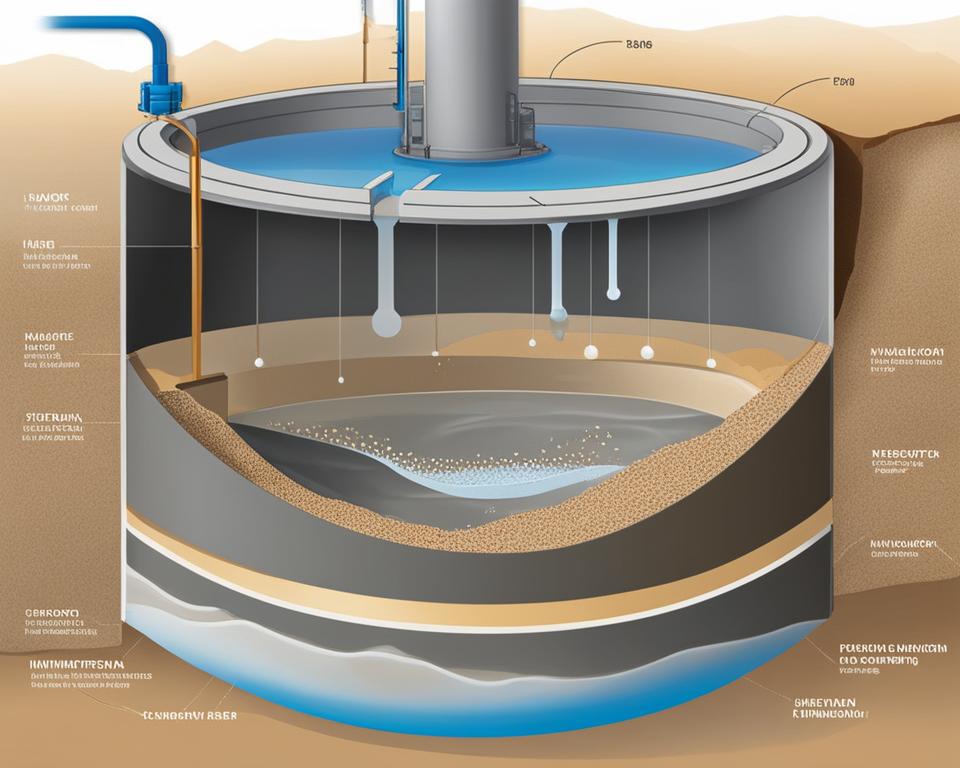
A sand filter, also known as a sand water filter, is a water filtration system that uses sand to remove dirt particles and impurities from water. It is commonly used for pre-filtration of disinfection equipment, micro- and ultra-filtration, recirculation systems, irrigation systems, and ground water cleaning. It works by allowing water to slowly sink through a bed of sand, which traps the dirt particles in its fine pores. It is important to note that a sand filter can only filter solid particles like algae and organic material, and it does not filter dissolved salts from water.
Key Takeaways:
- A sand filter is a water filtration system that uses sand to remove dirt particles and impurities from water.
- It works by allowing water to slowly sink through a bed of sand, trapping the dirt particles in its fine pores.
- It is commonly used for pre-filtration, recirculation systems, and ground water cleaning.
- A sand filter can’t filter dissolved salts from water, only solid particles.
- Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the sand filter.
Sand Filter Water Filtration Process
The sand filtration process is a crucial step in water treatment, removing impurities and improving water quality. Sand filters utilize a bed of sand, gravel, or another filter medium to trap dirt particles and suspended matter, providing effective physical filtration.
When unfiltered water enters the sand filter from the top, it slowly penetrates through the filter bed. The small pores of the sand act as a sieve, capturing particles and preventing them from passing through. This process helps to clarify the water by removing visible debris and sediment.
By employing sand filters in water treatment systems, the filtration process can be enhanced. The physical mechanism of sand filtration ensures that solid particles are efficiently trapped, resulting in cleaner and clearer water. Sand filters are versatile and widely used in various industries and applications where effective water purification is required.
Table: Sand Filter Water Filtration Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Unfiltered water enters the sand filter from the top. |
| 2 | The water slowly sinks through the filter bed. |
| 3 | The small pores of the sand trap dirt particles and suspended matter. |
| 4 | Clean, filtered water exits the sand filter. |
“The sand filtration process involves the gradual passage of water through a bed of sand, where the sand particles act as a natural filter, trapping impurities and ensuring cleaner water.”
