In a woman’s reproductive system, the ovaries play a vital role in fertility. But have you ever wondered how many follicles are considered normal in each ovary? Let’s explore this topic and understand the significance of follicles in determining fertility.
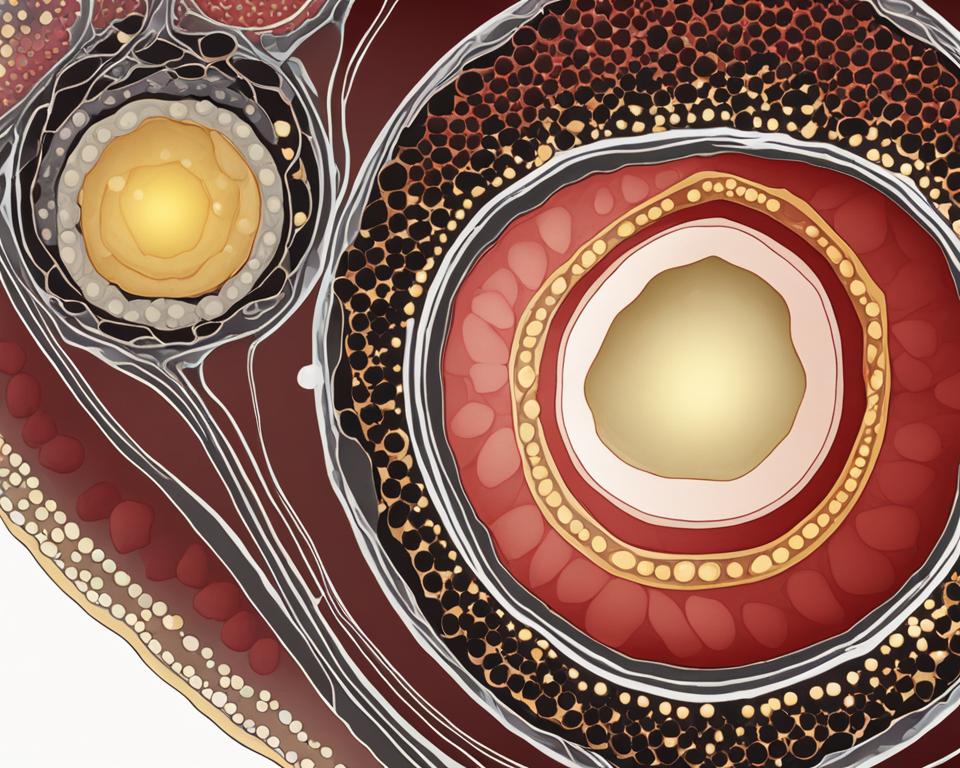
In a normal menstrual cycle, one follicle containing one egg grows and matures. The follicle is a small sac of fluid in the ovaries that contains a developing egg. While it is difficult to count all the follicles in each ovary, a transvaginal ultrasound can estimate the number of visible antral follicles, which are capable of growing to maturity. A normal ovarian reserve is considered to have an antral follicle count of 6-10.
Key Takeaways:
- A normal menstrual cycle usually involves the growth and maturation of one follicle containing one egg in each ovary.
- Transvaginal ultrasound can estimate the number of visible antral follicles in the ovaries, providing information about ovarian reserve.
- A normal ovarian reserve is typically defined by an antral follicle count of 6-10.
- The number of follicles in each ovary is not the sole determinant of fertility, but it is an important factor to consider when assessing fertility potential.
- Regular gynecological check-ups and discussions with healthcare professionals can help individuals understand their fertility health and make informed decisions.
Understanding Ovarian Follicles and Eggs
Each month, several follicles with eggs begin the process of maturing. However, usually only one follicle reaches maturity and releases the egg.
This dominant follicle grows to a size of 22 to 24 mm before rupturing and releasing the mature egg. Ovulation occurs around 14 days into the menstrual cycle.
It’s important to note that a follicle does not always contain a mature egg, and the growth of a follicle doesn’t guarantee fertility.
