As parents, it can be challenging to identify rashes and spots on our little ones. That’s why understanding the difference between heat rash and chickenpox is crucial for proper identification and care. Heat rash occurs when sweat glands become blocked, resulting in small red bumps and an itchy, prickly feeling. On the other hand, chickenpox is a viral infection that causes an itchy rash, spots, and fluid-filled blisters.
Recognizing the symptoms of each condition is essential to provide appropriate care and treatment. By familiarizing ourselves with the differences between heat rash and chickenpox, we can ensure the well-being of our children and make informed decisions about their health.
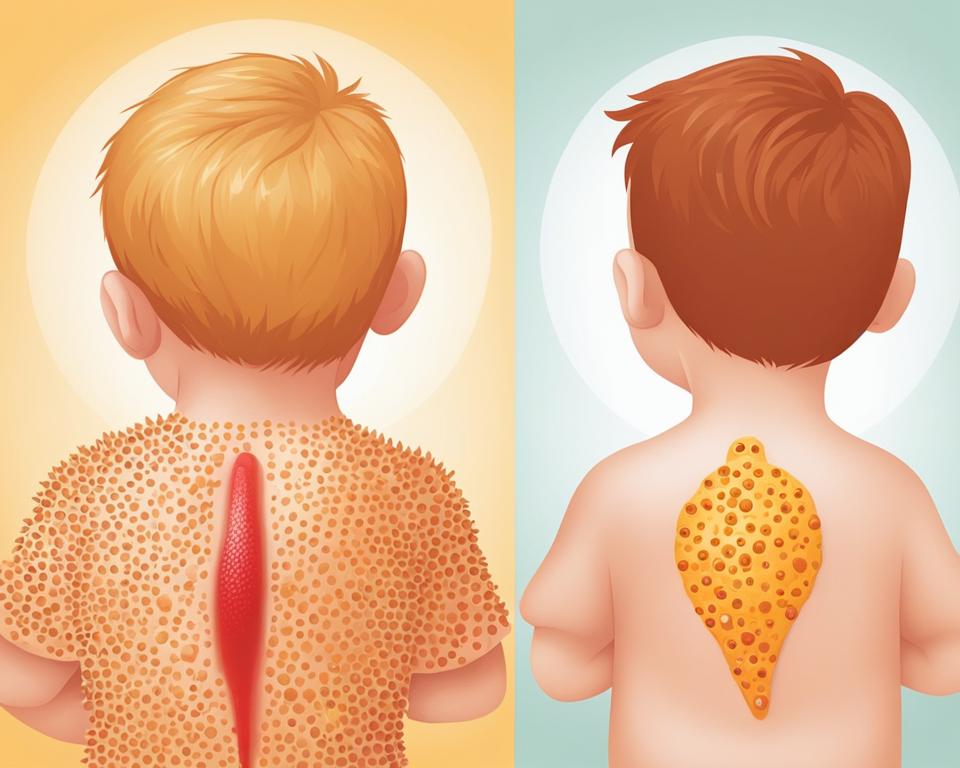
Key Takeaways:
- Heat rash is characterized by blocked sweat glands, resulting in small red bumps and itchiness.
- Chickenpox is a viral infection that causes an itchy rash, spots, and fluid-filled blisters.
- Understanding the symptoms of heat rash and chickenpox helps parents provide appropriate care and treatment.
- Proper identification of these conditions is crucial for making informed decisions about seeking medical attention.
- By recognizing the differences between heat rash and chickenpox, parents can ensure the well-being of their children.
Baby Rashes Checklist
When it comes to baby rashes, it’s essential for parents to follow a checklist to determine if further medical attention is necessary. By going through this checklist, you can ensure the well-being of your little one and provide them with the best care possible. Let’s take a closer look at the steps you should take:
- Check the baby’s temperature: Fever is often a sign that something is not right. Use a reliable thermometer to measure your baby’s temperature and monitor it closely.
- Observe any signs of illness: Be on the lookout for symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, or unusual behavior that might indicate an underlying condition.
- Perform the glass test: To check for signs of meningitis, press a clear glass against the baby’s rash. If the rash doesn’t fade under pressure, seek immediate medical attention.
- Ensure normal feeding: A baby with a rash should still have a healthy appetite. If your baby’s feeding routine is disrupted, consult a healthcare professional.
- Monitor urine and poo output: Keep track of your baby’s wet diapers and bowel movements. Any significant changes could be a cause for concern.
- Watch for signs of overheating: Excessive heat can worsen rashes and potentially cause other complications. Make sure your baby stays cool and comfortable.
- Evaluate skincare products: Consider if any new skincare products or washing powder have been introduced. Some ingredients may irritate your baby’s sensitive skin.
By completing this checklist, you can gather valuable information about your baby’s condition and make informed decisions regarding their care. Monitoring their symptoms, temperature, and overall well-being is crucial in ensuring their health and happiness.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a common viral illness that primarily affects children. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. The main symptom of chickenpox is an itchy rash that starts as red spots and develops into fluid-filled blisters. These blisters can cover the entire body, including the face, scalp, and genital area.
The rash typically appears in multiple stages, with new spots continuously erupting for several days. During the early stages, the spots may be small and red, resembling insect bites. As the disease progresses, the spots become itchy and eventually form blisters filled with clear fluid. These blisters can burst and crust over, leading to scab formation.
The varicella-zoster virus is highly contagious and spreads easily through direct contact with the fluid from the blisters or through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Individuals with chickenpox usually develop other symptoms as well, including a fever, headache, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
In rare cases, complications can arise from chickenpox, especially in adults, pregnant women, infants, and individuals with weakened immune systems. These complications may include bacterial infections of the skin, pneumonia, encephalitis (brain inflammation), and Reye’s syndrome (a rare but severe condition affecting the liver and brain).
