The Toyota Prius is a revolutionary hybrid car that has transformed the automotive industry. With its impressive fuel economy and low CO2 emissions, the Prius has gained tremendous popularity since its release. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics behind the Toyota Prius and explore how this hybrid vehicle works.
Key Takeaways:
- The Toyota Prius is a pioneering hybrid car known for its fuel efficiency.
- It offers impressive fuel economy, with a combined city and highway EPA fuel economy of 54 MPG in the 2020 model.
- The Prius reduces CO2 emissions and helps to save the environment.
- Its hybrid engine combines the best components of series and parallel engines for optimal performance.
- The Toyota Prius utilizes regenerative braking to maximize energy efficiency and improve fuel economy.
The Design of the Toyota Prius
The design of the Toyota Prius plays a crucial role in its efficiency. One of the key features of the Prius is its aerodynamic shape, which reduces drag and improves fuel efficiency. The sleek and streamlined design allows the car to cut through the air more easily, resulting in better overall performance and fuel economy. In fact, the Gen 3 Prius had a longer and wider body with sharper corners, further enhancing its aerodynamic capabilities.
In addition to its aerodynamic design, the Toyota Prius incorporates other design elements that contribute to its efficiency. Changes in transmission and engine size have also played a significant role in increasing fuel economy. For example, the Gen 4 Prius saw improvements in its MPG rating, going from 48 MPG to an impressive 51 MPG.
Another important aspect of the Toyota Prius design is the inclusion of a multi-function display. This display allows drivers to monitor the energy flow between the battery and the engine, as well as the battery levels and the performance of the braking systems. By providing real-time information, the display helps drivers optimize their driving habits and maximize the efficiency of the vehicle.
In summary, the design of the Toyota Prius is carefully engineered to prioritize efficiency and performance. From its aerodynamic shape to its advanced display system, every aspect of the design is aimed at maximizing fuel economy and reducing emissions. The Toyota Prius continues to push the boundaries of hybrid vehicle design, setting new standards for efficiency in the automotive industry.
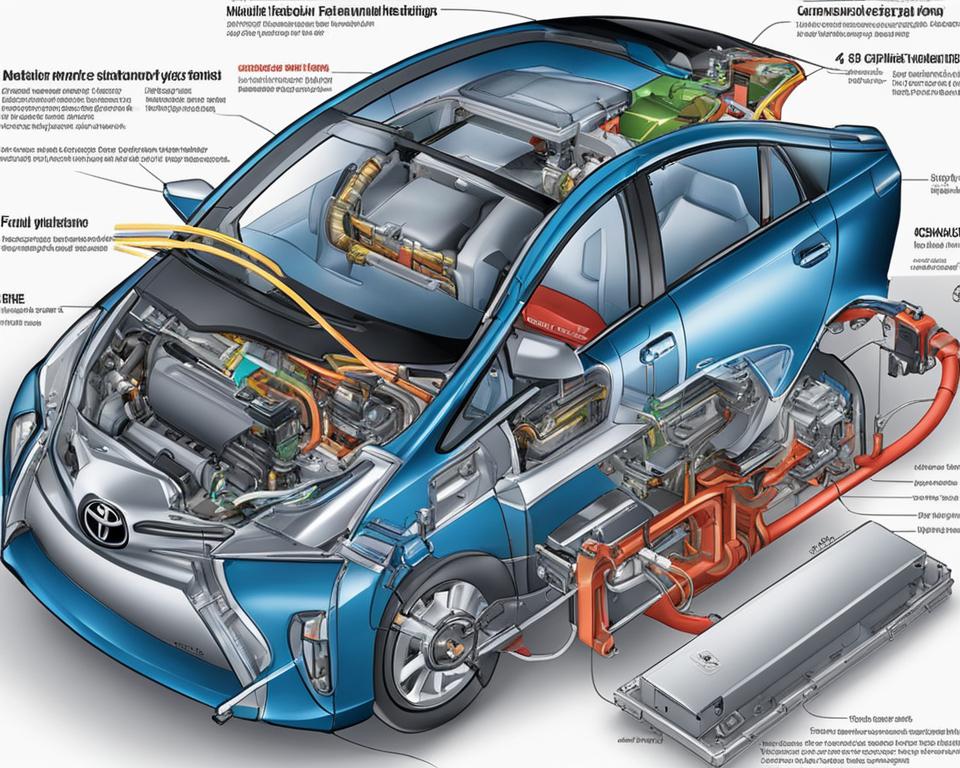
Hybrid Engine: How Does A Prius Work?
