Arthritis and bursitis are two common conditions that can cause joint pain and inflammation. Although they share similar symptoms, it is important to understand the differences between the two in order to receive accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
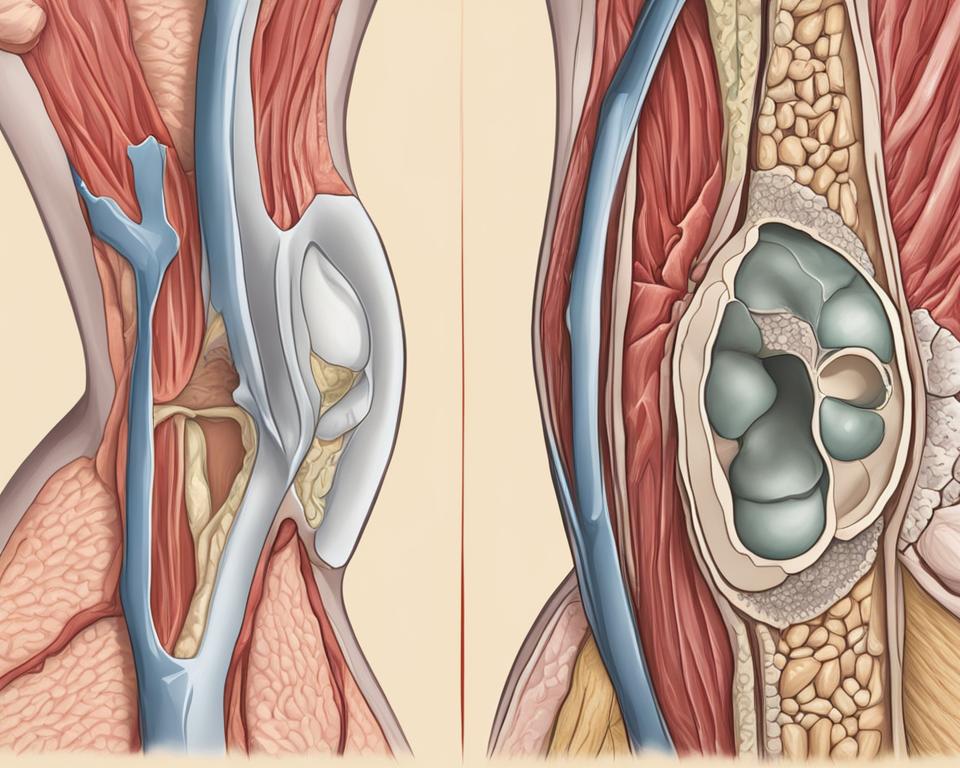
Arthritis refers to inflammation within the joints themselves, whereas bursitis involves inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion the joints. While both conditions can result in joint pain, swelling, and limited range of motion, the specific structures affected distinguish arthritis from bursitis.
Key Takeaways:
- Arthritis and bursitis are both conditions that cause joint pain and inflammation.
- The main difference between arthritis and bursitis lies in the specific structures involved.
- Arthritis refers to inflammation within the joints, while bursitis involves inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs called bursae.
- Accurate diagnosis is crucial for appropriate treatment.
- Consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Arthritis: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
Arthritis is a broad term that encompasses various conditions affecting the joints. The two most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis (OA) and inflammatory arthritis (IA).
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joints. It commonly occurs in weight-bearing joints such as the hips, knees, and spine. Aging, joint trauma, and obesity are common risk factors for developing OA. Inflammatory arthritis, on the other hand, involves the immune system mistakenly attacking the joints, leading to inflammation and joint damage. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis fall under the category of inflammatory arthritis.
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s daily activities and quality of life.
Table: Types of Arthritis
| Type of Arthritis | Description |
|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis (OA) | Gradual breakdown of joint cartilage |
| Inflammatory Arthritis (IA) | Immune system mistakenly attacks joints |
Diagnosing arthritis usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. Early diagnosis is crucial for implementing appropriate treatment strategies to manage symptoms, slow down disease progression, and improve joint function.
