A furnace is a crucial component of home heating systems, providing warmth and comfort during colder months. Understanding how a furnace works and its various components is essential for homeowners seeking to optimize their heating system.
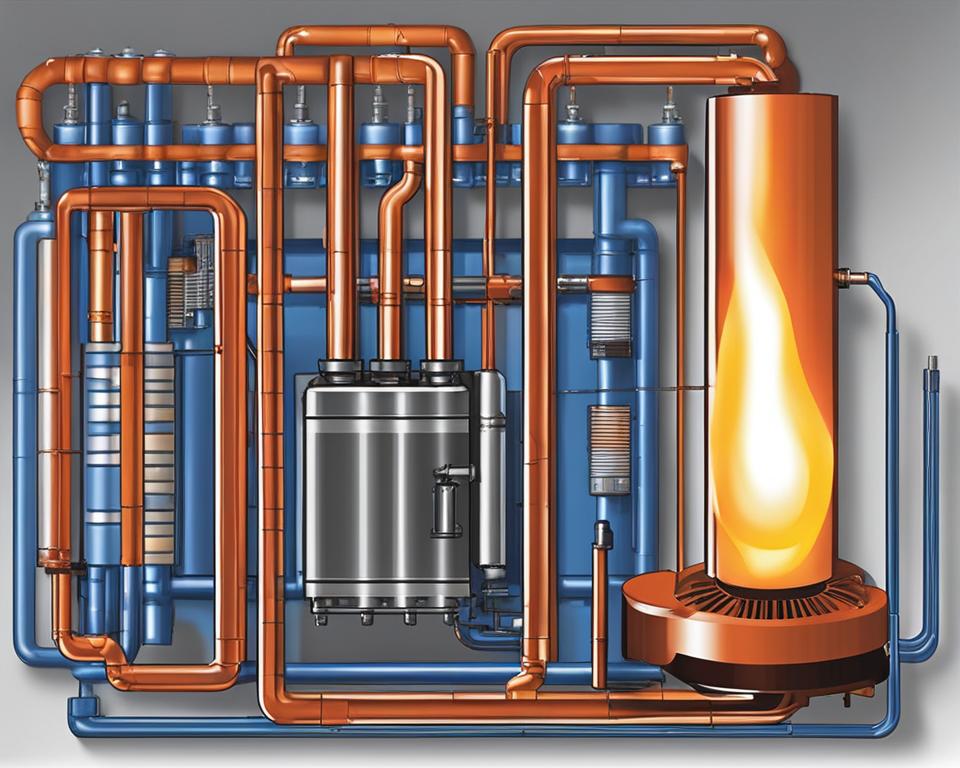
At its core, a furnace operates by burning propane or natural gas in a burner, generating heat. This heat passes through a heat exchanger, where air from the home’s ductwork is warmed. A blower fan then distributes the heated air throughout the house. The furnace consists of several components, including temperature control, draft induced fan, gas burners, ignition switch, heat exchanger, blower fan, and flue, all working together to ensure efficient heating.
Proper furnace sizing is crucial for optimal comfort and cost-efficiency. An undersized furnace may struggle to keep up with heating demands, resulting in increased utility bills. Conversely, an oversized furnace can cause temperature fluctuations and unnecessary wear and tear on components. Consulting a licensed HVAC technician is necessary to determine the correct furnace size for your space.
Maintaining a gas furnace is also essential for safe and efficient operation. Regular cleaning and maintenance by a certified technician, changing the air filter regularly, and keeping the furnace registers clean and unobstructed are necessary practices for proper furnace maintenance.
In conclusion, understanding the operation and components of a furnace, ensuring proper sizing, and maintaining regular maintenance are crucial for homeowners to have a reliable and efficient heating system.
Key Takeaways:
- A furnace operates by burning propane or natural gas to generate heat.
- The heat is then passed through a heat exchanger, warming air from the ductwork.
- A blower fan distributes the heated air throughout the house.
- Proper furnace sizing is important for comfort and cost-efficiency.
- Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for safe and efficient furnace operation.
Understanding BTUs and Furnace Sizing
When it comes to selecting a furnace for your home, understanding BTUs (British Thermal Units) and proper furnace sizing is crucial. The BTU output of a furnace determines its heating capacity. A higher BTU output means a more powerful heating system. On the other hand, an undersized furnace may struggle to keep up with heating demands on colder days, while an oversized furnace can cause temperature fluctuations and unnecessary wear and tear on components.
To ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency, it’s important to choose the proper furnace size for your space. Consulting a licensed HVAC technician is recommended as they have the knowledge and expertise to accurately assess your heating needs and determine the right size furnace for your home.