Follicle Development and Ovulation
During the menstrual cycle, the development and maturation of ovarian follicles are regulated by hormonal changes. Follicle development begins in the early stages of the cycle, as multiple follicles grow and reach various sizes.
As the cycle progresses, one follicle becomes dominant, absorbing all the nourishment and growing larger than the rest. This dominant follicle continues to mature and eventually releases the egg. This process is known as ovulation.
“Each month, several follicles with eggs grow, but usually only one follicle reaches maturity and releases the egg.” – Dr. Jane Johnson
The Role of Ovulation in Fertility
Ovulation is a crucial factor in achieving pregnancy. It marks the release of a mature egg from the ovary, ready to be fertilized by sperm.
Once the egg is released, it travels through the fallopian tube toward the uterus. If fertilization occurs during this journey, pregnancy can result. However, if fertilization does not occur within a certain timeframe, the egg disintegrates, and the uterine lining is shed through menstruation.
To increase the chances of conception, it is recommended to have regular sexual intercourse in the days leading up to and during ovulation.
Follicle Maturation and Fertility Treatments
In certain fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), multiple follicles are stimulated to grow and mature, increasing the chances of successful egg retrieval.
Medications are used to promote the growth and development of multiple follicles, allowing for the collection of several mature eggs. These eggs are then fertilized in a laboratory setting, and the resulting embryos are transferred to the uterus.
It’s important to note that while multiple follicles increase the chances of successful egg retrieval, the quality of the retrieved eggs and the overall success of the treatment can still vary.
The Importance of Ovarian Reserve
Ovarian reserve plays a crucial role in a woman’s fertility potential. It refers to the capacity of the ovaries to produce viable eggs for fertilization. Various tests, including hormonal analysis and the assessment of antral follicle count through ultrasound, can provide valuable insights into a woman’s ovarian reserve and overall fertility.
Counting antral follicles, which are small fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries, is an important component of fertility assessment. Antral follicles have the potential to develop into mature eggs. Generally, a normal antral follicle count ranges from 6 to 10 follicles. A count below 6 may indicate a low ovarian reserve, while a count above 12 suggests a high ovarian reserve.
Assessing ovarian reserve gives women valuable information regarding their fertility potential. By knowing their ovarian reserve, women can make informed decisions about family planning and seek appropriate medical guidance if necessary.
Benefits of Assessing Ovarian Reserve
Understanding your ovarian reserve through antral follicle count and hormonal analysis can provide insights into several aspects of fertility:
- Personalized Family Planning: With knowledge about ovarian reserve, individuals can plan their family goals according to their fertility potential.
- Timely Intervention: Early assessment of ovarian reserve can help identify potential fertility issues and allow for timely medical interventions if necessary.
- Informed Decision-Making: Assessing ovarian reserve can empower women to make informed decisions about fertility treatments and assisted reproductive technologies.
| Aspect | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Personalized Family Planning | Plan pregnancy goals based on fertility potential |
| Timely Intervention | Identify fertility issues early for appropriate medical assistance |
| Informed Decision-Making | Make educated choices regarding fertility treatments and assisted reproductive technologies |
Ovarian reserve assessment is an important tool in understanding a woman’s fertility potential. The data obtained through antral follicle count and hormonal analysis can guide individuals in their family planning journey, ensuring appropriate decisions and potential interventions if needed.
Factors Affecting Ovarian Follicles
When it comes to ovarian follicles, age plays a significant role. As women grow older, the number and quality of their ovarian follicles naturally decline, which can impact fertility and increase the risk of miscarriage. The quality of eggs may also diminish with age, leading to challenges in conceiving and carrying a pregnancy to term.
To assess a woman’s fertility potential and determine the quality of her ovarian follicles, healthcare professionals utilize hormonal analysis, such as Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) testing, and counting antral follicles. AMH levels provide insights into the quantity of eggs remaining in the ovaries, while counting antral follicles through ultrasound helps evaluate follicular development and ovarian reserve.
