Have you ever wondered why dogs have anal glands? These small glands, located near the anal opening, play a significant role in your furry friend’s life. Exploring the anatomy of dogs can shed light on the purpose and function of these intriguing glands.
Key Takeaways:
- Dogs have anal glands, also known as anal sacs, which release a scent marking fluid.
- Anal gland problems can cause discomfort and symptoms like scooting, excessive licking, and foul odor.
- Poor gastrointestinal health, allergies, and abnormal anatomy can contribute to anal gland issues in dogs.
- Understanding canine anal gland anatomy is crucial for recognizing and managing anal gland problems.
- Regular veterinary check-ups and preventative measures can help maintain healthy anal gland function in dogs.
The Function of Anal Glands in Dogs
Dogs have anal glands, also known as anal sacs, located near the anus. These small glands are responsible for releasing a strong, foul-smelling fluid that serves various functions in canines. One of the primary purposes of anal gland fluid is marking territory and communicating with other dogs. The unique scent of the fluid acts as a “signature” for each dog, allowing them to leave behind their scent and convey important information to other animals.
However, when the anal glands become overactive or the fluid becomes abnormally thick, it can lead to problems such as impaction, infection, or abscesses. This can cause discomfort for the dog and result in symptoms like scooting, excessive licking, swelling, and a fishy odor. Recognizing these signs is crucial for dog owners to ensure early diagnosis and proper treatment.
In order to maintain optimal anal gland health in dogs, it is important to provide regular care and seek veterinary attention when necessary. This may involve routine anal gland expression by a veterinarian, especially if the dog is prone to anal gland problems. Additionally, feeding a high-quality diet with the right nutrients can support healthy bowel movements and help prevent anal gland issues. Taking these preventative measures can contribute to the overall well-being and comfort of dogs.
Common Causes of Anal Gland Problems in Dogs
There are several common causes that can contribute to anal gland problems in dogs. Understanding these causes can help dog owners recognize and address potential issues early on.
Anatomy and Positioning:
Dogs with abnormal anal gland anatomy or positioning are more prone to developing anal gland problems. In some cases, the anal glands may be positioned too deep inside the rectum, making it difficult for the fluid to be released naturally. This can lead to blockages, inflammation, and potential infection.
Poor Gastrointestinal Health:
Poor gastrointestinal health can contribute to anal gland problems in dogs. When a dog has irregular bowel movements, such as small or loose stools, it can make it challenging for the anal glands to empty properly. This can result in gland blockages, discomfort, and potential infection.
Allergies and Skin Issues:
Allergies, including Atopy, can cause red and inflamed skin around the anal glands. This inflammation can lead to anal gland problems such as impaction or infection. Dogs with allergies may also have increased itching and licking, which can further irritate the anal gland area.
Frequent Gland Expression:
Regular expression of the anal glands is necessary for some dogs, but overexpression can also contribute to anal gland problems. If the glands are expressed too frequently, they may become irritated and inflamed, leading to potential blockages or infection.
| Causes | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Anatomy and Positioning | Abnormal anal gland anatomy or positioning can make it difficult for the fluid to be released naturally, leading to blockages and potential infection. |
| Poor Gastrointestinal Health | Irregular bowel movements can make it challenging for the anal glands to empty properly, resulting in blockages, discomfort, and possible infection. |
| Allergies and Skin Issues | Allergies can cause inflammation around the anal glands, leading to problems such as impaction or infection. |
| Frequent Gland Expression | Overexpression of the anal glands can cause irritation and inflammation, potentially resulting in blockages or infection. |
It’s essential for dog owners to be aware of these common causes and take appropriate measures to prevent and address anal gland problems. Regular veterinary check-ups and discussions about anal gland health can help identify any potential issues early on. By addressing these causes and providing proper care, dog owners can help maintain the overall health and well-being of their furry friends.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Anal Gland Problems in Dogs
Dogs can experience various symptoms when they have anal gland problems. It’s important for dog owners to be able to recognize these signs and seek prompt veterinary attention. Here are some common symptoms to look out for:
- Scooting or dragging the rear end on the floor: Dogs with anal gland problems may try to relieve their discomfort by rubbing their rear end on the ground or carpet.