Proper furnace sizing takes into account factors such as the square footage of your home, insulation levels, and desired indoor temperature. By working with a professional, you can avoid the pitfalls of an undersized or oversized furnace, ensuring both comfort and cost-efficiency.
Furnace Sizing Considerations
- BTU output: The heating capacity of a furnace, measured in BTUs.
- Proper furnace size: Choosing the right size furnace for your home based on factors like square footage and insulation levels.
- Undersized furnace: A furnace that is too small to adequately heat the space, resulting in reduced comfort and potentially higher energy bills.
- Oversized furnace: A furnace that is too large for the space, leading to temperature fluctuations and unnecessary wear on components.
| Furnace Size | BTU Output | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 40,000 – 60,000 | Smaller homes or individual rooms |
| Medium | 60,000 – 80,000 | Medium-sized homes |
| Large | 80,000 – 100,000+ | Larger homes or those with high heat loss |
Choosing the right size furnace is essential for maintaining a comfortable living environment and maximizing energy efficiency. By understanding BTUs and furnace sizing, you can make an informed decision and ensure your home stays warm during the cold winter months.
The Heating Cycle of a Gas Furnace
A gas furnace follows a specific heating cycle to generate warmth for a home. Understanding this cycle and how each component plays a role is essential for homeowners to optimize their furnace’s performance.
1. The Burner: The heating cycle begins with the burner, which ignites propane or natural gas. This combustion process generates heat that will be used to warm the home.
2. Heat Exchanger: The heat produced by the burner passes through a heat exchanger. This component separates the combustion process from the air entering the home’s ductwork.
3. Blower Fan: Once the heat is transferred to the exchanger, a blower fan forces the warmed air into the supply ductwork. This distributes the heated air throughout the house, ensuring a consistent and comfortable indoor temperature.
4. Thermostat: The temperature control, regulated by the furnace control board, starts the heating process when the thermostat calls for heat. This ensures that the furnace only operates when needed, maintaining energy efficiency.
By understanding the heating cycle of a gas furnace, homeowners can appreciate the importance of each component and how they work together to provide warm and comfortable living spaces.
Components of a Gas Furnace
A gas furnace is made up of several essential components that work together to provide efficient and reliable heating for your home. Understanding these components can help you better comprehend the inner workings of a gas furnace and enable you to make informed decisions when it comes to maintenance and troubleshooting.
Thermostat
The thermostat is the control center of your gas furnace. It measures and regulates the indoor temperature, signaling the furnace to turn on or off based on the desired temperature settings. A malfunctioning thermostat can result in temperature inconsistencies and discomfort in your home.
Control Board
The control board interprets electrical signals from the thermostat and triggers various furnace functions accordingly. It plays a crucial role in the operation and coordination of the different components within the furnace, ensuring proper functionality and efficient performance.
Burners and Igniter
The burners are responsible for emitting gas (propane or natural gas) into the combustion chamber. The igniter then ignites the gas, creating a flame that generates heat. A faulty igniter or dirty burners can lead to inefficient combustion and reduced heating performance.
Blower Fan
The blower fan forces the heated air produced by the furnace into the supply ductwork, distributing it throughout your home. It ensures proper airflow and consistent heating in every room. Regular maintenance of the blower fan and motor is essential to prevent issues such as reduced airflow or loud operation.
Flame Detector
The flame detector is a safety device that monitors the presence of a flame in the combustion chamber. If no flame is detected, it shuts off the gas flow to prevent the buildup of combustible gases. A malfunctioning flame detector can be a safety hazard and should be promptly replaced or repaired.
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger separates the combustion process from the air entering your home. It absorbs heat from the burning gas and transfers it to the air, which is then circulated throughout your home. A cracked or damaged heat exchanger can lead to carbon monoxide leakage, posing a serious health risk.
Plenums, Gas Valve, Air Filter, and Transformer
Plenums are the ductwork components that distribute the heated air to different rooms. The gas valve controls the flow of gas into the burners. The air filter traps dust, debris, and other particles to keep the furnace and indoor air clean. The transformer converts electricity to the appropriate voltage for the furnace. Regular maintenance of these components is necessary to ensure the optimal operation and longevity of your gas furnace.
By understanding the various components of a gas furnace, you can better appreciate the intricate system that provides warmth to your home. Regular maintenance and prompt repairs are essential to keep your furnace running efficiently and safely. Consult a licensed HVAC technician for professional advice and assistance in maintaining your gas furnace.
Types of Gas Furnaces
Gas furnaces come in different types, each offering unique features and benefits. Understanding these types can help homeowners make informed decisions when choosing a heating system that suits their needs.