AMH testing:
The Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) test measures the levels of a hormone secreted by cells in the ovarian follicles. It helps determine the quantity of eggs remaining in a woman’s ovaries, which is an essential factor in assessing fertility potential. Higher AMH levels indicate a greater ovarian reserve, while lower levels may suggest a diminished reserve.
Counting antral follicles:
Counting antral follicles involves using ultrasound imaging to visualize and estimate the number of antral follicles in the ovaries. Antral follicles are those that have the potential to grow and mature. A higher count suggests a healthier ovarian reserve, whereas a lower count may indicate a reduced fertility potential.
The Impact of Age
The decline in the number and quality of ovarian follicles with age can significantly affect a woman’s fertility journey. As women approach their late 30s and 40s, the chances of conceiving naturally decrease, primarily due to a diminished ovarian reserve. Additionally, advanced maternal age is associated with an increased risk of genetic abnormalities and pregnancy complications.
It’s important to note that individual variations exist, and not all women will experience a decrease in fertility at the same age. However, understanding the age-related decline in ovarian follicles is crucial for women who are planning to start a family or undergoing fertility treatment.
| Age Group | Average Antral Follicle Count |
|---|---|
| 20-30 | 8-15 |
| 31-35 | 6-12 |
| 36-40 | 4-9 |
| 41-45 | 1-4 |
Note: The table above represents average antral follicle counts across different age groups and is for illustrative purposes only. Individual variations are common.
While age is an essential factor in fertility, it’s not the sole determinant. Other factors, such as overall health, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions, can also influence fertility outcomes. If you have concerns about your ovarian follicles or fertility, it’s recommended to consult with a fertility specialist for personalized guidance and support.
Assessing Ovarian Follicles through Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a commonly used technique for assessing ovarian follicles and estimating ovarian reserve. By utilizing a vaginal ultrasound, medical professionals can examine the ovaries and count the number of antral follicles present. This test provides valuable insights into a woman’s fertility potential.
During an ultrasound, an ultrasound technician or doctor inserts a probe into the vagina to visualize the ovaries. They carefully observe and count the number of antral follicles, which are small fluid-filled sacs capable of developing into mature eggs. The count of visible antral follicles gives an indication of the total number of eggs remaining in the ovaries.
This ultrasound test for follicle assessment can be performed at any time, but it is often scheduled for the third day of the menstrual cycle. The timing allows for accurate observation and measurement of the antral follicles, providing valuable information about a woman’s ovarian reserve.
Ultrasound for follicle assessment is a non-invasive and painless procedure that provides valuable insights into a woman’s fertility potential. It allows medical professionals to assess the number of eggs available for ovulation and determine the appropriate course of action for enhancing fertility.
The Antral Follicle Count Test
The antral follicle count obtained through ultrasound is a crucial part of the fertility assessment process. It helps determine the ovarian reserve, which is an indication of a woman’s remaining egg supply. The antral follicle count test provides valuable information for both natural conception and assisted reproductive technologies.
Antral follicle count test results are typically classified into three categories:
- Low Ovarian Reserve: An antral follicle count below 6 may indicate a reduced number of eggs available for ovulation.
- Normal Ovarian Reserve: A count of 6-10 antral follicles is considered indicative of a normal ovarian reserve.
- High Ovarian Reserve: An antral follicle count above 12 suggests a larger number of eggs available for ovulation.
Understanding the antral follicle count test results helps individuals and healthcare professionals make informed decisions about fertility treatments or family planning options. It provides valuable guidance on the likelihood of successful natural conception or the need for assisted reproductive technologies.
| Advantages of Ultrasound for Follicle Assessment | Limitations of Ultrasound for Follicle Assessment |
|---|---|
| Non-invasive procedure | Limited ability to assess egg quality |
| Painless and well-tolerated | Unable to predict fertility outcomes with absolute certainty |
| Provides visual confirmation of antral follicles | Results may vary depending on the skill of the ultrasound technician |
| Can be performed at any time during the menstrual cycle | Does not provide details on the uterine environment |
Fertility Treatments and Ovarian Follicles
Fertility treatments play a crucial role in helping individuals and couples achieve their dream of starting a family. These treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI), involve various strategies to optimize the growth and development of ovarian follicles, ultimately increasing the chances of successful conception.