- Excessive licking of the anal area: If your dog is constantly licking their anal region, it could be a sign of anal gland issues.
- Discomfort while walking or sitting: Dogs with anal gland problems may exhibit signs of discomfort when moving or sitting down.
- Straining to defecate: Anal gland problems can sometimes cause difficulties in bowel movements, leading to straining.
- Foul odor: A strong, unpleasant odor coming from your dog’s rear end could indicate anal gland issues.
If you notice any of these symptoms in your dog, it’s crucial to consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment. They will be able to assess your dog’s anal glands and determine the best course of action to alleviate their discomfort and restore their anal gland health.
Diagnosing Anal Gland Problems in Dogs
Diagnosing anal gland problems in dogs requires a thorough examination by a veterinarian. During the examination, the vet will perform a rectal exam to evaluate the anal glands and surrounding structures. This allows them to check for any signs of blockage, swelling, or infection. If the glands are found to be full, the veterinarian will manually express them to relieve any discomfort and check the consistency and odor of the fluid.
If there are signs of infection or abscesses, additional diagnostic tests may be performed. This can include taking a sample of the fluid for analysis to determine if bacteria or other pathogens are present. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound may be used to get a better view of the anal gland area and assess the extent of any abnormalities or complications.
It’s important to seek veterinary attention if your dog is showing symptoms of anal gland problems, as these issues can be painful and lead to further complications if left untreated. A veterinarian is equipped with the expertise and tools necessary to accurately diagnose and treat anal gland problems in dogs.
| Diagnosing Anal Gland Problems in Dogs | Process |
|---|---|
| Rectal exam | Evaluate anal glands and surrounding structures |
| Manual expression | Relieve discomfort and check fluid consistency and odor |
| Fluid analysis | Determine presence of bacteria or pathogens |
| Imaging tests | Assess abnormalities or complications |
“Seeking veterinary attention for proper diagnosis and treatment of anal gland problems is crucial for your dog’s well-being and comfort.”
Taking Note of Symptoms
When visiting the veterinarian, it’s important to provide detailed information about your dog’s symptoms. This includes noting any changes in bowel movements, signs of discomfort or pain, excessive licking or scooting, and the presence of an unpleasant odor. The veterinarian will take these symptoms into consideration during the examination to help form an accurate diagnosis.
Consulting a Professional
If you suspect that your dog is experiencing anal gland problems, it’s best to consult a professional rather than attempting to diagnose or treat the issue yourself. A veterinarian has the knowledge and experience to properly diagnose the problem and recommend appropriate treatment options. They can also provide guidance on preventative measures and ongoing care to help maintain your dog’s anal gland health.
Treating Anal Gland Problems in Dogs
Treating anal gland problems in dogs requires a comprehensive approach to address the underlying causes and relieve discomfort. The treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and severity of the problem. One of the primary methods of treatment is manual expression of the anal glands, which involves emptying the glands manually. This can be done by a veterinarian or, in some cases, by experienced dog owners who have been trained in the technique.
In cases of impaction or infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat any bacterial growth and reduce inflammation. Additionally, anti-inflammatory medications can help alleviate discomfort and swelling in the anal gland area. In more severe cases, such as anal gland abscesses, surgical drainage may be necessary to remove the accumulated fluid and promote healing.
To prevent recurrence of anal gland problems, it is essential to address any underlying issues contributing to the condition. This can include improving gastrointestinal health through dietary changes, such as incorporating high-quality food with appropriate nutrients and adding fiber supplements to promote regular bowel movements. Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for monitoring anal gland health and ensuring timely expression of the glands, if necessary.
| Treatment options for anal gland problems in dogs |
|---|
| Manual expression of the anal glands |
| Prescription of antibiotics |
| Administration of anti-inflammatory medications |
| Surgical drainage for anal gland abscesses |
| Dietary changes to improve gastrointestinal health |
| Regular veterinary check-ups and anal gland expression |
Providing Relief and Preventing Recurrence
While immediate treatment is necessary to alleviate the discomfort caused by anal gland problems, long-term care is equally important to prevent recurrence. In addition to addressing any underlying health issues, there are measures that dog owners can take at home to support anal gland health.
