Have you ever wondered about the difference between being chubby and being fat? Although these terms are often used interchangeably, there is actually a clear distinction. Understanding the dissimilarities can help us appreciate and respect the diversity of body sizes and shapes.
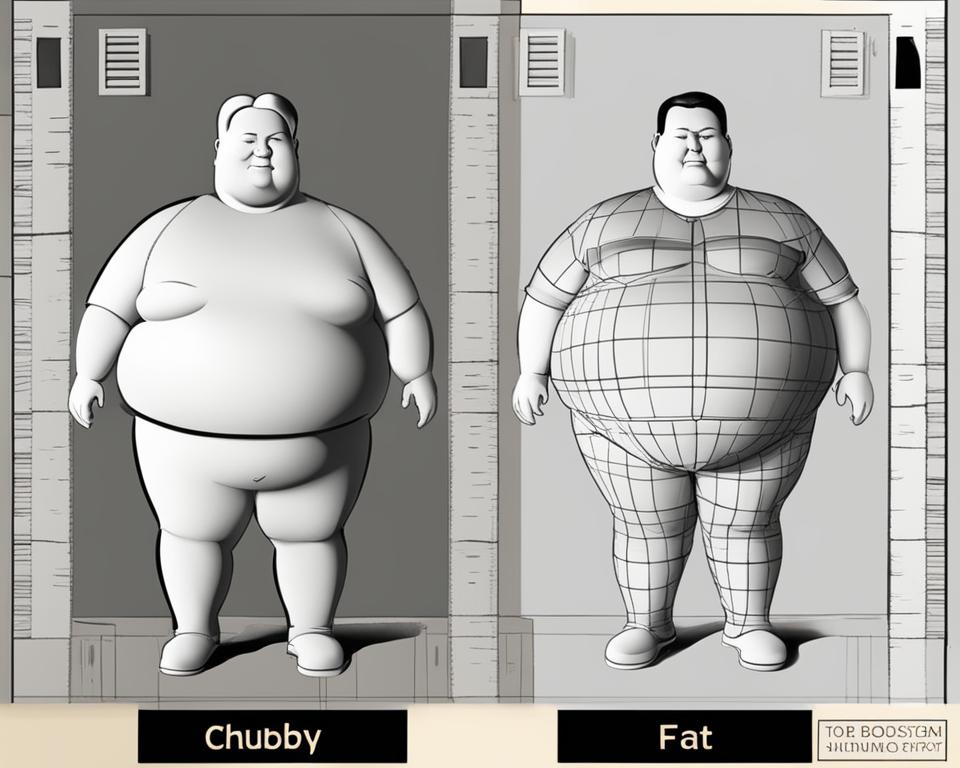
Being chubby refers to individuals with slightly raised body mass, giving them a plumper and fuller appearance. It does not necessarily mean being overweight or obese. On the other hand, being fat implies having an excess of body fat, resulting in a more rounded and bulkier shape. Fat individuals are generally classified as obese according to their Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference.
It’s important to note that everyone’s body is unique, and factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and gender can influence body size. Chubbiness and fatness are not solely determined by appearances but also by physiological factors and overall health.
Key Takeaways:
- Being chubby means having slightly raised body mass, while being fat refers to having an excess of body fat.
- The distinction is primarily determined by factors such as BMI and waist circumference.
- Chubby individuals have a plumper and fuller appearance, while fat individuals have a more rounded and bulkier shape.
- Factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and gender can influence body size.
- Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall health, regardless of whether someone is chubby or fat.
Understanding Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical measurement used to assess an individual’s body mass in relation to their height. It is a widely used indicator of whether a person’s weight is within a healthy range. BMI can be calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters.
Table: BMI Categories
| BMI | Weight Category |
|---|---|
| Less than 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal Weight |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30 or higher | Obese |
It is important to note that BMI alone does not provide a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s health. It does not take into account factors such as muscle mass and body composition. For example, a person with a high muscle mass may have a higher BMI, even though they have a low body fat percentage. Similarly, a person with a low muscle mass and high body fat percentage may have a normal BMI, despite being at an increased risk for certain health issues.
While BMI is a useful tool for assessing population trends and estimating health risks at a population level, it should be interpreted with caution on an individual basis. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to obtain a more accurate assessment of an individual’s overall health and to develop an appropriate plan for weight management.
Factors Affecting Body Size
The size and shape of our bodies can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and gender. Understanding these factors can help us gain insights into why individuals may have different body sizes and compositions.
Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in determining our body size and composition. Certain genes can influence our metabolism, fat storage, and overall body shape. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to being naturally lean or having a higher body mass. While we cannot change our genetic makeup, understanding our genetic predispositions can help us make informed decisions about our lifestyle choices.
Lifestyle Choices
Our daily habits and lifestyle choices can also impact our body size. Factors such as diet and exercise play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy weight. A diet rich in nutritious foods and regular physical activity can help us maintain a healthy body mass. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle and a diet high in processed foods and added sugars can contribute to weight gain and an increase in body fat.
Gender
Gender differences can also influence body size and composition. Hormonal differences between males and females can affect fat distribution and muscle mass. Generally, males tend to have a higher muscle mass and lower body fat percentage compared to females. However, it’s essential to remember that individual variations exist, and lifestyle choices can have a significant impact regardless of gender.
Understanding the factors that affect body size can empower us to make positive changes in our lives. While we cannot change our genetics, we can make conscious choices about our lifestyle, including our diet and exercise habits. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, we can work towards achieving a body size and composition that is optimal for our individual well-being and overall health.
Differentiating Between Chubby and Fat
Chubby and fat are two terms often used interchangeably, but there are distinct differences between the two. Chubby individuals have a slightly higher body mass than average, giving them a plumper and fuller appearance. Their bodies look healthy, and in some cultures, chubbiness is considered a sign of well-being and beauty. On the other hand, fat individuals have an excess of body fat that results in a rounded shape and visible signs of bulkiness. Fat falls into the obese category on the BMI chart, while chubby falls into the overweight category.
It’s important to note that the distinction between chubby and fat is primarily determined by factors such as Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference. BMI is a numerical measurement used to determine whether an individual’s body mass is healthy according to their height. While chubby individuals may have a higher BMI than average, their weight does not classify as overweight or obese. In contrast, fat individuals have a BMI that falls into the obese category, indicating a higher risk for various health issues.
Understanding the difference between chubby and fat is crucial for promoting a healthy body size. It’s important to note that body size can be influenced by factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and gender. Genetics plays a role in determining an individual’s metabolism, fat storage, and overall body size. Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, can also impact body size. Making positive changes to diet and exercise habits can help maintain a healthy body mass and reduce the risk of obesity-related health complications.
Table: Comparison between Chubby and Fat
| Chubby | Fat | |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Plumper and fuller | Rounded and bulky |
| BMI Category | Overweight | Obese |
| Health Risk | Lower | Higher |
Table: Comparison between Chubby and Fat
In summary, while chubby individuals may have a slightly higher body mass and a plumper appearance, they are not obese. Fat individuals, on the other hand, have an excess of body fat that can lead to various health issues. The distinction between the two is primarily determined by factors such as BMI and waist circumference. Understanding these differences can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Classifying Body Weight Categories
When it comes to classifying body weight, it is essential to understand the different categories that exist. This classification is primarily based on the Body Mass Index (BMI), which takes into account an individual’s weight and height. BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. Based on the resulting number, individuals can be categorized as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Chubby individuals fall into the overweight category on the BMI chart. They have a higher body mass than average, resulting in a plumper and fuller appearance. Despite being classified as overweight, being chubby does not necessarily mean being obese. Fat individuals, on the other hand, fall into the obese category. They have an excess of body fat, which contributes to a rounded shape and visible signs of bulkiness.
| Weight Category | BMI Range |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Below 18.5 |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 – 24.9 |
| Overweight | 25 – 29.9 |
| Obese | Above 30 |
Obesity is further classified into three classes based on BMI. Class I obesity refers to individuals with a BMI ranging from 30 to 34.9. Class II obesity includes individuals with a BMI between 35 and 39.9. Lastly, Class III obesity, also known as morbid obesity, applies to individuals with a BMI higher than 40.
It’s important to note that while BMI is a useful tool for classifying body weight, it does have limitations. It does not take into account factors such as muscle mass and body composition, which can impact an individual’s overall health. Therefore, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to get a comprehensive assessment of one’s body weight and health status.
Factors Influencing Body Size
Body size is influenced by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and gender factors. These elements play a significant role in determining an individual’s metabolism, fat storage, and overall body composition. Let’s explore each of these factors and how they contribute to variations in body size.