Non-Condensing Furnaces
Non-condensing furnaces are a popular choice for many homeowners. These furnaces vent exhaust gases outside of the home, ensuring safe and efficient operation. They are a reliable and cost-effective heating solution, providing consistent warmth during colder months.
Condensing Furnaces
Condensing furnaces are known for their high energy efficiency. These furnaces utilize a second heat exchanger, which extracts additional heat from the exhaust gases. This process increases the overall efficiency of the furnace, resulting in potential cost savings on utility bills. Condensing furnaces are an excellent option for homeowners looking for energy-efficient heating systems.
Modulating Gas Furnaces
Modulating gas furnaces are designed to maintain a steady and comfortable indoor temperature. These furnaces continuously regulate the amount of fuel burned to meet the heating demands of the home. By adjusting the heating output, modulating gas furnaces minimize temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent warmth throughout the house. They provide optimal comfort and energy efficiency while reducing wear and tear on the furnace components.
Choosing the right type of gas furnace depends on individual heating needs and energy efficiency goals. Consultation with a licensed HVAC technician can help homeowners select the most suitable furnace type based on their specific requirements.
The Working Process of a Furnace
A furnace operates by burning either propane or natural gas to generate heat. This heat is then transferred to the air through a heat exchanger, which is a crucial component of the furnace system. The heat exchanger warms the air that is circulated through the home’s ductwork. Once the air is heated, a blower fan forces it into the supply ductwork, distributing it evenly throughout the house. This process ensures that the entire home is effectively heated during colder temperatures.
To better understand the working process of a furnace, let’s break it down step by step:
- The furnace burns either propane or natural gas in its burner.
- The heat produced from the burning fuel passes through the heat exchanger.
- The heat exchanger warms the air from the home’s ductwork.
- A blower fan then forces the heated air into the supply ductwork.
- The heated air is distributed throughout the house, providing warmth to every room.
“The working process of a furnace involves the burning of propane or natural gas in the burner to produce heat. This heat passes through a heat exchanger, which warms air from the home’s ductwork.”
The working process of a furnace is essential for maintaining a comfortable and cozy home environment during colder temperatures. It is crucial to ensure that the furnace is properly functioning to optimize its performance and efficiency. Regular maintenance and servicing by a licensed HVAC technician can help identify any issues and ensure that the furnace operates smoothly.
Burning Propane vs. Burning Natural Gas
The choice between burning propane or natural gas in a furnace depends on several factors, including availability and cost. Propane is a liquefied petroleum gas that is more commonly used in rural areas where natural gas is not readily available. It is stored in tanks and delivered to the home. Natural gas, on the other hand, is a fossil fuel that is delivered to homes through a network of pipelines. Both propane and natural gas provide efficient and reliable heat, but their cost and accessibility may vary depending on location.
| Propane | Natural Gas | |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Requires storage tanks and delivery | Delivered through pipelines |
| Cost | Varies depending on market fluctuations | Generally lower than propane |
| Environmental Impact | Higher greenhouse gas emissions | Lower greenhouse gas emissions |
| Efficiency | Efficient combustion process | Highly efficient combustion process |
The Importance of Proper Furnace Sizing
Proper furnace sizing is crucial for ensuring both comfort and cost-efficiency in your home. A furnace that is too small for your space may struggle to maintain the desired indoor temperature on colder days, leading to discomfort and chilly rooms. On the other hand, an oversized furnace may cycle on and off frequently, causing temperature fluctuations and wasting energy unnecessarily. It’s important to consult a licensed HVAC technician who can accurately assess your home’s heating needs and recommend the proper furnace size.
When a furnace is correctly sized for your space, it can provide optimal heating performance while operating more efficiently. A properly sized furnace will heat your home evenly, eliminating cold spots and maintaining a consistent temperature throughout. This not only enhances your comfort but can also help lower your utility bills by ensuring that your furnace isn’t working harder than necessary to heat your home.
Working with a licensed HVAC technician during the furnace sizing process is essential. They have the knowledge and expertise to evaluate various factors like your home’s insulation, size, layout, and climate to determine the ideal furnace size. By choosing the right-sized furnace, you can enjoy maximum comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term cost savings.
Benefits of Proper Furnace Sizing
- Improved Comfort: A properly sized furnace ensures consistent temperature control and eliminates hot or cold spots in your home.
- Energy Efficiency: When a furnace is the right size, it operates at peak efficiency, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
- Longevity: Correctly sizing your furnace prevents excessive cycling, reducing wear and tear on components and extending the lifespan of your system.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing your furnace’s performance, you can save money on heating costs over time.