- Regularly clean the anal gland area with pet-safe wipes or gentle dog shampoo.
- Ensure the dog’s environment is clean and free from irritants that can exacerbate anal gland problems.
- Feed a balanced and nutritious diet to promote overall health and prevent gastrointestinal issues.
- Consider adding anal gland supplements to the dog’s diet, which are specifically formulated to support anal gland function.
- Monitor the dog’s behavior and seek veterinary attention if any signs of anal gland problems recur.
Proactive care and prompt treatment are essential in managing anal gland problems in dogs. By working closely with a veterinarian and implementing preventive measures at home, dog owners can ensure the overall well-being of their furry companions and minimize the discomfort associated with anal gland issues.
Preventing Anal Gland Problems in Dogs
Taking proactive measures to prevent anal gland problems in dogs can help maintain their overall health and well-being. By addressing potential causes and implementing preventative strategies, dog owners can minimize the risk of anal gland issues and ensure their pets remain comfortable and free from discomfort.
Proper Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in preventing anal gland problems in dogs. Providing a balanced and nutritionally complete diet can help regulate bowel movements and promote optimal gastrointestinal health. It is essential to choose high-quality dog food that contains the right ingredients and nutrients for your pet’s specific needs. Including fiber supplements like canned pumpkin or Metamucil in their diet can also help promote healthy bowel movements and assist in the natural emptying of the anal glands.
Routine Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are vital for monitoring your dog’s anal gland health and preventing potential issues. During these check-ups, your veterinarian can examine the anal glands and detect any early signs of inflammation, infection, or blockage. If necessary, they can perform anal gland expression to prevent impaction or infection. Your veterinarian will also provide guidance on how often your dog’s anal glands should be checked and expressed, based on their specific needs.
Maintaining Grooming Hygiene
Proper grooming hygiene is essential for preventing anal gland problems in dogs. Regularly bathing and cleaning your dog’s anal area can help remove any excess fecal matter or debris that may contribute to gland blockage or irritation. When cleaning the anal area, it is important to use pet-safe products such as dog shampoo, wipes, or grooming spray. Take caution to be gentle and avoid causing any discomfort or irritation to your dog during the grooming process.
| Preventive Measures for Anal Gland Problems in Dogs | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Feeding a healthy diet | Regulates bowel movements and promotes gastrointestinal health |
| Including fiber supplements | Bulks up stools and assists with natural anal gland emptying |
| Scheduling routine veterinary check-ups | Allows for early detection of anal gland issues and proper care |
| Maintaining grooming hygiene | Removes debris and prevents blockage or irritation of anal glands |
By following these preventive measures, dog owners can significantly reduce the risk of anal gland problems in their furry companions. However, if you notice any signs of anal gland issues such as scooting, excessive licking, or a foul odor, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian promptly for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
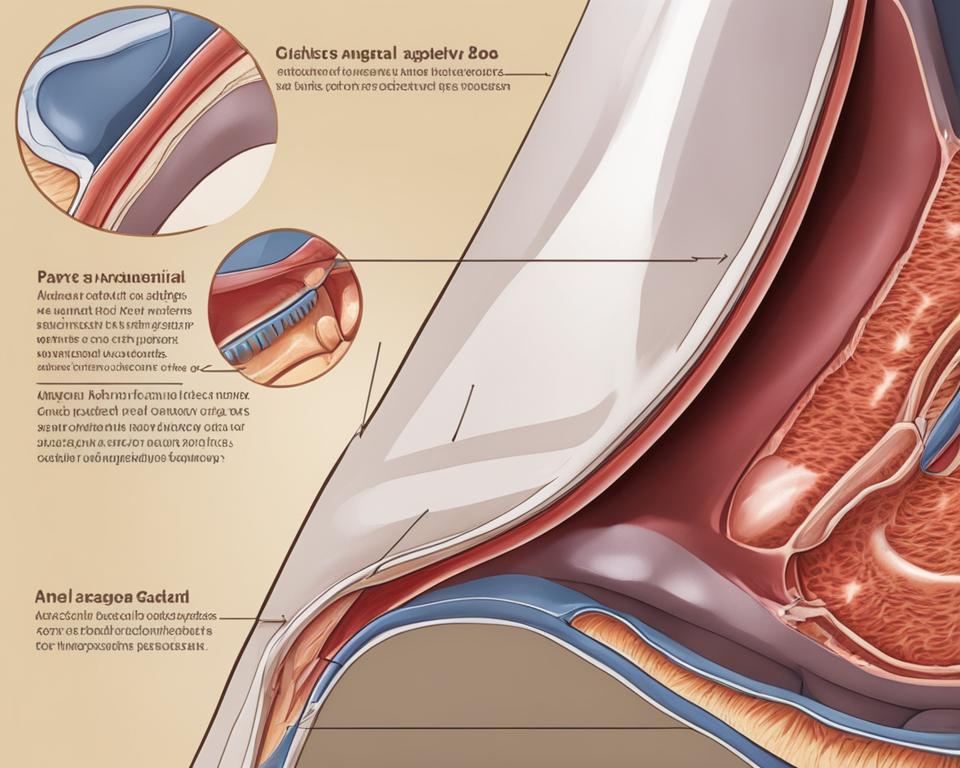
