Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how breast pumps work and how to use them effectively. Breast pumping can provide numerous benefits for both mothers and babies, and understanding the mechanics behind it can help you make the most of this valuable tool.
But first, let’s talk about why breastfeeding is important. Breast milk is the perfect source of nutrition for newborns, providing them with essential nutrients and antibodies that boost their immune system. For mothers, breastfeeding promotes faster recovery after childbirth and offers cost savings compared to formula feeding.
Now, let’s dive into how breast pumps work. Breast pumps are designed to mimic a baby’s natural sucking pattern. They create a cycle of suction and release, just like a nursing baby. The pump’s suction and speed settings can be adjusted to simulate the intensity of a baby’s suckling.
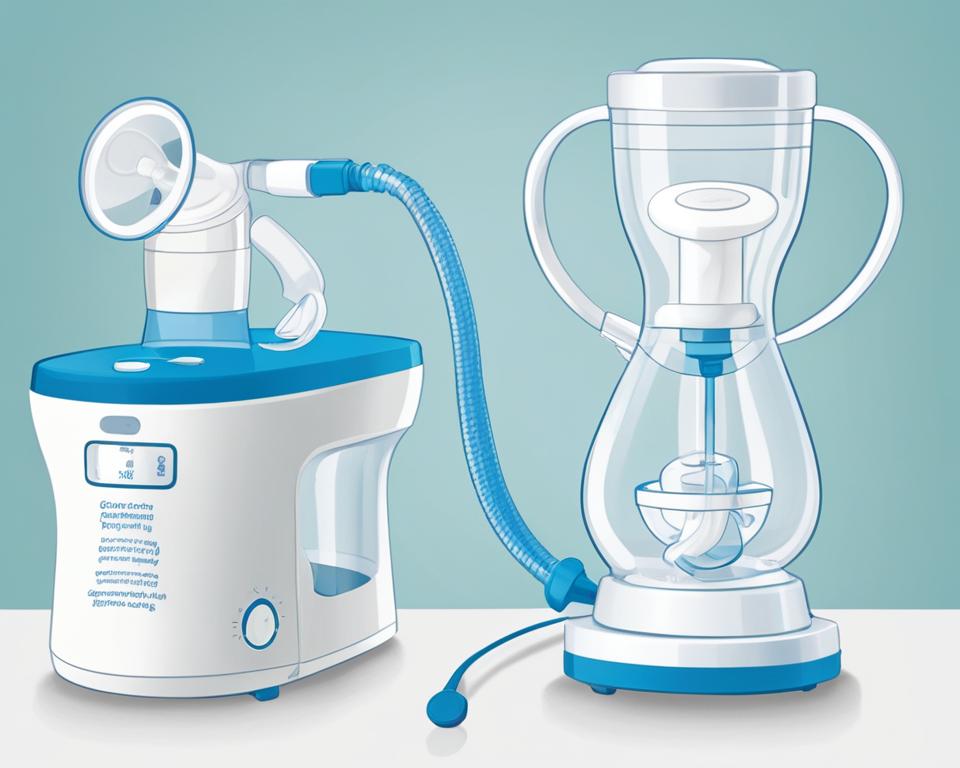
The breast pump consists of flanges or breast shields that fit over the nipple and create a seal. As the pump creates suction, it stimulates the release of the hormone oxytocin, which triggers the milk letdown reflex and causes the milk-producing tissue to contract. The expressed milk is collected in storage containers for later use.
Key Takeaways:
- Breast pumps are a valuable tool for various situations, including relieving engorgement, building and maintaining milk supply, and providing breast milk when nursing isn’t possible.
- Breast pumps mimic a baby’s suckling pattern through cycles of suction and release.
- The breast pump’s suction and speed settings can be adjusted to simulate the intensity of a baby’s sucking.
- Flanges or breast shields create a seal around the nipple and allow the milk to be collected in storage containers.
- Understanding how breast pumps work can help you make the most of your pumping experience and ensure successful breastfeeding.
