Regular stretching and flexibility exercises, proper warm-up before physical activity, and avoiding repetitive motions without rest breaks can help maintain flexor and extensor muscle health. Proper nutrition and hydration are also important.
Can you summarize flexors and extensors?
Flexor muscles decrease the angle between bones, while extensor muscles increase the angle. They work together to enable a wide range of movements and are crucial for daily activities and preventing injuries.