During fertility treatments, hormone medications are often used to stimulate follicle growth and promote the release of multiple mature eggs. This process, known as ovulation stimulation, aims to collect the most viable eggs for fertilization, improving the likelihood of pregnancy.
Through the administration of fertility drugs, the ovaries are encouraged to produce a larger number of follicles. By closely monitoring the follicle growth through ultrasound scans and hormonal assessments, fertility specialists can determine the appropriate timing for egg retrieval.
The Role of Hormone Medications
Hormone medications used in fertility treatments mimic the natural hormones responsible for follicle development and ovulation. These medications commonly include:
- Gonadotropins: These medications stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple follicles, increasing the chances of obtaining a higher number of mature eggs.
- Clomiphene citrate: This medication induces ovulation by blocking the normal feedback mechanism that regulates follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) release.
- Letrozole: It is an aromatase inhibitor that can also be used to stimulate ovulation in certain cases.
In addition to stimulating follicle growth, these medications can help regulate the timing of ovulation and improve the overall success rates of fertility treatments.
Follicle Monitoring and Egg Retrieval
Throughout the ovarian stimulation process, regular ultrasound scans are performed to assess follicle growth and development. These scans allow fertility specialists to monitor the number and size of the follicles, ensuring they reach an optimal size before proceeding with egg retrieval.
Once the follicles have reached the desired size, a procedure called transvaginal oocyte retrieval is performed. This minimally invasive procedure involves using a specialized needle to collect the mature eggs from the follicles under ultrasound guidance. The retrieved eggs are then fertilized in the laboratory, and the resulting embryos are transferred back into the uterus to facilitate pregnancy.
Success Rates of Fertility Treatments
The success rates of fertility treatments vary depending on various factors, including the woman’s age, the quality of the retrieved eggs, and the underlying cause of infertility. However, the stimulation of multiple follicles allows for a higher number of eggs available for fertilization, increasing the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
“Fertility treatments, such as IVF and IUI, utilize ovarian stimulation to optimize the number and quality of eggs for fertilization, improving the chances of successful conception.”
| Fertility Treatment | Success Rate |
|---|---|
| Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) | 10-20% per cycle |
| In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) | 40-50% per cycle |
Note: Success rates are approximate and can vary depending on individual circumstances and clinic-specific factors.
Fertility treatments offer hope to those facing difficulties conceiving naturally. By stimulating ovarian follicle growth and optimizing the chances of successful fertilization, these treatments help individuals and couples overcome infertility challenges and fulfill their desire for a family.
Empty Follicle Syndrome
Empty follicle syndrome is a rare occurrence during in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles. Despite adequate follicular growth and hormone levels, no eggs are retrieved. This puzzling phenomenon has left many experts searching for answers as to why it happens.
The exact cause of empty follicle syndrome remains unknown. However, it is more commonly observed in women with a history of primary infertility and a good follicle count. Researchers believe that factors such as low egg quality and abnormal ovarian function may contribute to this syndrome.
Nevertheless, it’s important to note that the occurrence of empty follicle syndrome does not indicate a fertility problem in most cases. In fact, some women who experience this syndrome may go on to successfully conceive naturally or through subsequent IVF cycles.
While empty follicle syndrome can be disheartening for couples undergoing IVF, it is crucial to remember that each fertility journey is unique. Discussing alternative treatment options with a fertility specialist and exploring other pathways to parenthood can help individuals navigate this challenging situation.
“Empty follicle syndrome can be disheartening, but it doesn’t necessarily mean there is a fertility problem. There are still other treatment options and pathways to parenthood to explore.”
Predicting Pregnancy with Follicles
When it comes to predicting pregnancy, understanding the role of mature follicles is essential. For natural conception, the release of a mature egg from a follicle is necessary. If you’re planning to conceive naturally, having one mature follicle is typically sufficient for pregnancy.