The Toyota Prius utilizes a hybrid engine system that combines the best features of both series and parallel engines. This innovative system allows the Prius to operate efficiently and deliver impressive fuel economy. So, how does the hybrid system in the Toyota Prius work?
The hybrid engine in the Toyota Prius consists of a power split device that connects the generator, gas engine, and electric motor. This device uses a planetary gear set to distribute power between the engine and motor, enabling seamless switching between the two as needed. When starting from a stop, the electric motor powered by the battery provides the initial power until speeds exceed 15 MPH, at which point the gasoline engine kicks in to assist.
One of the key advantages of the Prius’ hybrid system is its ability to charge the battery while driving. While the gasoline engine powers the car, it also charges the battery, which then supplies power to the electric motor. This allows the Prius to achieve excellent fuel economy by utilizing both the gasoline engine and the electric motor effectively.
Fuel Economy and Efficiency
The hybrid engine system in the Toyota Prius contributes to its exceptional fuel economy. By combining the power of the gasoline engine and the electric motor, the Prius can optimize power distribution for various driving conditions, resulting in improved efficiency. The continuous charging of the battery during operation ensures that the electric motor can assist the gasoline engine when needed, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
To further enhance fuel economy, the Prius also incorporates regenerative braking. As the vehicle slows down, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy from braking into electricity. This electricity is then stored in the battery for future use, reducing reliance on the gasoline engine and improving overall efficiency.
Overall, the hybrid engine system in the Toyota Prius is a remarkable feat of engineering. It combines the strengths of both gasoline and electric power to deliver exceptional fuel economy and efficiency. With advancements in hybrid technology, the future looks promising for even greater improvements in fuel economy and environmental sustainability.
Starting From the Stopped Position
When it comes to starting from a stop, the Toyota Prius utilizes its electric motor, which is powered by the battery. This electric motor provides the initial power until the vehicle reaches speeds exceeding 15 MPH. At that point, the gasoline engine kicks in to assist the electric motor, ensuring smooth acceleration and optimal performance. This reliance on electricity at low speeds and in start-and-stop traffic is one of the key factors contributing to the Toyota Prius’ impressive fuel savings and improved fuel economy.
One of the distinctive features of the Prius is its regenerative braking system. As the vehicle slows down, the electric motor functions as a generator, converting the kinetic energy from braking into electricity. This electricity is then stored in the battery, making it available for later use. This innovative regenerative braking process allows the Prius to recover approximately 70% of the energy that would otherwise be lost during braking. As a result, the Toyota Prius achieves exceptional fuel economy, enhancing its overall efficiency.
Regenerative Braking in Action
“The regenerative braking system in the Toyota Prius allows for the recovery of about 70% of the energy lost during braking, significantly improving fuel economy.”
Not only does the regenerative braking system improve the fuel economy of the Toyota Prius, but it also plays a role in making driving more environmentally friendly. By harnessing the energy that would otherwise be wasted, the Prius reduces the overall carbon footprint and contributes to a greener planet. Additionally, the vehicle’s intelligent energy management system ensures that the battery powers essential functions, such as lighting and air conditioning, while the car is stationary. This further optimizes energy usage and conserves fuel.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Fuel Economy Improvement | The regenerative braking system recovers approximately 70% of the energy lost during braking, resulting in enhanced fuel economy. |
| Environmental Impact | By reducing the overall carbon footprint, the regenerative braking system helps make driving more environmentally friendly. |
| Energy Conservation | The Prius intelligently manages energy usage, ensuring that the battery powers essential functions while the car is stationary, conserving fuel. |
Braking and Stopping
The Toyota Prius utilizes regenerative braking system to maximize energy efficiency. As the vehicle slows down, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy into electricity and storing it in the battery. This regenerative braking process allows for the recovery of about 70% of the energy lost during braking, significantly improving fuel economy.
