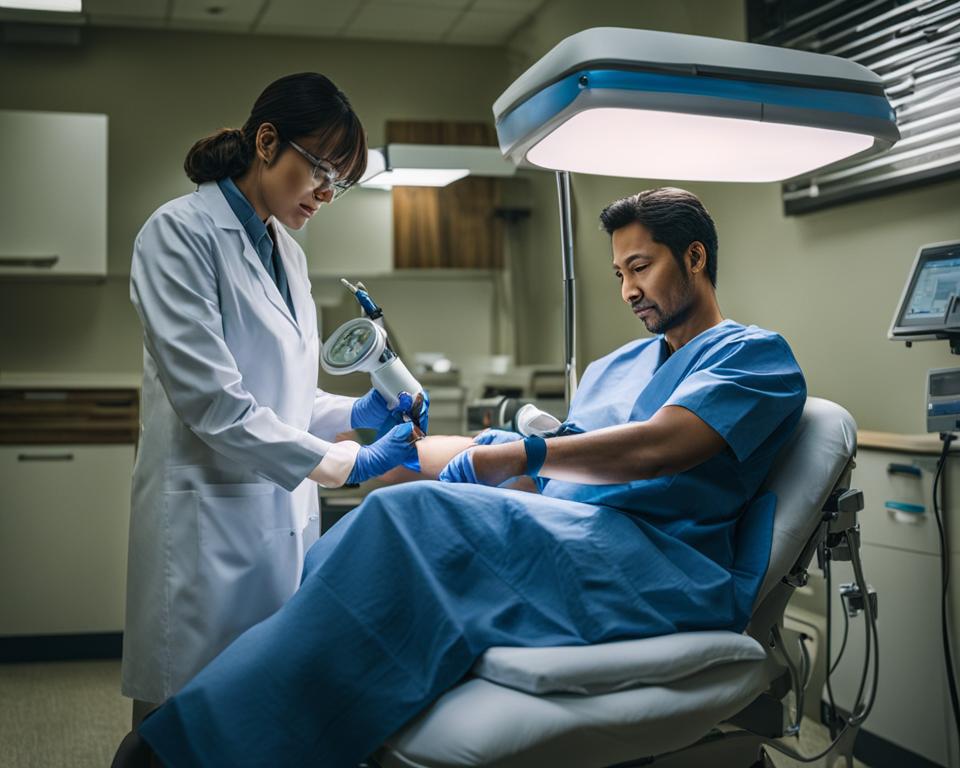
If you’ve ever donated plasma or are considering doing so, you may have wondered why phlebotomists carefully examine your elbows during the screening process. The answer lies in the importance of ensuring your health and safety, as well as the quality of the collected plasma.
Plasma donation is a critical medical procedure that involves extracting plasma, the largest component of blood, to create lifesaving medical therapies. To ensure that the donation process goes smoothly and that the plasma collected is of high quality, thorough medical screening and examination are essential.
During the screening process, phlebotomists pay close attention to the condition of your elbows for several reasons. First and foremost, they need to locate suitable veins for the venipuncture process. The antecubital area of the arm, which includes the elbows, contains large, superficial veins that are ideal for accessing and collecting plasma.
Additionally, the examination of your elbows helps phlebotomists assess the health of your veins. They look for signs of good vein anchoring, resilience, and quick refill after compression. By ensuring that your veins are in optimal condition, they can minimize the risk of complications such as collapsing or infiltration during the donation process.
Inspecting your elbows also allows phlebotomists to identify any skin conditions that may affect the venipuncture site. They check for rashes, wounds, dermatitis, scabs, moles, lesions, or other abnormalities that could increase the risk of infection or interfere with the placement of the needle. Maintaining intact and healthy skin at the venipuncture site is crucial for minimizing the risk of complications.
In addition to vein and skin assessment, phlebotomists inspect the elbows to avoid accidental contact with vital structures such as arteries, nerves, and tendons. The brachial artery, median nerve, and ulnar nerve are located in the elbow area and must be carefully avoided during the venipuncture process to ensure patient comfort and safety.