Sand Filter Operation and Backwash
A sand filter operates by allowing water to pass through a bed of sand, where the dirt particles and impurities are trapped. However, over time, the sand filter becomes polluted and its filtering efficiency decreases. To maintain optimal performance, the sand filter undergoes a process called backwashing.
During backwashing, the filter switches to a reverse flow mode. This causes the filter bed to expand and the trapped dirt particles to be dislodged and flushed out of the filter. The backwash water, along with the dirt, is then discharged from the filter. This process helps prevent the sand filter from getting blocked and ensures its continued purification capabilities.
To ensure the proper functioning of a sand filter, periodic maintenance and checking of the sand filter’s filling are necessary. This includes inspecting the sand bed for any signs of clogging or damage and replenishing the sand if needed. Regular maintenance helps prolong the lifespan of the sand filter and ensures its efficient operation in removing solid particles from water.
Table: Sand Filter Maintenance Checklist
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inspect sand bed for clogging or damage | Monthly |
| Check sand filter’s filling level | Quarterly |
| Replace sand if necessary | Every 3-5 years |
| Monitor backwash process and adjust settings if needed | Regularly |
By following these maintenance guidelines, sand filters can continue to effectively remove dirt particles and impurities from water, ensuring the provision of clean and safe water for various applications.
Sand Filter Components and Diameter
A sand filter is composed of several essential components that work together to effectively filter water and remove impurities. These components include:
- The filter tank: This is the container that holds the sand bed and controls the flow of water through the filter.
- The sand bed: This is the media through which the water passes, trapping and removing dirt particles.
- Laterals or nozzles: These components evenly distribute water across the sand bed, ensuring optimal filtration.
- The backwash system: This system is responsible for the backwashing process, which cleans the filter by enlarging the pores of the sand bed.
The diameter of the sand used in a sand filter depends on various factors, such as the size of the filter, desired flow rate, and desired filtration level. Typically, sand with a diameter of 0.8 mm to 1.25 mm is used for the filtration process. The size of the sand particles affects the efficiency of the filter, as smaller particles can trap finer dirt particles, while larger particles may allow some impurities to pass through. It is important to select the appropriate sand diameter to ensure efficient and effective filtration.
Filtration Component Comparison
Let’s compare the key components of different types of sand filters:
| Component | Gravity Sand Filter | Pressure Sand Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Filter Tank | Large and open-top | Pressure vessel |
| Sand Bed | Deep bed of sand, typically 0.9 – 1.5 m high | Shallow bed of sand, typically 0.6 – 0.9 m high |
| Laterals or Nozzles | Distribution laterals located at the bottom of the tank | Distribution nozzles located at the top of the tank |
| Backwash System | Requires manual or semi-automatic backwashing | Automated backwashing using pressure difference or timer |
“The components of a sand filter, such as the filter tank, sand bed, laterals or nozzles, and backwash system, are essential for its operation and efficiency. The choice of sand diameter is crucial to achieve the desired flow rate and filtration level. When comparing different types of sand filters, it is important to consider factors such as tank design, sand bed depth, distribution mechanism, and backwash system.”
Sand Filter Troubleshooting
While sand filters are generally reliable water filtration systems, they can encounter some common issues that may require troubleshooting. By identifying and addressing these problems promptly, you can ensure the continued effectiveness of your sand filter.
1. Inadequate Filtration
If you notice that your sand filter is not effectively removing dirt particles from the water, it may indicate a clogged sand bed or damaged laterals. To troubleshoot this issue, perform backwashing to remove any trapped debris. If the problem persists, you may need to clean or replace the sand bed and inspect the laterals for any signs of damage.
2. Loss of Pressure
A noticeable drop in water pressure is another common problem with sand filters. This can be caused by a dirty filter or a malfunctioning backwash system. To address this issue, thoroughly clean the filter and ensure that the backwash system is functioning properly. If the pressure loss persists, consider consulting a professional to assess and repair the filter system.