It’s important to note that arthritis is a chronic condition, and there is currently no cure. However, various treatment options are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, assistive devices, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Bursitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Bursitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the bursae, which are fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions around the joints. The inflammation can be caused by various factors, including overuse of the joint, injury, or infection. The most common locations for bursitis include the shoulders, hips, elbows, and knees.
The symptoms of bursitis typically include pain, swelling, tenderness, and limited movement in the affected joint. The pain may worsen with movement or pressure on the area. It is important to note that the symptoms of bursitis can sometimes be similar to those of other conditions, such as osteoarthritis or tendinitis, so a proper medical evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for bursitis. In mild cases, rest and avoiding activities that aggravate the condition may be sufficient to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also help manage pain and reduce swelling. In more severe cases, a healthcare professional may recommend cortisone injections to provide targeted relief. Physical therapy can be beneficial in improving joint function and preventing future episodes of bursitis. In rare cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the inflamed bursa.
| Causes of Bursitis | Symptoms of Bursitis | Treatment for Bursitis |
|---|---|---|
| Overuse of the joint | Pain in the affected area | Rest and avoiding aggravating activities |
| Injury or trauma to the joint | Swelling and tenderness | Over-the-counter pain relievers (NSAIDs) |
| Infection in the bursa | Limited movement | Cortisone injections |
| Physical therapy | ||
| Surgical intervention (in rare cases) |
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent joint pain or suspect you may have bursitis. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan to help relieve symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Similarities and Overlapping Symptoms
Arthritis and bursitis share many similarities in terms of symptoms, which can make it challenging to differentiate between the two without a medical evaluation. Both conditions can cause joint pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness, making it difficult for individuals to pinpoint the exact cause of their discomfort. However, there are certain clues that can help determine whether the issue is related to arthritis or bursitis.
Location of Pain
While both arthritis and bursitis can affect various joints in the body, there are specific locations that are commonly impacted by both conditions. The shoulders and hips are often prone to both arthritis and bursitis. If the pain is localized in these areas, it may indicate the presence of either condition. However, other joints such as the knees, elbows, and ankles can also be affected by arthritis or bursitis, so it is important to consider other factors as well.
Onset and Duration
The onset and duration of symptoms can also provide valuable information in distinguishing between arthritis and bursitis. Arthritis typically has a gradual onset, with symptoms worsening over time. The pain and discomfort associated with arthritis may also be present for extended periods, sometimes lasting for weeks or even months. On the other hand, bursitis often has a more acute onset, with symptoms appearing suddenly and typically lasting for a shorter duration.
Non-Joint Symptoms
Although joint pain and inflammation are common in both arthritis and bursitis, there are some non-joint symptoms that can help differentiate between the two. Arthritis is often associated with systemic symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and weight loss, which are not typically present in bursitis. If an individual is experiencing additional symptoms beyond joint discomfort, it may suggest that arthritis is the underlying cause.
| Similarities | Arthritis | Bursitis |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Joint pain | Joint pain |
| Swelling | Joint swelling | Joint swelling |
| Redness | Joint redness | Joint redness |
| Stiffness | Joint stiffness | Joint stiffness |
It is important to note that while there are similarities between arthritis and bursitis, a proper medical evaluation is essential for an accurate diagnosis. Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional will ensure that the appropriate treatment is provided for effective pain management and improved joint function.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Accurately diagnosing arthritis and bursitis requires a comprehensive medical evaluation. When you experience joint pain, swelling, or limited mobility, it is essential to seek medical expertise to determine the underlying cause. Healthcare professionals typically begin the diagnosis process with a thorough physical examination, where they assess the location of the pain and look for signs of inflammation.
In addition to the physical examination, your doctor may also order further tests to confirm the diagnosis. X-rays are commonly used to visualize the bones and joint spaces, providing valuable information about the structure and possible damage. Ultrasounds and MRIs can help assess soft tissues, such as tendons, ligaments, and bursae, providing a more detailed view of the affected area.
