Welcome to our article on the difference between the pelvis and hip! Many people often confuse these two structures, but they have distinct roles in the human body. Understanding their differences is essential for maintaining optimal movement patterns and preventing injuries. So let’s dive in and explore the unique characteristics of the pelvis and hip.
Key Takeaways:
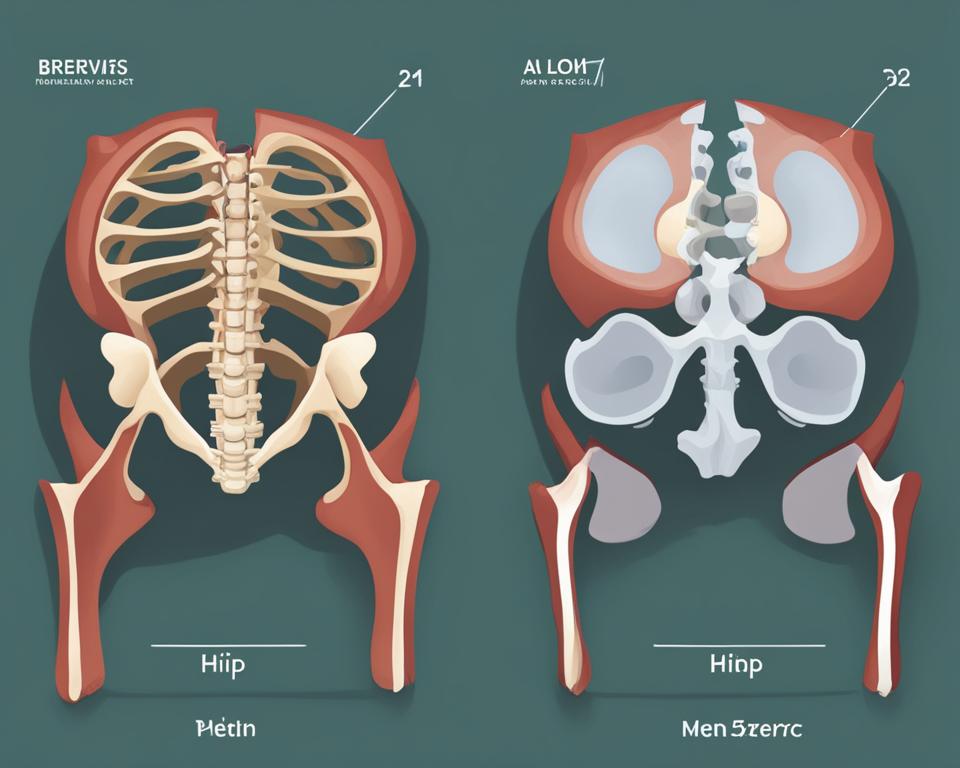
- The pelvis is a larger bony structure located in the lower part of the body, while the hip is a specific joint formed by the pelvis and the femur.
- The pelvis provides support, stability, and protection for the internal organs, while the hip joint enables weight transfer and a wide range of motion.
- Proper alignment and coordination between the pelvis and hip are crucial for engaging the correct muscles and achieving controlled movement.
- Imbalances or dysfunctions in the pelvis and hip can lead to various injuries, highlighting the importance of understanding the biomechanics of these structures.
- Developing awareness of the movements and alignment of the pelvis and hip is crucial for effective and safe training.
Anatomy of the Pelvis and Hip
The pelvis and hip are complex structures that play vital roles in the human body’s movement and stability. The pelvic girdle, also known as the hip girdle, is formed by the hip bone or coxal bone, which is connected to the lower limbs and the spine via the sacrum. The hip bone consists of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
The ilium forms the superior portion of the hip bone and has important bony landmarks such as the iliac crest and anterior and posterior superior iliac spines. The ischium is located posteriorly and supports the body when sitting, while the pubis is situated anteriorly and forms the front part of the hip bone. Together, these bones create a cup-shaped cavity called the acetabulum, which functions as part of the hip joint.