3. Excessive Backwashing
If your sand filter seems to require frequent and excessive backwashing, it may indicate a problem with the filter’s settings or flow rate. Check the settings to ensure they are optimized for your specific filtration needs. Additionally, evaluate the flow rate and make adjustments as necessary. Consulting the manufacturer’s guidelines can help troubleshoot this issue effectively.
4. Sand Leakage
Sand leakage can occur if the sand bed is not properly contained within the filter tank. Inspect the filter for any signs of sand leakage, such as sand particles in the water discharge. If leakage is detected, make sure the filter tank is securely sealed and consider replacing any damaged or deteriorating components.
Regular maintenance and careful troubleshooting can help resolve these common sand filter issues. By addressing these problems promptly, you can maintain the optimal performance of your sand filter and ensure clean, filtered water for your intended applications.
Sand Filter Applications
Sand filters have a wide range of applications in various industries and processes. They are commonly used in drinking water production, swimming pool filtration, wastewater treatment, groundwater treatment, and industrial applications. Sand filters are also used for pre-filtration in membrane systems, as a polishing filter in recirculation systems, and for the filtration of surface water and aquaculture seawater. The filtration mechanism of sand filters, which involves the physical trapping of solid particles, makes them effective in removing suspended matter, improving water quality, and reducing pathogens.
Sand filters are particularly useful in drinking water production, where they can remove undesirable particles and improve the taste and color of the water. They are also employed in swimming pools to remove dirt, debris, and bacteria, ensuring clean and safe water for swimmers. In wastewater treatment, sand filters play a crucial role in removing suspended solids and organic matter, improving the water quality before it is discharged into the environment. The versatility of sand filters makes them suitable for various industrial applications, such as the treatment of process water, cooling tower water, and effluent water.
Sand Filter Applications:
- Drinking water production
- Swimming pool filtration
- Wastewater treatment
- Groundwater treatment
- Industrial applications
- Pre-filtration in membrane systems
- Polishing filter in recirculation systems
- Filtration of surface water and aquaculture seawater
Overall, sand filters are versatile and effective filtration systems that find applications in various sectors. They help improve water quality, remove solid particles, and ensure the safety and reliability of water sources in different settings.
Sand Filter Advantages and Disadvantages
A sand filter offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for water filtration systems. One of the main advantages is its simplicity. The design and operation of a sand filter are relatively straightforward, making it easy to install and maintain. Additionally, sand filters are cost-effective compared to other filtration methods, as they require minimal power consumption and have low running costs.
Another advantage of sand filters is their potential for wastewater re-use. The filtration process removes dirt particles and impurities from water, resulting in clearer and cleaner water that can be reused for various purposes such as irrigation or industrial processes. By implementing a sand filter, businesses and industries can reduce their water consumption and promote sustainable practices.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider when using sand filters. One potential drawback is the need for chemical additives to enhance filtration efficiency. In some cases, the addition of chemicals may be necessary to improve water quality and remove specific contaminants. These chemicals need to be carefully selected and dosed to ensure optimal performance without causing adverse effects on the environment or human health.
“Sand filters offer simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and potential for wastewater re-use.”
– Water Filtration Expert
Another disadvantage of sand filters is the generation of heavily polluted rinse water during the backwashing process. Backwashing is necessary to clean the sand bed and remove trapped dirt particles. The polluted rinse water requires proper treatment and disposal to prevent environmental contamination. Implementing preliminary sedimentation can help reduce the load on the filter and minimize the need for frequent backwashing, mitigating this issue.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplicity | Chemical additives may be required |
| Cost-effectiveness | Generation of polluted rinse water |
| Potential for wastewater re-use |
In summary, sand filters offer simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and the potential for wastewater re-use. However, they may require the use of chemical additives and can generate heavily polluted rinse water during backwashing. By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages, businesses and water treatment facilities can determine if a sand filter is the right choice for their specific needs and take appropriate measures to maximize its effectiveness and minimize potential drawbacks.
Sand Filter Media Selection and Characteristics
When it comes to sand filters, the selection of the right filter media is essential for optimal filtration performance. The media used in a sand filter plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and longevity of the filtration system. Let’s take a closer look at the characteristics of sand filter media and how they impact the overall performance of the filter.