Finally, the inspection of the elbows helps identify any signs of intravenous (IV) drug use. Phlebotomists look for track marks, pitting, bruising, or sclerosis, which could indicate recent or chronic IV drug use. Plasma donation centers have strict policies to prevent individuals who engage in IV drug use from donating plasma, ensuring the safety and integrity of the donation pool.
By understanding the reasons behind elbow examinations during plasma donation, you can appreciate the importance of this step in the process. It serves as a crucial safeguard for your health and safety, as well as the quality of the collected plasma.
Key Takeaways:
- Phlebotomists check your elbows during plasma donation to locate suitable veins for venipuncture.
- Elbow examination helps assess the health of your veins and identify any skin conditions that may affect the venipuncture site.
- The inspection of the elbows ensures the avoidance of vital structures such as arteries, nerves, and tendons.
- Checking for signs of IV drug use is essential to maintain the safety and integrity of the donation pool.
- Understanding the reasons behind elbow checks can help you understand the importance of this step in the plasma donation process.
An Overview of Plasma Donation
Plasma donation is a process where individuals voluntarily donate plasma, which is the largest component of blood, accounting for about 55% of total blood volume. Plasma contains water, proteins, nutrients, and clotting factors, making it a crucial component in the transportation of various substances throughout the body. Donated plasma is processed into lifesaving medical therapies that are used to treat a wide range of conditions.
Plasma-based therapies derived from donated plasma are utilized in the treatment of immunodeficiencies, bleeding disorders, burn victims, shock and trauma patients, and organ transplant recipients. Additionally, plasma-based therapies can be used to treat diseases such as rabies, tetanus, hepatitis B, and respiratory illnesses. The medical community greatly relies on plasma donations to provide these essential treatments.
Uses of Plasma in Medical Therapies:
| Condition | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Immunodeficiencies | Plasma contains antibodies that help boost the immune system in individuals with immunodeficiencies. |
| Bleeding Disorders | Plasma contains clotting factors that can help control and prevent excessive bleeding in individuals with bleeding disorders. |
| Burn Victims | Plasma is used to replace lost fluids and proteins in burn victims, aiding in their recovery. |
| Shock and Trauma Patients | Plasma is administered to stabilize patients who have experienced shock or trauma, as it helps restore blood volume and prevent further complications. |
| Organ Transplant Recipients | Plasma-based therapies can be used to prevent organ rejection and manage complications following organ transplantation. |
| Diseases (e.g., Rabies, Tetanus, Hepatitis B, Respiratory Illnesses) | Plasma can be used to create specific therapies for treating various diseases, providing targeted treatment options. |
By understanding the crucial role of plasma in medical therapies and the impact of plasma donations, individuals can appreciate the significance of donating plasma and the value it holds in saving lives.
Importance of Donor Screening
Donor screening is a critical step in the plasma donation process as it ensures the health and safety of both donors and recipients. The screening process involves a thorough review of the donor’s medical history, a physical examination, and testing for infectious diseases. By implementing these measures, plasma donation centers can identify any potential risks or contraindications for plasma donation, safeguarding the quality of the collected plasma and protecting the well-being of donors.
During the medical history review, donors are asked to provide detailed information about their past and present health conditions, medications, and lifestyle habits. This information helps the healthcare professionals assess the donor’s eligibility for plasma donation and determine if any additional testing or precautions are necessary. The physical examination includes vital sign checks, such as pulse and blood pressure measurements, as well as a visual examination of the donor’s overall health, including the inspection of the elbows.
The infectious disease testing is a crucial component of donor screening as it helps prevent the transmission of infectious diseases through donated plasma. Donors are tested for a variety of infectious diseases, including HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, and others, depending on the local guidelines and regulations. By identifying any potential infections, plasma donation centers can ensure that only safe and healthy plasma is collected, minimizing the risk of transmitting diseases to patients who receive plasma-based therapies.