When the Prius comes to a complete stop, the engine and motor switch off, conserving energy. The battery powers essential functions like lighting and air conditioning until the car is started again. This intelligent system not only saves fuel but also reduces emissions, making the Toyota Prius an environmentally friendly option.
With regenerative braking, the Toyota Prius showcases its commitment to sustainable technology. By harnessing and reusing otherwise wasted energy, the Prius maximizes fuel economy, reducing the need for frequent stops at gas stations. It’s a prime example of how hybrid technology can enhance the driving experience while minimizing environmental impact.
Regenerative Braking in Action:
“The regenerative braking system in the Toyota Prius allows for the recovery of up to 70% of the energy lost during braking, contributing to the vehicle’s impressive fuel economy. It’s an innovative feature that not only enhances efficiency but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions, making the Prius a greener choice for eco-conscious drivers.” – Toyota Engineer
By optimizing the energy efficiency during braking and stopping, the Toyota Prius sets itself apart as a leader in the hybrid car market. Its regenerative braking system not only saves fuel but also reduces wear on traditional braking components, leading to cost savings and reduced maintenance requirements. The Prius continues to be a symbol of innovation and sustainability, driving us towards a greener future.
Cruising and Acceleration
The Toyota Prius is designed to optimize power distribution between the gasoline engine and the electric motor during cruising and acceleration. At steady speeds over 15 MPH, the gasoline engine powers the generator, which produces electricity to charge the battery. This dual power source allows for efficient utilization of energy and enhances both performance and fuel economy. When rapid acceleration is required, the gasoline engine and the electric motor work together to provide extra power, ensuring a smooth and responsive driving experience.
The Toyota Prius achieves its impressive fuel economy through the intelligent coordination of its hybrid system components. The power split device, a key component of the hybrid system, effectively combines the torque from the gasoline engine and the electric motor, delivering power to the wheels as needed. This dynamic power distribution system allows the Prius to adapt seamlessly to different driving conditions, optimizing fuel efficiency without compromising performance.
With its innovative hybrid technology, the Toyota Prius offers drivers the best of both worlds – the efficiency of an electric motor and the power of a gasoline engine. By intelligently utilizing both power sources, the Prius maximizes fuel economy while maintaining excellent performance. Whether cruising on the highway or accelerating to merge into traffic, the Toyota Prius delivers a smooth and efficient driving experience.
| Toyota Prius Hybrid System | Toyota Prius Fuel Economy |
|---|---|
| Optimizes power distribution between gasoline engine and electric motor | Delivers impressive fuel efficiency |
| Seamlessly switches between power sources for optimal performance | Reduces fuel consumption and CO2 emissions |
| Enhances acceleration through combined power output | Provides a smooth and responsive driving experience |
With its advanced hybrid system and intelligent power distribution, the Toyota Prius continues to set the standard for fuel-efficient vehicles. By harnessing the power of both the gasoline engine and the electric motor, the Prius delivers exceptional fuel economy without sacrificing performance. Whether you’re cruising on the highway or accelerating from a stop, the Toyota Prius offers a seamless and efficient driving experience.
Problems With Hybrid Vehicles
While hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius offer numerous benefits, they can also encounter certain issues, particularly with their batteries. Over time, hybrid batteries may lose their ability to hold a charge effectively, which can lead to reduced performance and fuel efficiency. Additionally, faulty cells within the battery can further exacerbate these problems, resulting in increased gasoline costs for the owner.
However, it’s important to note that Toyota offers battery warranties for eight years or 100,000 miles in most states, providing peace of mind for Prius owners. In the event of battery-related complications, repairs or replacements can be conducted to ensure the vehicle maintains optimal performance levels.