The hip joint, also known as the acetabulofemoral joint, is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the conjunction of the pelvis and the femur. It allows for a wide range of motion and is reinforced by strong ligaments and supported by surrounding muscles. The structure of the hip joint enables weight transfer from the pelvis to the legs and facilitates movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
Pelvic Structure:
| Pelvic Bone | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Ilium | Superior portion of the hip bone | Forms landmarks such as the iliac crest and iliac spines |
| Ischium | Located posteriorly | Supports body weight when sitting |
| Pubis | Situated anteriorly | Forms the front part of the hip bone |
| Acetabulum | Cup-shaped cavity | Part of the hip joint, facilitates movement |
Functions of the Pelvis and Hip
The pelvis and hip play vital roles in the human body, contributing to overall movement, stability, and protection. Understanding their functions is essential for optimizing physical performance and preventing injuries. Here are the key functions of the pelvis and hip:
1. Weight Support and Transfer
The pelvis provides support for the weight of the upper body, particularly when sitting or standing. It acts as a stable base that transfers the weight from the spine to the lower limbs, allowing for balanced posture and movement. The hip joint, formed by the pelvis and femur, facilitates the transfer of weight from the pelvis to the legs, enabling walking, running, and other weight-bearing activities.
2. Muscle Attachment Point
The pelvis serves as an attachment point for various muscles of the trunk and lower limbs. Muscles such as the glutes, hip flexors, and adductors originate or insert on the pelvis, allowing for coordinated movements of the pelvis and hip joint. Strong and well-functioning muscles around the pelvis and hip contribute to stability, power, and control in various physical activities.
3. Protection of Internal Organs
The pelvis acts as a protective structure for the internal organs in the lower abdomen, including the urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and parts of the digestive system. Its bony structure and surrounding muscles provide a shield against external impact and support the proper functioning of these vital organs.
By understanding and appreciating the functions of the pelvis and hip, individuals can prioritize exercises and movements that enhance stability, mobility, and overall well-being.
| Functions | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight Support and Transfer | Transfers the weight from the spine to the lower limbs, enabling balanced posture and movement. |
| Muscle Attachment Point | Serves as an attachment point for muscles of the trunk and lower limbs, allowing for coordinated movements of the pelvis and hip joint. |
| Protection of Internal Organs | Acts as a protective structure for the internal organs in the lower abdomen, safeguarding their proper functioning. |
“Understanding and appreciating the functions of the pelvis and hip can help individuals prioritize exercises and movements that enhance stability, mobility, and overall well-being.”
Biomechanics of the Pelvis and Hip
The biomechanics of the pelvis and hip play a crucial role in our everyday movements and activities. These structures work together to provide stability, support, and mobility, but imbalances or dysfunctions can lead to various injuries and limitations in our physical performance.
When we talk about the biomechanics of the pelvis and hip, we are referring to the way these structures move and interact with each other. The pelvis acts as a foundation for the hip joint, which is a ball-and-socket joint formed between the pelvis and the femur. This joint allows for a wide range of motion and is responsible for transferring weight from the pelvis to the legs.
Understanding the biomechanics of the pelvis and hip is essential for maintaining optimal movement patterns and preventing injuries.
Proper alignment and coordination between the pelvis and hip are important for engaging the correct muscles and achieving controlled movement. When there are imbalances or dysfunctions in these structures, it can lead to issues such as strains, sprains, and joint instability. For example, if the pelvis is tilted or rotated incorrectly, it can affect the alignment of the hip joint and put additional stress on the surrounding muscles and ligaments.
| Common Pelvis and Hip Injuries | Causes |
|---|---|
| Hip impingement | Abnormal contact between the ball and socket causing pain and limited range of motion |
| Labral tears | Tears in the cartilage that lines the inside of the hip joint, often caused by repetitive movements or trauma |
| SI joint dysfunction | Pain and inflammation in the sacroiliac joint, often caused by imbalances or trauma |
| Snapping hip syndrome | Snapping or popping sensation in the hip joint, caused by tendons moving over bony structures |
By understanding the biomechanics of the pelvis and hip, we can take steps to prevent injuries and optimize our movement patterns. This includes maintaining proper alignment, strengthening the muscles around the pelvis and hip, and performing exercises that promote stability and mobility in these areas. Additionally, working with a qualified healthcare professional or physical therapist can provide valuable guidance and help address any imbalances or dysfunctions that may be present.