Donor Screening Process
The donor screening process involves several steps to evaluate the donor’s eligibility and ensure their suitability for plasma donation. It begins with an initial phone screening, during which the donor’s basic information is collected and a preliminary assessment is conducted. This is followed by an in-person screening, which includes the medical history review, physical examination, and infectious disease testing.
Regular donors also undergo screenings at each visit to monitor their health and update their medical information. The process is designed to ensure that only eligible donors with good overall health are allowed to donate plasma, reducing the potential risks associated with the collection and administration of plasma-based therapies.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Phone Screening | Initial assessment and collection of basic information |
| In-person Screening | Medical history review, physical examination, and infectious disease testing |
| Regular Screening | Ongoing monitoring of donor’s health and updates on medical information |
Finding the Best Veins for Venipuncture
One of the key factors in the successful plasma donation process is the ability to locate suitable veins for venipuncture. Phlebotomists meticulously examine the elbows to identify the most appropriate veins for the procedure.
Veins for Venipuncture
The antecubital area of the arm, which includes the elbows, is home to large and easily accessible veins that are ideal for collecting plasma. The primary veins used for venipuncture in this area include:
- Basilic Vein: This vein runs along the inside of the arm, close to the elbow, and is often the preferred choice for plasma donation.
- Cephalic Vein: Located along the outer part of the arm, the cephalic vein is another suitable option for venipuncture during plasma donation.
It’s important to note that the median cubital vein, which connects the basilic and cephalic veins, is typically avoided for plasma donation.
Importance of Proper Vein Selection
Choosing the right veins for venipuncture is crucial to ensure a smooth and successful plasma donation process. The basilic and cephalic veins located in the elbows provide easy access and sufficient blood flow, allowing for efficient plasma collection. By visually inspecting the elbows, phlebotomists can determine the best veins to use, minimizing discomfort for the donor and reducing the risk of complications.
| Vein | Location | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Basilic Vein | Inside of the arm, near the elbow | Deep and easily accessed |
| Cephalic Vein | Outer part of the arm | Accessible and suitable for venipuncture |
By carefully considering the condition and location of these veins, phlebotomists can ensure a safe and efficient plasma donation experience for both the donor and the recipient.
Checking Vein Health
During the screening process for plasma donation, one important aspect that phlebotomists focus on is assessing the health of the veins in the elbows. The condition of the veins plays a crucial role in ensuring a successful plasma donation process.
Phlebotomists examine various factors to determine the health of the veins. They check if the veins are well anchored under the skin, meaning they are securely held in place. This anchoring is essential to prevent any movement or displacement of the vein during the donation process. Additionally, phlebotomists assess the resilience of the veins by gently pressing on them to observe how quickly they refill after compression. A healthy vein should bounce back and refill promptly.
In addition, phlebotomists look for signs of damage to the veins in the elbows. They check for any leaks, thinning, or other abnormalities that could compromise the integrity of the veins. It is crucial to ensure that the veins are strong and intact to withstand the pressure of blood flow during the donation process without collapsing or infiltrating. By thoroughly assessing the vein health in the elbows, phlebotomists can ensure the safety and effectiveness of the plasma donation process.
| Vein Condition Assessment | Symptoms of Healthy Veins | Symptoms of Damaged Veins |
|---|---|---|
| Vein anchoring | Securely held in place | Movement or displacement |
| Vein resilience | Prompt refilling after compression | Slow or delayed refilling |
| Signs of damage | No leaks, thinning, or abnormalities | Leaks, thinning, or other abnormalities |
Identifying Skin Conditions
The inspection of the elbows during the plasma donation process includes a thorough assessment of the donor’s skin condition. Phlebotomists carefully examine the elbows for any rashes, wounds, dermatitis, scabs, or other skin abnormalities that could affect the venipuncture site. The presence of these conditions may increase the risk of infection or interfere with the placement of the needle.