Understanding Breast Pump Operation
Breast pumps mimic a nursing baby’s suckling pattern by creating a cycle of suction and release. The average baby sucks about 50 to 90 times per minute. Electric breast pumps initiate milk let down by producing one pull per second, stimulating the release of the hormone oxytocin, which contracts the milk-producing tissue. Breast pump suction goes through phases like let down and expression, mirroring a baby’s sucking pattern. Breast pumps come with flanges or breast shields that create a seal around the nipple, allowing milk to be collected in storage containers.
Using a breast pump effectively requires an understanding of its mechanism and suction. By replicating a baby’s natural sucking pattern, breast pumps can stimulate milk release and collect breast milk efficiently. Breast pumps use a suction mechanism to create a cycle of suction and release, imitating a baby’s suckling rhythm. This suction is generated through the use of flanges or breast shields that create a seal around the nipple, allowing for the collection of milk in attached storage containers.
It’s important to note that breast pump suction goes through phases, including a letdown phase and an expression phase. During the letdown phase, breast pump suction stimulates the release of the hormone oxytocin, which triggers the contraction of the milk-producing tissue and initiates the flow of milk. The expression phase follows, where the breast pump continues to mimic a baby’s sucking pattern, effectively extracting milk from the breast.
“Using a breast pump effectively requires an understanding of its mechanism and suction.”
Knowing how a breast pump operates can enhance the overall pumping experience and maximize milk production. By understanding the breast pump mechanism and suction patterns, you can optimize the settings and adjust them according to your comfort and milk flow. The proper utilization of a breast pump ensures a smooth pumping experience and allows you to express breast milk conveniently for your baby’s needs.
Does Breast Pumping Hurt?
Breast pumping is an essential part of the breastfeeding journey for many mothers. While it should not be painful, some discomfort may be experienced initially, which can be alleviated by implementing the right techniques and adjustments.
One important factor to consider is the correct flange size. Ensuring that the flange fits properly around the breast is crucial for preventing pain and discomfort. Positioning the nipple in the center of the flange helps create a proper seal and allows for optimal milk expression.
Adjusting the suction and speed settings of the breast pump can also contribute to a more comfortable experience. Finding the right combination that mimics your baby’s feeding pattern is key. Gradually increase the suction strength to a level that feels comfortable and effective for milk expression.
Over-pumping can lead to soreness, so it is important to be mindful of the pumping duration and frequency. Avoid excessive pumping sessions that may strain the breasts. Stick to a pumping schedule that allows for adequate milk production without causing discomfort.
Before pumping, using warm compresses or gently massaging the breasts can promote milk flow and make the process more comfortable. These techniques help stimulate milk let-down, making it easier for the breast pump to extract milk.
Pumping should be a comfortable sensation, similar to breastfeeding. If you experience persistent pain or any difficulties, it is recommended to consult with a lactation consultant or healthcare provider for guidance and support.
How to Set Up Your New Breast Pump
When receiving a breast pump through insurance, it’s important to set it up before delivery. Familiarize yourself with the instruction manual and any additional resources provided by the manufacturer. Sterilize the pump parts, ensuring they are completely air-dried before assembly. Take the time to learn the different suction settings and pumping cycles of your pump. Consider getting essential accessories, such as nursing pads, a breast pump tote bag, a hands-free bra, or a nursing pillow, to make the pumping process more comfortable and efficient.
How to Use a Breast Pump
Using a breast pump effectively is essential for successful breast pumping. Whether you are looking to build a milk supply, provide milk for partner feedings, or prepare for the return to work, knowing how to use a breast pump correctly is crucial. Follow these steps to ensure an effective breast pumping experience:
- Read the Instructions: Start by familiarizing yourself with the instructions provided with your specific breast pump model. Every breast pump may have different features and settings, so understanding how to operate your pump is essential.
- Position the Breast Shield: Before starting the pumping session, make sure the breast shield, also known as a flange, is properly placed over your nipple. A correctly fitted breast shield will help ensure comfortable and efficient milk expression.
- Relax and Find a Comfortable Space: Create a calm and relaxing environment for your pumping session. Find a quiet and private space where you can sit back and relax. This will help stimulate milk let-down and make the experience more enjoyable.
- Set the Pump: Set the pump to your desired suction and speed settings. Every mother may have different preferences, so experiment to find the setting that works best for you. Gradually increase the suction level until you feel a comfortable, gentle pull on your breasts.