While battery issues may present themselves in some hybrid vehicles, it’s crucial to consider the overall benefits of hybrid technology. The Toyota Prius, for example, boasts impressive fuel economy and reduced CO2 emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. With proper maintenance and care, the Prius can continue to provide years of energy-efficient and eco-friendly driving.
| Battery Issues | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of charge capacity | Reduced performance and fuel efficiency | Repairs or replacement |
| Faulty battery cells | Increased gasoline costs | Repairs or replacement |
The Benefits of Hybrid Technology
Hybrid vehicles, like the Toyota Prius, offer numerous benefits that make them a compelling choice for eco-conscious drivers. One of the primary advantages of hybrid technology is its exceptional fuel economy, reflected in the Toyota Prius’s high MPG rating. With its efficient hybrid engine system, the Prius consumes less fuel compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, resulting in significant savings on fuel costs over time.
Furthermore, the Toyota Prius’s fuel economy contributes to reduced CO2 emissions, making it an environmentally friendly option. By choosing a hybrid vehicle, drivers can actively play a part in minimizing their carbon footprint and promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
Despite the potential issues with hybrid batteries over time, Toyota offers battery warranties and repair/replacement options to ensure the optimal performance of the Prius. With proper maintenance and battery care, the Toyota Prius can provide years of energy-efficient driving, making it a reliable and long-lasting investment for environmentally conscious drivers.
In conclusion, the benefits of hybrid technology, as exemplified by the Toyota Prius, extend beyond fuel efficiency and environmental friendliness. By choosing a hybrid vehicle, drivers can enjoy not only significant fuel savings but also the peace of mind that comes with reducing their impact on the environment. The future of hybrid technology looks promising, with ongoing advancements and a commitment to environmental sustainability, making hybrid vehicles an attractive choice for the eco-conscious driver.
Table: Fuel Efficiency Comparison
| Vehicle Model | Fuel Type | MPG (City) | MPG (Highway) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota Prius | Hybrid | 54 | 50 |
| Honda Civic | Gasoline | 32 | 42 |
| Ford Focus | Gasoline | 27 | 35 |
Table: Fuel efficiency comparison between the Toyota Prius and other popular models. The Toyota Prius stands out with its hybrid technology, offering significantly higher MPG (miles per gallon) in both city and highway driving compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles like the Honda Civic and Ford Focus.
The Future of Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid car technology continues to evolve, and the future looks promising for vehicles like the Toyota Prius. Advancements in engine efficiency and battery technology are driving the development of more efficient and sustainable hybrid systems.
The Toyota Prius has been at the forefront of hybrid technology, and it has set the stage for more environmentally friendly transportation options. As engineers continue to refine and improve hybrid engines, we can expect even greater fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. These advancements will not only benefit the environment but also help drivers save on fuel costs.
Battery technology is another area that is rapidly progressing. Longer battery life and improved performance are essential for the continued success of hybrid vehicles. Toyota and other manufacturers are committed to recycling hybrid batteries, ensuring that they have a minimal ecological footprint. This focus on sustainability is crucial for reducing waste and maximizing the lifespan of hybrid vehicles.
The Potential of Hybrid Car Technology
With ongoing research and development, hybrid car technology holds immense potential for the future. As hybrid systems become more efficient and sophisticated, we can expect to see increased adoption of this technology across a wide range of vehicles. From compact cars to SUVs, hybrid options will provide drivers with the benefits of improved fuel economy and reduced emissions.
As we move towards a greener future, hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius will play a crucial role in achieving our sustainability goals. With their combination of electric and gasoline power, they offer a practical and viable solution for reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. The ongoing advancements in hybrid technology will ensure that these vehicles continue to contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system.
The Importance of Battery Recycling
Battery recycling plays a crucial role in the sustainable development of hybrid technology. With the increasing popularity of hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius, it becomes essential to ensure the responsible disposal and recycling of hybrid batteries. Toyota recognizes this importance and has taken significant steps to minimize the environmental impact of these batteries.