“Accurate diagnosis of arthritis and bursitis requires a thorough medical evaluation.”
During the evaluation, it is important to provide your healthcare provider with detailed information about your symptoms, medical history, and any previous injuries or conditions that may be relevant. This will help them make an informed diagnosis and create an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your needs.
| Diagnosing Arthritis | Diagnosing Bursitis | |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Assess joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. | Check for localized swelling, tenderness, and movement limitations. |
| X-rays | Visualize joint spaces and assess for cartilage damage or bone abnormalities. | May be used to rule out other conditions or assess for structural abnormalities in the affected joint. |
| Ultrasound or MRI | Can provide a more detailed view of soft tissues, such as inflammation in the joint lining or buildup of fluid. | Help evaluate the extent and location of inflammation in the bursae. |
By combining the findings from the physical examination and diagnostic tests, healthcare professionals can make an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment options for you. Remember that early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent further joint damage.
Treatment Options for Arthritis and Bursitis
When it comes to treating arthritis and bursitis, the approach may vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. For arthritis, treatment options typically include a combination of lifestyle modifications, pain medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
In the case of bursitis, treatment generally involves rest, over-the-counter pain relievers, cortisone injections, physical therapy, and, in severe cases, fluid aspiration or surgery. The goal of treatment for both arthritis and bursitis is to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function.
It’s important to note that each individual’s treatment plan may be tailored to their specific needs and circumstances. A healthcare professional will evaluate the extent of the condition and recommend the most suitable treatment options accordingly. It’s crucial to follow their advice and guidance for optimal outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between arthritis and bursitis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. While both conditions can cause joint pain and inflammation, it is essential to distinguish between them to provide targeted care. Arthritis specifically affects the joints themselves, while bursitis involves inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion the joints.
To differentiate arthritis from bursitis, a medical evaluation is necessary. This typically includes a physical examination and may involve additional tests such as X-rays or ultrasounds. By assessing the location of the pain and considering other factors like non-joint symptoms and the onset of the condition, healthcare professionals can determine the underlying cause and provide the most effective treatment plan.
Treatment options for both arthritis and bursitis aim to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function. Depending on the type and severity of the condition, treatment may involve lifestyle modifications, pain medications, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgery. Seeking medical expertise is crucial to ensure an accurate diagnosis and to receive appropriate care tailored to your specific condition.
If you are experiencing joint pain or inflammation, it is important not to self-diagnose. Consult a healthcare professional who can help distinguish between arthritis and bursitis and guide you towards the best course of action. Remember, early detection and proper treatment significantly improve the chances of managing these conditions and maintaining a good quality of life.
FAQ
What is the difference between arthritis and bursitis?
Arthritis refers to inflammation within the joints themselves, while bursitis involves inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion the joints.
What are the types of arthritis?
The two most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis (OA) and inflammatory arthritis (IA).
What are the causes of arthritis?
Risk factors for arthritis include aging, joint trauma, obesity, and certain autoimmune disorders.
What are the symptoms of arthritis?
Symptoms of arthritis include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
What causes bursitis?
Bursitis can be caused by overuse, injury, or infection.
What are the symptoms of bursitis?
Symptoms of bursitis include pain, swelling, tenderness, and limited movement.
How do you differentiate between arthritis and bursitis?
The location of the pain and the specific structures affected can provide clues. Additional factors, such as non-joint symptoms and the gradual onset of arthritis in contrast to the acute onset of bursitis, can also help distinguish between the two conditions.
How are arthritis and bursitis diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis of arthritis and bursitis requires a thorough medical evaluation, typically involving a physical examination and potentially additional tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs.
What are the treatment options for arthritis?
Treatment options for arthritis may include lifestyle modifications, pain medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
What are the treatment options for bursitis?
Bursitis treatment usually involves rest, over-the-counter pain relievers, cortisone injections, physical therapy, and fluid aspiration or surgery in severe cases.
How can I distinguish arthritis from bursitis?
Understanding the difference between arthritis and bursitis requires a medical evaluation, so consulting a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.