- Start Pumping: Begin the pumping session by turning on the breast pump. Pump for a duration of 15 to 30 minutes or until your breasts feel empty. It’s recommended to pump in the morning or between feedings when your milk supply is generally higher.
- Clean and Store Expressed Milk: After each session, clean the breast pump parts thoroughly according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Proper hygiene is crucial to maintain the quality and safety of the expressed milk. Store the expressed milk in appropriate storage containers and refrigerate or freeze it as needed.
Remember, every mother’s breastfeeding journey is unique, and it may take time to find the right pumping routine that works for you. Be patient, listen to your body, and seek support from lactation consultants or breastfeeding support groups if needed.
How Often Should I Breast Pump?
The frequency of breast pumping varies depending on individual needs and circumstances. For new mothers, it is recommended to start by pumping every 2 to 3 hours to establish milk supply. As the milk supply becomes established, pumping sessions can be reduced to every 3 to 4 hours. However, it’s important to note that every mother’s situation is unique and individual preferences may differ.
The baby’s feeding schedule, milk supply goals, and personal preferences are factors that may influence the pumping frequency. Listening to your body and adjusting the pumping schedule accordingly is crucial. Some mothers may find it helpful to pump more frequently during the early morning hours when milk supply is typically higher.
Tip: Remember to stay hydrated and practice self-care while pumping. Creating a relaxing environment and finding a comfortable space can enhance the pumping experience.
If you are unsure about your pumping schedule, consult with a lactation consultant or a healthcare professional who can provide guidance tailored to your specific needs.
| Factors | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Baby’s feeding schedule | Consider pumping around the same time as the baby’s usual feedings to maintain a synchronized milk supply. |
| Milk supply goals | If you are looking to build a freezer stash or meet specific milk supply goals, pumping more frequently may be necessary. |
| Personal preferences | Some mothers may find it more practical to pump at certain times of the day based on their daily routine or work schedule. |
Remember, the most important aspect of breast pumping is to listen to your body and adapt the schedule to meet your personal needs and goals.
Testimonial:
“Finding the right pumping schedule took time and experimentation, but once I established a routine that worked for me, it made the whole process much easier. Being flexible and adjusting as needed is key!” – Emily, mother of two.
How Much Milk Should I Pump?
The amount of milk that can be pumped varies from woman to woman. On average, newborns consume about 2 to 3 ounces of milk per feeding. Initially, mothers may pump smaller amounts of milk, but as their milk supply increases, they can expect to pump larger volumes. It’s important to remember that breast milk production is a supply and demand process, so consistent and frequent pumping can help increase milk supply.
It can be helpful to establish a pumping routine that aligns with your baby’s feeding schedule. By pumping around the same time your baby typically feeds, you can maximize the amount of milk you express.
Bonus Breast Pumping Tips!
Here are some additional tips for successful breast pumping:
- Create a comfortable and relaxing environment for pumping.
- Use breast massage or warm compresses before pumping to stimulate milk flow.
- Consider using a double breast pump for more efficient pumping and time-saving.
- Experiment with different suction and speed settings to find what works best for you.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to support milk production.
“Breast pumping has been a game-changer for me. It gave me the flexibility to provide breast milk for my baby even when I couldn’t be there physically. These tips made my pumping journey so much easier and more comfortable!” – Sarah
Seek support from lactation consultants or breastfeeding support groups for guidance and assistance. They can provide valuable advice tailored to your specific needs and concerns.
Getting a Breast Pump Through Insurance
Many insurance plans cover the cost of a breast pump as a required benefit. Check with your insurance provider to understand the specific coverage and requirements. To get a breast pump through insurance, you may need a prescription from your healthcare provider. Some insurance plans only cover manual or single electric pumps, while others may provide coverage for higher-grade pumps. Research different suppliers and models to find the best option that meets your needs.
Conclusion
Breast pumping is an essential aspect of a breastfeeding journey, enabling mothers to provide breast milk in various situations. By understanding how breast pumps work and utilizing them effectively, mothers can ensure a comfortable and efficient pumping experience.