Key Takeaways:
- The pelvis and hip work together to provide stability, support, and mobility.
- Understanding the biomechanics of the pelvis and hip is essential for maintaining optimal movement patterns and preventing injuries.
- Imbalances or dysfunctions in the pelvis and hip can lead to various injuries, such as strains, sprains, and joint instability.
- Proper alignment and coordination between the pelvis and hip are important for engaging the correct muscles and achieving controlled movement.
- Strengthening the muscles around the pelvis and hip and performing exercises that promote stability and mobility can help prevent injuries and optimize movement patterns.
Comparison Between Pelvis and Hip
When comparing the pelvis and hip, it’s essential to understand their distinct functions and structures. The pelvis is a bony structure that connects the spinal column and the legs, providing support, stability, and protection for the internal organs in the lower abdomen. On the other hand, the hip is a joint formed by the pelvis and the femur, enabling weight transfer and a wide range of motion.
The pelvis acts as a foundation for the upper body and transfers the weight to the lower limbs when standing. It also serves as an attachment point for muscles of the trunk and lower limbs, contributing to overall body stability. In contrast, the hip joint allows for various movements such as walking, running, and other weight-bearing activities. It provides a wide range of motion and is crucial for maintaining balance during movement.
To summarize:
- The pelvis is a larger bony structure that supports and protects the internal organs in the lower abdomen.
- The hip is a joint formed by the conjunction of the pelvis and the femur, enabling weight transfer and a wide range of motion.
- The pelvis provides support, stability, and attachment for muscles, while the hip joint facilitates various movements and balance.
Understanding the differences between the pelvis and hip is essential for comprehending their roles in movement and overall body function.
| Pelvis | Hip |
|---|---|
| Connects the spinal column and the legs | Connects the pelvis and the femur |
| Supports and protects the internal organs in the lower abdomen | Enables weight transfer and a wide range of motion |
| Provides stability and attachment for muscles | Facilitates various movements and balance |
By understanding the unique contributions of the pelvis and hip, individuals can better appreciate the intricate mechanics involved in movement and ensure optimal physical performance.
Pelvis and Hip Movements
The movements of the pelvis and hip are closely interconnected, often requiring coordinated action. In certain exercises and positions like splits, lunges, warriors, and backbends, the alignment and flexibility of the pelvis and hip joints are crucial. The pelvis’s tilting, extension, and rotation directly affect the movement and flexibility of the hip joint. For example, incorrect pelvic alignment can result in compensatory movements in the lower back, leading to insufficient hip mobility. Understanding and practicing proper pelvic and hip movements are essential for effective and safe training.
When it comes to hip movements, the dance world highlights the importance of lower back flexibility and strong hips. According to dance experts, incorporating exercises that target the lower back and hip muscles can improve overall performance and reduce the risk of injuries. Strengthening the glutes, hip flexors, and core can enhance stability and power during dynamic movements, while also supporting proper posture and alignment.
“Proper alignment and coordination between the pelvis and hip are key factors in preventing injuries and optimizing movement patterns. By fine-tuning the movements of the pelvis and hip, individuals can improve their technique, range of motion, and overall body control,”
The Role of Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
- Stretching exercises that target the hip flexors, glutes, and muscles surrounding the pelvis can help improve the flexibility and range of motion in these areas. Dynamic stretches like lunges and hip circles can be performed as part of a warm-up routine, while static stretches such as the pigeon pose and butterfly stretch can be done after a workout.
- Strength training exercises that focus on the glutes, hip abductors, and core muscles can help stabilize the pelvis and enhance hip strength and control. Squats, deadlifts, side leg lifts, and planks are examples of exercises that can be incorporated into a strength training routine.