Sand filter media should have specific characteristics to ensure effective filtration. The effective size of the sand determines its ability to trap particles, with smaller effective sizes providing better filtration. The shape of the sand particles is also important, as irregularly shaped grains can create voids that reduce filtration efficiency. Hardness is another critical factor, as softer sands can break down more easily, leading to shorter filter life.
The uniformity coefficient (Cu) is a measure of the size distribution of the sand particles. A lower Cu value indicates a more uniform particle size distribution, which can improve flow rate and reduce the risk of clogging. Additionally, a well-washed filter media is crucial to remove fine particles and impurities that can affect the performance of the sand filter.
Sand Filter Media Characteristics:
- Effective size: Determines particle trapping ability
- Shape: Irregular shapes reduce filtration efficiency
- Hardness: Softer sands have shorter filter life
- Uniformity coefficient (Cu): Indicates particle size distribution
Table: Comparison of Sand Filter Media
| Sand Type | Effective Size (mm) | Shape | Hardness (Mohs) | Uniformity Coefficient (Cu) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Sand | 0.45 – 0.55 | Rounded | 5-6 | 1.40-1.65 |
| Filter Sand | 0.45 – 0.55 | Rounded | 6-7 | 1.35-1.60 |
| Garnet Sand | 0.25 – 0.35 | Irregular | 7-8 | 1.30-1.40 |
Proper selection and quality control of sand filter media are crucial for ensuring effective filtration and maintaining the longevity of the sand filter. By considering the characteristics such as effective size, shape, hardness, and uniformity coefficient, you can optimize the performance of your sand filter and ensure the highest quality of filtered water.
Sand Filter and Water Filtration Systems
Sand filters play a crucial role in water treatment systems, effectively removing suspended matter and solid particles to improve water quality. They are widely utilized in various applications, including drinking water purification, wastewater treatment, and industrial water filtration. By understanding the mechanisms and components of sand filters, we can appreciate their importance in water filtration processes.
One of the key applications of sand filters is in drinking water systems. They can function as standalone filtration systems or be integrated into multi-media filtration setups. Sand filters work in conjunction with other treatment techniques such as coagulation/flocculation, sedimentation, and active carbon treatments to ensure the removal of impurities and contaminants from the water.
“Sand filters are an essential component of water filtration systems, providing efficient removal of suspended matter and solid particles.”
It is crucial to use sand filter media that is NSF certified for drinking water systems, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards for water safety. Proper maintenance and media selection are vital to ensure the effective operation and longevity of sand filters.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Drinking water production | Removal of suspended matter and solid particles. |
| Wastewater treatment | Purification of wastewater in industrial settings. |
| Industrial water filtration | Effective removal of solid particles in various industries. |
Sand filters are versatile and can be implemented in a wide range of sectors and processes that require the removal of suspended matter from water or wastewater. Some examples include iron removal from groundwater, the final purification of wastewater in industrial settings, and the purification of wastewater containing sand-blasting grit and paint particles. Additionally, sand filters find application in greenhouse horticulture as a drain-water disinfectant.
With their ability to efficiently remove solid particles and improve water quality, sand filters play a significant role in water treatment and purification processes, ultimately safeguarding human health and the environment.
Sand Filter Implementation and Application Examples
Implementing a sand filter is a practical solution for various sectors and processes that require the removal of suspended matter from water or wastewater. With their efficient solid particle removal and water purification capabilities, sand filters find application in a range of industries and settings.
One example of sand filter implementation is in the removal of iron from groundwater. Sand filters effectively trap and remove the iron particles, improving water quality and making it suitable for drinking and other purposes. In industrial settings, sand filters serve as a final purification step for wastewater treatment, ensuring that any remaining impurities or particles are effectively removed before the water is discharged.
“Sand filters play a crucial role in improving water quality and safeguarding human health.”
Another application of sand filters is in the purification of wastewater containing sand-blasting grit and paint particles. The sand filter’s physical trapping mechanism proves highly effective in removing these solid particles, resulting in cleaner water that can be safely reused or discharged. Sand filters also find use in greenhouse horticulture as a drain-water disinfectant, helping prevent the spread of pathogens and contaminants in the irrigation system.