Understanding Dog Anal Gland Anatomy
Understanding the anatomy of dog anal glands is crucial for dog owners and can help shed light on potential issues that may arise. Dog anal glands, also known as anal sacs, are located near the anus between two layers of muscle internally. These glands are responsible for releasing a strong, foul-smelling fluid that helps with marking territory and communicating with other dogs. The fluid in the anal glands has a unique scent for each dog, acting as their “signature.”
Normal emptying of the anal glands occurs as stool passes over them and exerts outward pressure. However, if the glands become blocked or inflamed, it can lead to various conditions such as anal sacculitis, where the glands get infected and impacted. Anal sacculitis can cause discomfort for dogs and may result in symptoms such as scooting, licking, swelling, and a fishy odor.
To better visualize the anatomy of dog anal glands, here is a table summarizing their key characteristics:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Located near the anus between two layers of muscle internally |
| Function | Releasing a strong, foul-smelling fluid for marking territory and communication |
| Emptying | Occurs as stool passes over the glands and exerts outward pressure |
| Issues | Blockage or inflammation can lead to conditions like anal sacculitis |
By understanding the anatomy of dog anal glands, pet owners can have a better grasp of the potential issues that may arise and seek appropriate veterinary care to ensure their furry friends’ anal gland health and overall well-being.
Expressing Dog Anal Glands at Home
If you are considering expressing your dog’s anal glands at home, it is important to proceed with caution and consult a veterinarian beforehand. While some pet owners may choose to learn how to express the anal glands themselves, it is crucial to understand the potential risks and complications that can arise.
Expressing dog anal glands requires a delicate touch and knowledge of proper technique. If done incorrectly, it can cause injury or discomfort to your dog. Additionally, expressing the anal glands can be a messy process, so it is essential to be prepared with the right tools and a clean environment.
If you are determined to express your dog’s anal glands at home, there are instructional videos available that can guide you through the process. However, it is highly recommended to seek veterinary attention if your dog is experiencing any signs of anal gland problems or discomfort. A professional veterinarian will have the expertise and experience to ensure the procedure is performed safely and effectively.
Remember, the anal glands play a crucial role in your dog’s health, and any issues should be addressed promptly by a veterinary professional. When it comes to expressing the anal glands, it is always best to leave it to the experts to avoid any unnecessary risks or complications.
Dealing with the Odor of Anal Gland Fluid
Anal gland fluid in dogs has a strong and unpleasant odor that can be challenging to eliminate. If your dog releases this fluid, it may leave behind an undesirable smell on various surfaces. Fortunately, there are ways to address and minimize the odor effectively.
When it comes to cleaning fabric, such as carpets or upholstery, white vinegar can be a handy solution. Mix equal parts of white vinegar and water, then apply the mixture to the affected area. Blot the spot with a clean cloth or paper towel until the odor dissipates. Additionally, pet deodorizing wipes can be useful for removing the smell from fabrics.