In addition to examining the elbows for visible skin conditions, phlebotomists also pay attention to moles or lesions that may need to be avoided during the donation process. This is done to ensure that the venipuncture is performed in an area of intact and healthy skin, minimizing the risk of complications.
By conducting a comprehensive assessment of the skin condition in the elbow area, healthcare professionals can ensure the safety and well-being of the donor and maintain the quality of the collected plasma.
Avoiding Nerves and Other Anatomy
The elbow area contains several important anatomical structures that must be avoided during the venipuncture process. These include the brachial artery, median nerve, and ulnar nerve. Phlebotomists take special care in selecting the vein and site for donation to minimize the risk of accidental contact with these structures.
The brachial artery, located deep within the arm, is a vital blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the forearm and hand. Accidentally puncturing this artery can result in severe bleeding and complications. The median nerve and ulnar nerve, on the other hand, are important nerves that provide sensation and motor function to the hand and forearm. Any accidental contact with these nerves during venipuncture can cause sharp pain, numbness, tingling, or even nerve damage.
By closely inspecting the elbows, phlebotomists can visually assess the location of these structures and choose a suitable site for venipuncture that minimizes the risk of complications. This careful evaluation helps ensure patient comfort and safety throughout the donation process.
Anatomy of the Elbow Area
In the elbow area, the brachial artery runs along the inner side of the arm, while the median nerve and ulnar nerve are positioned near the inner and outer aspects of the elbow, respectively. These structures are all located relatively close to the surface of the skin, making them susceptible to accidental contact during the venipuncture process.
Avoiding Accidental Contact
Phlebotomists carefully palpate the antecubital area of the arm, which includes the elbows, to identify the optimal vein for donation while avoiding the brachial artery, median nerve, and ulnar nerve. They also use visual cues such as the presence of veins crossing over these structures to guide their selection. By paying close attention to the anatomy of the elbow area, phlebotomists can minimize the risk of complications and ensure a safe and successful plasma donation.
Table: Anatomy of the Elbow Area
| Anatomical Structure | Location |
|---|---|
| Brachial Artery | Runs along the inner side of the arm near the elbow |
| Median Nerve | Located near the inner aspect of the elbow |
| Ulnar Nerve | Positioned near the outer aspect of the elbow |
Detecting Signs of IV Drug Use
During the screening process for plasma donation, phlebotomists carefully inspect the elbows to identify any signs of intravenous (IV) drug use. This is an important step in ensuring the safety and integrity of the plasma donation pool. By detecting indicators such as injection sites, track marks, pitting, bruising, and sclerosis, phlebotomists can determine if an individual has engaged in IV drug use.
Injection sites and track marks are visible scars caused by repeated needle punctures. These linear scars can often be found on the arms, particularly near the elbows. Phlebotomists look for these track marks as they can indicate a history of IV drug use. Additionally, they check for pitting, which refers to small dents in the skin resulting from frequent needle punctures.
Bruising or redness around the elbow area can also be an indicator of recent IV drug use. These marks may be the result of injections or vein damage caused by drug use. Phlebotomists pay close attention to any signs of bruising or redness during the inspection process.
Sclerosis, the hardening of veins due to chronic injections, is another sign that an individual may have a history of IV drug use. Phlebotomists assess the condition of the veins in the elbows, looking for any signs of sclerosis. Hardened veins may be difficult to access and pose a higher risk of complications during plasma donation.
By identifying these signs of IV drug use, plasma donation centers can uphold strict policies to prevent individuals who engage in drug use from donating plasma. This safeguards the quality of the collected plasma and ensures the safety of all recipients who rely on plasma-based therapies.
Table: Indicators of IV Drug Use
| Signs |
|---|
| Injection sites |
| Track marks |
| Pitting |
| Bruising or redness |
| Sclerosis |
Conclusion
The careful examination of elbows during plasma donation plays a vital role in ensuring donor safety and the quality of collected plasma. Phlebotomists meticulously inspect the elbows to find suitable veins and assess their health, identifying any potential risks or contraindications for donation. This process helps minimize the risk of complications and ensures the comfort of donors throughout the procedure.