Furthermore, sand filters are utilized in drinking water production, surface treatment of metals, and fruit and vegetable processing. They are integral to the solid particle removal process in these industries, ensuring the water used is clean and free from impurities. With their versatility and efficiency, sand filters have become an essential tool in water treatment and purification processes, contributing to improved water quality and environmental sustainability.
| Application | Industry | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Iron removal from groundwater | Drinking water production | Improve water quality for safe consumption |
| Final purification of wastewater | Industrial settings | Remove remaining impurities before discharge |
| Purification of wastewater containing sand-blasting grit and paint particles | Various industries | Clean water for reuse or safe discharge |
| Greenhouse horticulture as a drain-water disinfectant | Agriculture | Prevent spread of pathogens in irrigation system |
| Drinking water production, surface treatment of metals, fruit and vegetable processing | Various industries | Clean water for use in industrial processes |
Conclusion
In conclusion, sand filters are a vital component of water filtration systems, offering an efficient solution for the removal of suspended matter and solid particles. By allowing water to pass through a bed of sand, these filters effectively trap dirt particles, resulting in improved water clarity. Sand filters have several advantages, including their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for various applications.
However, it is important to note that sand filters may require the addition of chemicals to enhance filtration efficiency, and the backwashing process can generate heavily polluted rinse water that needs proper treatment and disposal. Regular maintenance and proper media selection are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance of sand filters. With their broad range of applications, sand filters play a crucial role in water treatment and purification processes, contributing to the improvement of water quality and safeguarding human health.
So, whether it’s for drinking water production, wastewater treatment, or industrial filtration, sand filters are a reliable and effective solution for removing solid particles from water. Their proven filtration mechanism makes them a valuable asset in various industries, providing clean and clear water for different purposes. By investing in proper maintenance and understanding the unique characteristics of sand filter media, you can ensure the long-term efficiency and functionality of your water filtration system.
FAQ
How does a sand filter work?
A sand filter works by allowing water to slowly sink through a bed of sand, which traps dirt particles and impurities. It is a physical filtration process that improves the quality and clarity of water.
What is the sand filtration process?
The sand filtration process involves distributing unfiltered water at the top of the sand filter, allowing it to pass through the sand bed. The sand traps dirt particles, effectively removing them from the water and improving its quality.
How does a sand filter operate and what is backwash?
A sand filter operates by filtering water through a bed of sand. When a certain quantity of water has been filtered or when the sand is polluted, the filter switches to backwashing. Backwashing enlarges the pores of the sand, allowing trapped dirt to be washed away and maintaining the filter’s effectiveness.
What are the components of a sand filter and what is their purpose?
A sand filter consists of a filter tank, sand bed, laterals or nozzles, and a backwash system. The filter tank holds the sand bed and controls water flow. The sand bed filters the water, while the laterals evenly distribute water across the sand bed. The backwash system performs the backwashing process to keep the filter functioning optimally.
What are common issues and troubleshooting steps for sand filters?
Common issues with sand filters include inadequate filtration, loss of pressure, excessive backwashing, and sand leakage. These issues can be addressed through regular maintenance, checking the sand filter’s filling, and troubleshooting specific components or settings.
What are the applications of sand filters?
Sand filters have a wide range of applications, including drinking water production, swimming pool filtration, wastewater treatment, groundwater treatment, and industrial processes. They are used for pre-filtration in membrane systems, polishing in recirculation systems, and the filtration of surface water and aquaculture seawater.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sand filters?
Sand filters offer advantages such as simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and potential water re-use. However, they may require chemical additives and generate polluted rinse water during backwashing. Regular maintenance is necessary. Sand filters have various applications in water treatment and purification processes.
How is sand media selected for sand filters?
Sand media selection is crucial for optimal filtration performance. The media should have specific characteristics such as effective size, shape, hardness, and uniformity coefficient. Proper selection and quality control contribute to the efficiency and longevity of the sand filter.
How are sand filters used in water filtration systems?
Sand filters can be used as standalone filtration systems or as components of multi-media filtration systems. They are compatible with various treatment techniques and are widely employed in drinking water purification, wastewater treatment, and industrial water filtration.
How are sand filters implemented and what are some application examples?
Sand filters are implemented in sectors and processes that require the removal of suspended matter from water or wastewater. Examples include iron removal from groundwater, final purification of industrial wastewater, and purification of wastewater containing sand-blasting grit and paint particles.