When it comes to cleaning your dog, it’s important to use pet-safe products to ensure their well-being. Dog shampoos that specifically target odor control are available and can effectively neutralize the anal gland odor. You can also use grooming sprays or wipes that are formulated to eliminate odor-causing bacteria. Take care to be gentle while cleaning the anal gland area to avoid causing any irritation or discomfort to your dog.
It’s worth noting that while these methods can help manage the odor, it’s essential to address any underlying anal gland problems your dog may have. If your dog experiences frequent anal gland issues or discomfort, it’s best to consult your veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Regular Monitoring and Care of Anal Glands in Dogs
Regular monitoring and care of your dog’s anal glands are essential for maintaining their overall health and well-being. By including the area around the anal glands in your weekly dog wellness exam, you can detect any early signs of anal gland problems. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Visually check for swelling, redness, or irritation around the anal region. These may indicate a potential issue with the anal glands.
- Observe your dog’s behavior for any signs of discomfort or abnormality. Excessive licking, scooting, or difficulty sitting or defecating may be indicators of anal gland problems.
- If you notice any concerning symptoms, it is important to consult your veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Being proactive in monitoring your dog’s anal glands can help prevent minor issues from escalating into more significant problems. Early detection allows for prompt intervention and appropriate treatment, which can alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of anal gland health in dogs is essential for responsible pet ownership. Anal gland problems can cause discomfort and lead to various symptoms such as scooting, licking, and foul odor. By knowing the function of anal glands and recognizing the signs of issues, dog owners can take proactive steps to maintain their pet’s anal gland health.
Regular veterinary check-ups and proper nutrition play a significant role in preventing anal gland problems. Feeding a high-quality diet and incorporating fiber supplements can support healthy bowel movements and proper anal gland emptying. Additionally, scheduling routine anal gland expression with a veterinarian can help prevent impaction or infection.
If any symptoms of anal gland problems are observed, it is crucial to seek prompt veterinary attention. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent complications and ensure the well-being of the dog. By prioritizing anal gland health, dog owners contribute to their pet’s overall comfort and quality of life.
FAQ
Why do dogs have anal glands?
Dogs have anal glands to release a strong, foul-smelling fluid that helps with marking territory and communicating with other dogs.
What is the function of anal glands in dogs?
The function of anal glands in dogs is to release a unique scent that acts as their “signature” for marking territory and communicating with other dogs.
What are the common causes of anal gland problems in dogs?
Common causes of anal gland problems in dogs include poor gastrointestinal health, allergies, and abnormal anatomy.
What are the symptoms of anal gland problems in dogs?
Symptoms of anal gland problems in dogs include scooting or dragging the rear end on the floor, excessive licking of the anal area, discomfort while walking or sitting, straining to defecate, and a foul odor.
How are anal gland problems in dogs diagnosed?
Anal gland problems in dogs are diagnosed through a thorough examination, including a rectal exam to evaluate the anal glands and surrounding structures.
How are anal gland problems in dogs treated?
Treatment for anal gland problems in dogs depends on the specific condition and may include manual expression of the glands, medications, or surgical drainage in severe cases.
How can anal gland problems in dogs be prevented?
Anal gland problems in dogs can be prevented by feeding a healthy diet, adding fiber supplements, and regularly having the anal glands expressed by a veterinarian.
What is the anatomy of dog anal glands?
Dog anal glands are located near the anus between two layers of muscle and can become blocked or inflamed, leading to various conditions such as infections or impacted glands.
Can I express my dog’s anal glands at home?
Expressing a dog’s anal glands at home can be challenging and may not be suitable for everyone. It is recommended to seek veterinary attention for anal gland problems or discomfort.
How can I deal with the odor of anal gland fluid?
To deal with the odor of anal gland fluid, you can use white vinegar or pet deodorizing wipes for fabric surfaces and pet-safe products like dog shampoo or wipes when cleaning your dog.
How should I monitor and care for my dog’s anal glands?
Regularly monitor your dog’s anal glands by visually checking for swelling, redness, or irritation and observing your dog’s behavior. Include the area in a weekly dog wellness exam.
What is the conclusion about canine anal gland health?
Understanding why dogs have anal glands, recognizing and managing anal gland problems, and providing regular care can help maintain anal gland health in dogs and contribute to their overall well-being.