In fertility treatments like intrauterine insemination (IUI), higher success rates are typically associated with one or two mature follicles. The presence of multiple mature follicles increases the chances for successful fertilization.
The size of a mature follicle before ovulation is typically around 22 to 24 mm. This size indicates that the follicle is ready for release, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
In the context of in vitro fertilization (IVF), the goal is to stimulate the growth of multiple follicles to retrieve a higher number of eggs per cycle. Fertility medications are used to promote the growth of follicles, aiming to retrieve more than 10 eggs per cycle. This allows for a greater selection of mature eggs for fertilization, increasing the chances of successful implantation.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Follicles
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) often have an elevated number of antral follicles compared to women without PCOS. PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances that interfere with ovulation, causing the follicles to struggle to release mature eggs.
These ovulation difficulties in PCOS can make it challenging for women to conceive naturally. Fortunately, there are treatment options available to help manage PCOS and improve fertility outcomes.
Medications like metformin, Clomid, or letrozole may be prescribed to induce ovulation in women with PCOS. These medications help stimulate the growth and release of eggs, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
In more severe cases, where medications alone may not be effective, in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended. During IVF, fertility specialists retrieve multiple mature eggs directly from the ovaries for fertilization in a lab setting.
The Role of Medications in PCOS Treatment
Metformin: This medication is commonly used to manage insulin resistance, a common symptom of PCOS. By improving insulin sensitivity, metformin can help regulate hormone levels, restore ovulation, and promote fertility.
Clomid (clomiphene citrate): Clomid is a fertility drug that stimulates the ovaries to produce more follicles and eggs. It increases the chances of ovulation and can be beneficial for women with PCOS.
Letrozole: Letrozole is another medication often prescribed for ovulation induction in women with PCOS. It works by suppressing estrogen production, stimulating the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and promoting the growth and release of mature eggs.
It’s important to note that the choice of medication and treatment approach may vary depending on individual circumstances and the recommendations of a healthcare professional.
Managing PCOS and addressing ovulation difficulties can greatly improve the chances of conception for women with PCOS. By utilizing appropriate medications and seeking the guidance of medical professionals, individuals with PCOS can take proactive steps towards their fertility goals.
Routine Check-ups and Ovarian Reserve
A routine gynecological check-up is an essential part of maintaining reproductive health. In addition to addressing any concerns or symptoms, these regular visits also provide an opportunity to assess a woman’s ovarian reserve.
Assessing ovarian reserve involves evaluating the quantity and quality of eggs remaining in the ovaries. One of the methods used is a vaginal ultrasound, which allows the gynecologist to count antral follicles and estimate ovarian reserve.
Antral follicles are small, fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries that contain immature eggs. By counting these follicles, doctors can gain insight into a woman’s fertility potential. A higher number of antral follicles suggests a greater ovarian reserve, while a lower count may indicate diminished ovarian function.
This information obtained during a routine check-up is valuable for women who are planning to start a family in the future. It can help them make informed decisions about their reproductive options and seek appropriate medical guidance if necessary.
It’s important to note that assessing ovarian reserve is just one aspect of fertility evaluation and does not guarantee future fertility. Other factors, such as egg quality and overall health, also play a role in conception and pregnancy.
The Role of Routine Gynecological Check-ups
Routine gynecological check-ups are recommended for all women, regardless of their plans for pregnancy. These visits allow healthcare providers to monitor reproductive health, detect early signs of potential issues, and provide necessary interventions or treatments.
During a routine check-up, the gynecologist will typically perform a pelvic examination, which may include a vaginal ultrasound. This non-invasive procedure involves inserting an ultrasound probe into the vagina to visualize the ovaries and assess their follicular activity.
The ultrasound technician or doctor will count the number of antral follicles seen on the ovaries. This count provides an estimate of the remaining eggs in the ovaries and offers insight into the woman’s ovarian reserve. Additionally, the doctor may also analyze other hormonal markers, such as Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH), to further assess ovarian reserve.