It is crucial for mothers to prioritize self-care, listen to their bodies, and seek support when needed. Taking care of oneself includes maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and creating a comfortable and relaxing environment for pumping.
Remember, successful breastfeeding is a result of a combination of factors, including proper breast pump operation, self-care, and support from lactation consultants or breastfeeding support groups. With the right knowledge and resources, mothers can embark on a successful breastfeeding journey.
FAQ
How does a breast pump work?
Breast pumps mimic a nursing baby’s suckling pattern by creating a cycle of suction and release. Electric breast pumps stimulate milk let down by producing one pull per second, which triggers the release of the hormone oxytocin. Breast pump suction goes through phases like let down and expression, similar to a baby’s sucking pattern. Milk is collected in storage containers through flanges or breast shields that create a seal around the nipple.
What is the mechanism behind breast pump suction?
Breast pump suction is achieved by creating a vacuum, which draws the nipple into the breast shield or flange. This vacuum pressure stimulates milk flow by triggering the release of oxytocin and mimicking a baby’s sucking motion. The suction strength can typically be adjusted to accommodate personal comfort.
Does breast pumping hurt?
Breast pumping should not be painful, although some discomfort may be experienced initially. Pain or soreness can be avoided by ensuring the correct flange size, positioning the nipple in the center of the flange, adjusting suction and speed settings, and avoiding over-pumping. The sensation should be similar to breastfeeding, and with proper technique and settings, it can become a comfortable practice.
How do I set up my new breast pump?
When receiving a breast pump through insurance, it’s important to set it up before delivery. Familiarize yourself with the instruction manual and any additional resources provided by the manufacturer. Sterilize the pump parts, ensuring they are completely air-dried before assembly. Take the time to learn the different suction settings and pumping cycles of your pump. Consider getting essential accessories, such as nursing pads, a breast pump tote bag, a hands-free bra, or a nursing pillow, to make the pumping process more comfortable and efficient.
How do I use a breast pump effectively?
Breast pumping can begin shortly after birth, depending on individual circumstances. It’s recommended to pump in the morning, between feedings, and for a duration of 15 to 30 minutes. Follow the instructions provided with your specific pump model, ensuring the breast shield is properly placed over the nipple. Relax and find a comfortable space for pumping, and remember to clean and store the expressed milk properly.
How often should I breast pump?
The frequency of breast pumping varies depending on individual needs and circumstances. New mothers may start by pumping every 2 to 3 hours, and as their milk supply becomes established, pumping sessions can be reduced to every 3 to 4 hours. Factors such as the baby’s feeding schedule, milk supply goals, and personal preferences can influence the pumping frequency. It’s important to listen to your body and adjust the pumping schedule accordingly.
How much milk should I pump?
The amount of milk that can be pumped varies from woman to woman. On average, newborns consume about 2 to 3 ounces of milk per feeding. Initially, mothers may pump smaller amounts of milk, but as their milk supply increases, they can expect to pump larger volumes. Consistent and frequent pumping can help increase milk supply, as breast milk production is a supply and demand process.
What are some bonus breast pumping tips?
Here are some additional tips for successful breast pumping:
– Create a comfortable and relaxing environment for pumping.
– Use breast massage or warm compresses before pumping to stimulate milk flow.
– Consider using a double breast pump for more efficient pumping and time-saving.
– Experiment with different suction and speed settings to find what works best for you.
– Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to support milk production.
– Seek support from lactation consultants or breastfeeding support groups for guidance and assistance.
How can I get a breast pump through insurance?
Many insurance plans cover the cost of a breast pump as a required benefit. To get a breast pump through insurance, you may need a prescription from your healthcare provider. Some insurance plans only cover manual or single electric pumps, while others may provide coverage for higher-grade pumps. Check with your insurance provider to understand the specific coverage and requirements. Research different suppliers and models to find the best option that meets your needs.
Conclusion
Breast pumping is a valuable tool that can help mothers provide breast milk to their babies in various situations. Understanding how breast pumps work and how to use them effectively can make the pumping experience comfortable and efficient. Remember to take care of yourself, listen to your body, and seek support when needed to ensure a successful breastfeeding journey.