Proper furnace sizing is crucial for both comfort and cost-efficiency. It ensures your heating system operates optimally, providing reliable warmth while keeping your energy bills in check. Don’t underestimate the importance of professional guidance from a licensed HVAC technician when determining the proper furnace size for your home.
A Complete Guide to Furnace Sizing
| Furnace Size | Square Footage | BTU Output |
|---|---|---|
| Small | Up to 1,200 sq ft | 40,000-80,000 BTU |
| Medium | 1,200-2,000 sq ft | 60,000-100,000 BTU |
| Large | 2,000-3,000 sq ft | 80,000-150,000 BTU |
Keep in mind that these are general guidelines, and there are other factors to consider, such as insulation quality, number of windows, ceiling height, and climate. Consulting with a licensed HVAC technician will ensure an accurate assessment of your specific heating needs and help you choose the right furnace size for your home.
Maintaining a Gas Furnace
Proper maintenance of your gas furnace is essential for its safe and efficient operation. By following some simple safety precautions and performing regular cleaning and upkeep, you can ensure that your furnace continues to provide reliable heat during the colder months.
Safety Precautions:
- Keep flammable items, such as paper, clothing, and cleaning products, safely away from the furnace to prevent fire hazards.
- Install carbon monoxide (CO) detectors in your home and test them regularly to detect any potential leaks, as CO gas is odorless and can be harmful.
Cleaning:
Regular cleaning of your gas furnace helps maintain its efficiency and longevity. Here are some cleaning tasks you should perform:
- Change the air filter regularly to prevent dust and debris from entering the furnace. A clogged filter can restrict airflow and reduce efficiency.
- Clean the furnace registers and vents to ensure proper airflow and avoid excessive heat buildup.
- Dust or vacuum the furnace components, such as the burners and blower fan, to remove any accumulated dirt or debris.
Professional Inspection:
In addition to regular cleaning, it is recommended to schedule an annual maintenance inspection by a certified HVAC technician. They will perform a thorough examination of your furnace, checking for any potential issues and ensuring all components are working properly. Regular professional maintenance can help identify and fix problems early, preventing costly repairs and improving the overall lifespan of your furnace.
By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your gas furnace in optimal condition and enjoy reliable, cost-effective heating throughout the winter season.
Table: Gas Furnace Maintenance Checklist
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Change air filter | Every 1-3 months |
| Clean furnace registers and vents | Annually |
| Dust or vacuum burners and blower fan | Annually |
| Schedule professional inspection | Annually |
Proper maintenance and regular cleaning of your gas furnace can help ensure its safe and efficient operation, providing you with reliable heat during the winter months. By following the recommended safety precautions, performing routine cleaning tasks, and scheduling professional inspections, you can extend the lifespan of your furnace and enjoy consistent warmth in your home.
Types of Furnace Shape and Efficiency
When it comes to gas furnaces, there are different shapes that homeowners can choose from based on their heating needs and space requirements. The two main types of gas furnaces are non-condensing furnaces and condensing furnaces.
Non-condensing furnaces are the traditional and more commonly used type. They typically vent exhaust gases outside of the home through the roof. These furnaces are known for their reliability and are suitable for most residential heating needs.
On the other hand, condensing furnaces offer higher efficiency by utilizing a second heat exchanger to extract additional heat from the exhaust gases. This improves the overall efficiency of the furnace and can result in cost savings over time. Condensing furnaces are especially beneficial in areas where energy efficiency is a top priority.
Comparing Non-Condensing and Condensing Furnaces
| Furnace Type | Efficiency | Exhaust Gas Handling | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-condensing furnaces | Typically 80-85% | Vent exhaust gases outside through the roof | Lower upfront cost |
| Condensing furnaces | Typically 90-98% | Utilize a second heat exchanger to extract additional heat from exhaust gases | Higher upfront cost, but potential energy savings |
Choosing the right furnace shape and efficiency largely depends on personal preferences, budget, and energy efficiency priorities. Consult with a licensed HVAC technician to determine which type of gas furnace is the best fit for your home and heating requirements.
Benefits and Considerations of Gas Furnaces
Gas furnaces offer numerous benefits that make them a popular choice for residential heating. Understanding these benefits and considering important factors can help homeowners make an informed decision when selecting a gas furnace for their homes.
Benefits of Gas Furnaces
- Energy Efficiency: Gas furnaces are known for their high energy efficiency, offering cost savings and reducing utility bills over time.
- Heating Performance: Gas furnaces provide reliable and consistent heating performance, ensuring comfort during colder temperatures.