By incorporating a combination of stretching and strengthening exercises into their fitness regimen, individuals can improve lower back flexibility, enhance hip movement, and promote overall musculoskeletal health. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or certified fitness trainer before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have any pre-existing injuries or medical conditions.
Importance of Pelvis and Hip Awareness in Movement
Developing awareness of the movements and alignment of the pelvis and hip is crucial in various physical activities and exercises. By understanding the structure and function of the pelvic girdle and hip socket, individuals can optimize their movement patterns, enhance muscle activation, and prevent injuries.
Proper engagement of the correct muscles and controlled movement rely on a clear understanding of the actions and relationship between the pelvis, hip joint, and lower back. By maintaining proper pelvic and hip alignment, individuals can improve stability, mobility, and overall movement quality.
Practicing exercises that target the muscles around the pelvis and hip, such as hip bridges, squats, and hip rotations, can help strengthen and stabilize these areas. Additionally, incorporating stretching and mobility exercises, like hip flexor stretches and pelvic tilts, can improve flexibility and range of motion in the pelvis and hip joint.
| Pelvic Girdle | Hip Socket |
|---|---|
| Consists of the ilium, ischium, and pubis bones | Forms the acetabulum, which connects the pelvis and femur |
| Mainly supports the weight of the upper body | Allows for weight transfer from the pelvis to the legs |
| Provides stability and protection for the internal organs | Enables a wide range of motion in various activities |
Understanding and practicing proper movements and alignment of the pelvis and hip can significantly impact overall physical performance and reduce the risk of injuries. By prioritizing pelvic and hip awareness in movement, individuals can unlock their full potential and enjoy safe and effective workouts.
Conclusion
The pelvis and hip are integral components of the human body, each serving unique functions while closely working together. The pelvis, comprised of the ilium, ischium, and pubis bones, provides crucial support, stability, and protection for the lower abdomen’s internal organs.
Conversely, the hip joint, formed by the pelvis and the femur, allows for weight transfer and an extensive range of motion, contributing significantly to various movements and activities. Understanding the differences, functions, and biomechanics of the pelvis and hip is paramount in maintaining optimal movement patterns and preventing injuries.
By developing a keen awareness of the movements and alignment of the pelvis and hip, individuals can enhance their overall physical performance and well-being. Engaging the correct muscles and practicing controlled movement is vital for effective training and injury prevention.
Incorporating exercises that target the pelvic and hip muscles can improve stability, mobility, and muscle activation in these areas. By embracing the importance of the hip joint, pelvic bone, functions of the pelvis and hip, and their biomechanics, individuals can optimize their movement quality and live a healthier, more active life.
FAQ
What is the difference between the pelvis and the hip?
The pelvis is a larger bony structure located in the lower part of the body, while the hip is a specific joint formed by the pelvis and the femur.
How is the pelvis and hip joint structured?
The pelvis is formed by the ilium, ischium, and pubis bones, while the hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the conjunction of the pelvis and the femur.
What are the functions of the pelvis and hip?
The pelvis provides support, stability, and protection for the internal organs in the lower abdomen, while the hip joint enables weight transfer and a wide range of motion.
How do the pelvis and hip movements influence each other?
The movements of the pelvis and hip joints are closely related and interconnected, with proper alignment and coordination being crucial for controlled movement.
How do imbalances or dysfunctions in the pelvis and hip affect the body?
Imbalances or dysfunctions in the pelvis and hip can lead to various injuries, such as strains, sprains, and instability.
What exercises target the pelvis and hip muscles?
Exercises such as splits, lunges, warriors, and backbends require proper alignment and flexibility of the pelvis and hip joints.
Why is awareness of pelvic and hip movements important in physical activities?
Understanding and practicing proper pelvic and hip movements are essential for effective and safe training, improving stability, mobility, and preventing injuries.
How can understanding the pelvic and hip biomechanics enhance physical performance?
By developing awareness of the pelvis and hip movements and practicing exercises that target these areas, individuals can optimize their movement quality and improve overall well-being.