Furthermore, the inspection of elbows allows phlebotomists to identify any skin conditions or abnormalities that could increase the risk of infection or interfere with the donation process. By maintaining intact and healthy skin at the venipuncture site, the chances of complications are significantly reduced.
Lastly, the examination of elbows helps in avoiding accidental contact with arteries, nerves, and tendons present in the area. This precautionary measure ensures the safety and well-being of donors during the plasma donation process.
In summary, the thorough inspection of elbows during plasma donation emphasizes the importance placed on donor safety. By understanding the significance of these checks, donors can appreciate the careful attention given to every aspect of the plasma donation process, ultimately contributing to the lifesaving medical therapies derived from donated plasma.
FAQ
Why do they check your elbows when donating plasma?
Donating plasma involves collecting blood from large veins in the elbows. Checking the elbows helps to identify suitable veins for venipuncture and ensures that the veins are healthy and can withstand the donation process. It also helps to avoid accidental contact with arteries, nerves, and tendons. Additionally, examining the elbows helps to detect any signs of IV drug use, which is not permitted for plasma donation.
What is plasma donation?
Plasma donation is the process of donating plasma, which is the largest component of blood. Plasma is used to create lifesaving medical therapies for various conditions, including immunodeficiencies, bleeding disorders, burn victims, shock and trauma patients, and organ transplant recipients. Plasma-based therapies can also be used to treat diseases such as rabies, tetanus, hepatitis B, and respiratory illnesses.
Why is donor screening important?
Donor screening is important to ensure the health and safety of both the donor and the recipients of plasma-based therapies. During the screening process, potential donors undergo a review of their medical history, a physical examination, and testing for infectious diseases. Regular donors are also screened at each visit to identify any potential risks or contraindications for plasma donation.
How do phlebotomists find suitable veins for venipuncture?
Phlebotomists locate suitable veins in the elbows, such as the basilic vein and the cephalic vein, which are large and easily accessible. The median cubital vein, which connects these two veins, is usually avoided for plasma donation. Phlebotomists carefully examine the condition of the veins, ensuring they are well anchored, resilient, refill quickly after compression, and show no signs of damage.
Why do phlebotomists check the condition of the veins in the elbows?
Checking the condition of the veins in the elbows is essential to ensure that the veins can withstand the pressure of blood flow during plasma donation without collapsing or infiltrating. Phlebotomists look for signs of damage, such as leaks or thinning, and assess the overall health and strength of the veins.
What skin conditions do phlebotomists look for during elbow inspection?
Phlebotomists examine the elbows for any skin conditions that may affect the venipuncture site. This includes checking for rashes, wounds, dermatitis, scabs, and other abnormalities that could increase the risk of infection or interfere with needle placement. They also identify moles or lesions that may need to be avoided during the donation process.
Why is it important to avoid nerves and other anatomy during venipuncture?
The elbow area contains arteries, nerves, and tendons that must be avoided during venipuncture. Accidental contact with structures such as the brachial artery, median nerve, and ulnar nerve can cause severe bleeding, sharp pain, numbness, tingling, or other complications. Proper vein selection and site inspection help ensure patient comfort and safety during the donation process.
How do phlebotomists detect signs of IV drug use?
Phlebotomists look for common indicators of IV drug use, such as track marks (linear scars from repeated injections), pitting (small dents in the skin caused by needle punctures), bruising or redness (indicating recent IV drug use), and sclerosis (hardened veins from chronic injections). Plasma donation centers have strict policies to prevent individuals who engage in IV drug use from donating plasma to ensure the safety of the donation pool.

![Ray Dalio Quotes [Principles, Life, Investment]](https://tagvault.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Screen-Shot-2023-04-19-at-7.57.49-PM.png)