- Quick and Responsive Heating: Gas furnaces heat up quickly, providing warmth to the home faster compared to other heating systems.
- Long Lifespan: With proper maintenance, gas furnaces can last for many years, offering long-term value.
- Environmentally Friendly: Gas furnaces produce fewer emissions compared to other heating options, making them a more environmentally friendly choice.
Considerations for Gas Furnaces
- Upfront Costs: Gas furnaces can have higher upfront costs compared to other heating systems. However, the long-term energy savings can often offset these initial expenses.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular maintenance by a certified technician is necessary to ensure optimal performance and safety of a gas furnace. Homeowners should consider the ongoing maintenance requirements and associated costs.
- Gas Availability: Gas furnaces require a natural gas supply. Homeowners not connected to a natural gas line may need to consider alternative heating options.
- Space and Sizing: Gas furnaces come in different sizes, and it is important to choose the right size for the space to ensure efficient heating and avoid energy waste.
By weighing the benefits and considerations, homeowners can make an informed decision when selecting a gas furnace that suits their heating needs, energy efficiency goals, and budget. Consulting with licensed HVAC professionals can provide valuable guidance in choosing the most suitable gas furnace for a home.
Conclusion
Understanding how a furnace works and the components involved is essential for homeowners looking for a reliable and efficient heating system. By ensuring proper furnace sizing and maintenance, homeowners can optimize comfort and cost-efficiency. Gas furnaces, with their reliable operation and cost savings, are a popular choice for residential spaces.
When selecting a gas furnace, it is vital to consult with licensed HVAC technicians who can provide expert advice based on individual heating needs. By considering factors such as furnace working process, proper furnace sizing, and furnace maintenance, homeowners can make informed decisions to ensure a warm and comfortable home.
By staying informed about the different types of gas furnaces available and their benefits, homeowners can select the heating system that best fits their energy efficiency goals and heating performance requirements. Gas furnaces offer a reliable, cost-effective, and comfortable heating solution for residential spaces. So, whether you are looking for a non-condensing furnace, a condensing furnace, or a modulating gas furnace, there is a gas furnace type that’s right for you.
FAQ
How does a furnace work?
A furnace operates by burning propane or natural gas in a burner to generate heat. The heat then passes through a heat exchanger, warming air from the home’s ductwork. A blower fan distributes the heated air throughout the house.
What is the importance of proper furnace sizing?
Proper furnace sizing is essential for optimal performance. An undersized furnace may struggle to keep up on colder days and result in increased utility bills. An oversized furnace can cause temperature fluctuations and premature wear and tear on components.
How does the heating cycle of a gas furnace work?
The heating cycle starts with the burner igniting propane or natural gas. The heat produced passes through a heat exchanger, warming air from the ductwork. A blower fan then forces the heated air into the supply ductwork, distributing it throughout the house.
What are the components of a gas furnace?
Gas furnaces consist of various components, including the thermostat, control board, burners, igniter, blower fan, flame detector, heat exchanger, plenums, gas valve, air filter, and transformer.
What are the types of gas furnaces?
Gas furnaces can be categorized into non-condensing furnaces, condensing furnaces, and modulating gas furnaces, each offering unique advantages based on functionality and energy efficiency goals.
How does a furnace generate warmth for a home?
A furnace generates warmth by burning propane or natural gas in the burner. The heat produced passes through a heat exchanger, which warms air from the home’s ductwork. The blower fan then distributes the heated air throughout the house.
Why is proper furnace sizing important?
Proper furnace sizing is crucial for comfort and cost-efficiency. An undersized furnace may struggle to maintain the desired indoor temperature on colder days, while an oversized furnace can cause temperature fluctuations and unnecessary wear and tear on its components.
What maintenance and safety precautions should be taken for a gas furnace?
It is important to keep flammable items away from the furnace and schedule regular cleaning and maintenance by a certified technician. Changing the air filter regularly, installing carbon monoxide detectors, and keeping furnace registers clear of obstruction are also crucial for safe and efficient operation.
What are the different types of furnace shape and efficiency?
Gas furnaces can come in various shapes, including non-condensing furnaces, which vent exhaust gases outside of the home, and condensing furnaces, which use a second heat exchanger for higher efficiencies.
What are the benefits and considerations of gas furnaces?
Gas furnaces offer efficient heating performance, cost savings, and reliable operation. However, homeowners should consider factors such as energy efficiency ratings, maintenance requirements, and upfront costs when selecting a gas furnace.
![Ray Dalio Quotes [Principles, Life, Investment]](https://tagvault.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Screen-Shot-2023-04-19-at-7.57.49-PM.png)