Over 90% of hybrid batteries from Toyota vehicles are already being recovered, and the company has set a target of achieving 100% battery recovery. This commitment to recycling ensures that valuable resources are not wasted and that the environmental footprint of hybrid vehicles is kept to a minimum.
Recycled hybrid batteries can serve various purposes. They can be repurposed for the production of new batteries, extending the life cycle of these essential components. Additionally, recycled batteries can be used for other forms of stationary energy storage, contributing to the development of sustainable energy solutions.
“Toyota is committed to recycling hybrid batteries to minimize environmental impact.”
The Future of Battery Recycling
The future of battery recycling looks promising as technology continues to advance. Innovations in recycling processes and materials are expected to further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of battery recycling. Additionally, research and development efforts are focused on improving the sustainability of battery production and reducing the environmental footprint associated with the entire lifecycle of hybrid vehicles.
As hybrid technology evolves, so does the need for more efficient and environmentally friendly battery recycling methods. Toyota and other industry leaders are investing in research and partnerships to drive innovation in this field. These efforts will not only benefit the environment but also ensure the availability of critical resources for future hybrid vehicles and sustainable energy solutions.
Conclusion
The Toyota Prius is an impressive example of hybrid car technology that offers exceptional fuel efficiency and performance. Understanding how the Toyota Prius works and its hybrid engine system can help appreciate the innovative design behind this eco-friendly vehicle.
From starting from a stopped position to cruising and acceleration, the Toyota Prius maximizes efficiency through its regenerative braking system and optimized power distribution. While hybrid vehicles may encounter battery-related issues, Toyota provides warranties and solutions for repairs or replacements, ensuring continued enjoyment of the Prius for years to come.
The future of hybrid technology looks promising as advancements continue to be made in engine efficiency and battery technology. With ongoing commitments to sustainability and environmental impact reduction, hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius will continue to be a crucial part of the transition to more sustainable transportation solutions.
FAQ
How does a Toyota Prius work?
The Toyota Prius works using a series-parallel hybrid engine, which combines the best components of series and parallel engines. The gasoline engine charges the car’s battery, which then powers the electric motor. The car can switch between the electric motor and gasoline engine as needed, resulting in excellent fuel economy and performance.
What is the fuel economy of the Toyota Prius?
The Toyota Prius offers impressive fuel economy, with a combined city and highway EPA fuel economy of 54 MPG in the 2020 model. This means it can travel 54 miles on one gallon of gasoline, saving you money on fuel costs.
How does regenerative braking work in the Toyota Prius?
The Toyota Prius uses regenerative braking to maximize energy efficiency. As the vehicle slows down, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy into electricity and storing it in the battery. This process allows for the recovery of about 70% of the energy lost during braking, significantly improving fuel economy.
What are the potential issues with hybrid batteries?
Over time, hybrid batteries may lose their ability to hold a charge, requiring repairs or replacement. Faulty cells in the battery can also affect fuel efficiency and increase gasoline costs. However, Toyota offers battery warranties for eight years or 100,000 miles in most states, ensuring continued optimal performance of the vehicle.
What are the benefits of hybrid technology?
The Toyota Prius and other hybrid vehicles offer excellent fuel economy, saving you money on fuel costs over time. They also contribute to reduced CO2 emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice. Despite potential battery issues, with proper maintenance and care, the Toyota Prius can provide many years of efficient and enjoyable driving.
What is the future of hybrid vehicles?
As technology continues to advance, hybrid systems in vehicles like the Toyota Prius are becoming more efficient and sophisticated. The engines are designed to optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions, with improvements in size and power. Battery technology is also evolving, ensuring longer battery life and improved performance. The future looks bright for hybrid vehicles, offering even greater fuel efficiency and environmental benefits.
How does Toyota ensure battery recycling for hybrid vehicles?
Toyota is committed to recycling hybrid batteries to minimize environmental impact. Over 90% of hybrid batteries from Toyota vehicles are already being recovered, with a target of achieving 100% recovery. The recycled batteries can be repurposed for new batteries or used for other forms of stationary energy storage. This commitment to sustainability ensures that hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius have a minimal ecological footprint.