Based on the results of these assessments, the gynecologist can provide personalized recommendations and guidance for achieving optimal reproductive health. This may include lifestyle modifications, fertility treatments, or further diagnostic tests if necessary.
“Routine gynecological check-ups are an important part of proactive healthcare and reproductive planning. Assessing ovarian reserve through techniques like vaginal ultrasound can offer valuable insights into a woman’s fertility potential.”
In conclusion, routine gynecological check-ups are crucial for monitoring ovarian reserve, fertility potential, and overall reproductive health. By including a vaginal ultrasound, healthcare providers can estimate the number of antral follicles and provide valuable information for women planning their future fertility. It is essential for women to prioritize regular check-ups and maintain open communication with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding their reproductive journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of ovarian follicles in assessing fertility potential is essential for individuals trying to conceive. Ovarian reserve, measured by counting antral follicles, provides valuable information about a woman’s reproductive capacity. While the exact number of follicles is not the sole determining factor for fertility, it plays a significant role in understanding a woman’s fertility potential.
Regular check-ups and open discussions with healthcare professionals are paramount in making informed decisions about reproductive health. By monitoring and assessing ovarian follicles, individuals can gain valuable insights into their fertility potential and explore appropriate options and treatments if necessary.
Assessing fertility potential through ovarian follicle assessment empowers individuals to take control of their reproductive health. It allows proactive planning, potential fertility preservation, and provides guidance for assisted reproductive interventions. By understanding the importance of ovarian follicles, individuals can optimize their chances of successful conception and parenthood.
FAQ
How many follicles are normal in each ovary?
In a normal menstrual cycle, each ovary typically has an antral follicle count of 6-10, which are capable of growing to maturity.
What is the role of ovarian follicles in fertility?
Ovarian follicles contain eggs and play a crucial role in fertility. Each month, several follicles start maturing, but usually only one follicle reaches maturity and releases the egg for fertilization.
What is ovarian reserve and why is it important?
Ovarian reserve refers to the potential of the ovary to produce eggs that can be fertilized. It is assessed through tests such as counting antral follicles, which provides valuable information about a woman’s fertility potential.
How does age affect ovarian follicles?
The number and quality of ovarian follicles decrease with age. Older women may have a lower ovarian reserve and a higher risk of miscarriage due to a reduced number and potentially lower quality of eggs.
How are ovarian follicles assessed through ultrasound?
Vaginal ultrasound is commonly used to assess ovarian follicles. A healthcare professional uses a probe inserted into the vagina to examine and count the number of antral follicles on the ovaries.
What is the role of follicles in fertility treatments?
In fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI), stimulating the growth of multiple follicles is often necessary to increase the chances of success. Fertility medications are used to promote follicle growth and increase the number of mature eggs available for retrieval.
What is empty follicle syndrome?
Empty follicle syndrome is a rare event in which no eggs are retrieved during an IVF cycle, despite adequate follicular growth and hormone levels. The exact cause is unknown, and it doesn’t necessarily indicate a fertility problem in most cases.
How many follicles are needed for pregnancy?
When trying to conceive naturally, one mature follicle is usually sufficient for pregnancy. However, in fertility treatments like IUI, one or two mature follicles are preferred for higher success rates.
How does polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affect follicles?
Women with PCOS often have an elevated number of antral follicles compared to those without PCOS. However, hormonal imbalances in PCOS can interfere with ovulation, making it challenging for follicles to release mature eggs.
How can routine check-ups help assess ovarian reserve?
A routine gynecological check-up, including a vaginal ultrasound, can provide information about a woman’s ovarian reserve. Counting antral follicles helps estimate the number of eggs remaining in the ovaries and assess fertility potential.
Why is understanding ovarian follicles important?
Understanding the role of ovarian follicles in fertility is crucial for individuals trying to conceive or assess their fertility potential. Knowing the number and quality of follicles can help make informed decisions about reproductive health.