Genetics
Genetics plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s body size. Certain genes can affect how efficiently the body metabolizes food and stores fat. This means that some people may have a genetic predisposition to be naturally leaner or larger. However, it’s important to note that genetics are not the sole determinant of body size, and lifestyle choices can still have a significant impact.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, can greatly influence body size. A sedentary lifestyle and a diet high in calories and unhealthy fats can contribute to weight gain and an increase in body fat. Conversely, a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy body mass and promote overall well-being.
Gender
Gender differences also play a role in body size. Hormonal variations and differences in muscle mass between males and females can affect body composition. For example, males tend to have a higher percentage of muscle mass, which can lead to a higher metabolic rate and potentially lower body fat levels compared to females. However, it’s essential to remember that these variations are not absolute and can differ among individuals.
| Factor | Influence on Body Size |
|---|---|
| Genetics | Can determine metabolism, fat storage, and overall body composition. |
| Lifestyle Choices | Diet and exercise impact weight and body fat levels. |
| Gender | Hormonal and muscle mass differences can affect body composition. |
Understanding the factors that influence body size can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and well-being. While genetics and gender may be beyond our control, lifestyle choices are within our power to modify. By adopting a balanced diet, staying physically active, and making positive lifestyle changes, individuals can work towards achieving their optimal body size and promoting overall wellness.
Health Implications of Being Chubby and Fat
While being chubby may not necessarily have serious health implications, being fat increases the risk of developing various health issues. These can include diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer. Chubby individuals may be slightly more at risk for these health problems, but the risk is generally lower than that of fat individuals. It’s important for individuals who are overweight or obese to focus on maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and other lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of these health complications.
“Obesity is associated with significantly increased rates of morbidity and mortality, making it a major public health concern.” – World Health Organization
Research has shown that excess body fat can lead to chronic inflammation, which is a risk factor for many diseases. Fat accumulation around the abdominal area, known as visceral fat, is particularly harmful as it can release inflammatory substances that affect the functioning of organs and increase the risk of chronic conditions.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, it was found that individuals classified as obese had a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, compared to those in the normal weight range.
| Health Implications | Chubby | Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Slightly higher risk | Significantly increased risk |
| High Blood Pressure | Slightly higher risk | Significantly increased risk |
| Heart Disease | Slightly higher risk | Significantly increased risk |
| Stroke | Slightly higher risk | Significantly increased risk |
| Certain types of Cancer | Slightly higher risk | Significantly increased risk |
Preventing and managing obesity is essential for maintaining good overall health. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance on achieving a healthy weight, making sustainable lifestyle changes, and reducing the risk of obesity-related health problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is important to understand the difference between being chubby and being fat. Chubby individuals have a slightly higher body mass, giving them a plumper and fuller appearance, while fat individuals have an excess of body fat, resulting in an obese and overweight appearance. These terms are not interchangeable, and the distinction is primarily determined by factors such as Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference.
Body size can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and gender. Genetics play a role in determining an individual’s metabolism, fat storage, and overall body size. Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, can also impact body size. It’s important to note that maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall health, regardless of whether someone is chubby or fat.
While being chubby may not necessarily have serious health implications, being fat increases the risk of developing various health issues. These can include diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer. It is important for individuals who are overweight or obese to focus on making positive changes to their diet and exercise habits in order to reduce the risk of these health complications and promote a healthier body composition.
By understanding the difference between being chubby and being fat and taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy weight, individuals can improve their overall well-being and reduce the risk of various health concerns. It is important to embrace a balanced and healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a nutritious diet, and regular monitoring of one’s body mass and waist circumference.
FAQ
Is there a difference between being chubby and being fat?
Yes, being chubby refers to individuals with slightly raised body mass, giving them a plumper and fuller appearance. Being fat means having an excess of body fat, resulting in an appearance of obesity and being overweight.
How is the distinction between chubby and fat determined?
The distinction is primarily determined by factors such as Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference.
What is Body Mass Index (BMI) and how is it calculated?
BMI is a numerical measurement used to determine whether an individual’s body mass is healthy according to their height. It can be calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters.
Are chubby and fat interchangeable terms?
No, chubby and fat are not interchangeable. Chubby falls into the overweight category on the BMI chart, while fat falls into the obese category.
What factors can influence body size?
Body size can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and gender.
Are there health implications associated with being chubby and fat?
While being chubby may not necessarily have serious health implications, being fat increases the risk of developing various health issues such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.

![Ray Dalio Quotes [Principles, Life, Investment]](https://tagvault.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Screen-Shot-2023-04-19-at-7.57.49-PM.png)