It is important to recognize the symptoms of chickenpox to ensure proper care and prevent the spread of the virus. If you suspect that you or your child has chickenpox, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on treatment and management.
| Symptoms | Severity | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Itchy rash | Mild to severe | Appears 10-21 days after exposure and lasts 1-2 weeks |
| Spots | Multiple | Continuous outbreak over several days |
| Fluid-filled blisters | May burst and crust over | Progresses as the disease advances |
| Fever | Varies | Usually presents with other symptoms |
Heat Rash (Prickly Heat)
Heat rash, also known as prickly heat, occurs when sweat glands become blocked due to excessive sweating. It presents as small raised spots on the skin and is accompanied by an itchy and prickly feeling. Heat rash can occur anywhere on the body but is often seen in areas covered by clothing.
To prevent heat rash, it is important to keep the skin cool and well-hydrated. Avoiding excessive sweating through adequate ventilation, wearing loose and breathable clothing, and staying in a cool environment can help minimize the risk. Additionally, practicing good hygiene and keeping the affected areas clean can promote healing and prevent further irritation.
“Heat rash is a common condition that can be uncomfortable and irritating. It is important to take proactive measures to prevent and manage heat rash to ensure the comfort and well-being of your skin.”
In most cases, heat rash resolves on its own within a few days. However, if the rash persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as mild swelling or infection, it is recommended to seek medical advice.
Symptoms of Heat Rash (Prickly Heat)
Heat rash typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Small raised spots on the skin
- Itchy and prickly feeling
- Mild swelling in the affected areas
- Excessive sweating
Tips for Managing Heat Rash (Prickly Heat)
To manage heat rash and alleviate discomfort, consider the following:
- Keep the affected areas cool and dry
- Avoid tight and restrictive clothing
- Use gentle and hypoallergenic skincare products
- Avoid excessive exposure to heat and humidity
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Keep the affected areas clean and dry | Avoid scratching or picking at the rash |
| Apply calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream to soothe itching | Use oily or heavy moisturizers |
| Wear loose and breathable clothing | Expose the affected areas to direct sunlight |
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral illness caused by the paramyxovirus family. It spreads through infected saliva, making it essential to take proper precautions to prevent its transmission. Measles is characterized by various symptoms, including:
- A high temperature
- Runny or blocked nose
- Sneezing
- Coughing
- Red, sore, or watery eyes
- A fine red rash that starts small and becomes blotchy
If you suspect that you or someone you know has measles, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate care. Measles can also cause sensitivity to light, making it important to seek medical attention promptly.
“Measles is a highly contagious disease that can lead to serious health complications, especially in young children. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent measles and protect against its severe consequences.”
– Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Eczema
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. It is characterized by dry and cracked skin that can be itchy and sore. Environmental factors can play a significant role in triggering eczema flare-ups. Factors such as weather changes, exposure to dust mites and pollen, certain fabrics, and food allergies can worsen the symptoms of eczema.
One of the most common forms of eczema in children is atopic eczema. It typically appears as small areas of dry skin that occasionally itch. It can be challenging to manage atopic eczema, but with the right approach, it can be kept under control.
Proper management of eczema involves identifying and avoiding triggers that worsen the condition. This may include using hypoallergenic skincare products, wearing breathable fabrics, and regularly moisturizing the skin to prevent dryness. In severe cases, topical steroids may be prescribed by a healthcare professional to reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
It is important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for eczema. They can provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, recommend suitable skincare products, and prescribe appropriate medications to manage eczema effectively.
| Environmental Factors | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Weather changes | – Dry and cracked skin |
| Dust mites and pollen | – Itching and soreness |
| Certain fabrics | – Skin irritation |
| Food allergies | – Flare-ups |
Quotes:
“Living with eczema can be challenging, but with proper management and the right skincare routine, it is possible to lead a comfortable life.”
- Identify and avoid triggers that worsen eczema.
- Use hypoallergenic skincare products.
- Moisturize regularly to prevent dryness.
- Wear breathable fabrics.
- Consult with a dermatologist for personalized treatment options.
Meningitis
Meningitis is a serious infection that affects the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacteria or viruses and requires immediate medical attention. One of the key symptoms of meningitis is a non-blanching rash, which means that the rash does not fade when pressed with a glass. This type of rash is a crucial sign of meningococcal septicaemia, a severe form of meningitis.
Other symptoms of meningitis may include:
- High fever
- Poor feeding
- Pale eyelids
- Blueness on the inside of the mouth
- A high-pitched cry
If your baby or child shows any of these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Meningitis can progress rapidly and lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
Understanding the Non-Blanching Rash
The non-blanching rash associated with meningitis is characterized by red or purple spots that do not fade when pressed. It is important to note that not all cases of meningitis will present with a rash. However, if a rash is present and does not fade under pressure, it should be considered a medical emergency.
The non-blanching rash in meningitis is caused by bleeding under the skin, resulting from damage to blood vessels. It is essential to recognize this symptom as it indicates a severe infection that requires urgent treatment.
Signs of Meningococcal Septicaemia
Meningococcal septicaemia is a life-threatening form of meningitis caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis. In addition to the non-blanching rash, there are other signs that may indicate the presence of septicaemia:
- Rapid breathing
- Cold hands and feet
- Lethargy (excessive sleepiness or lack of energy)
- Irritability
- Stiff neck and body
If your baby or child exhibits any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Meningococcal septicaemia can progress rapidly and cause severe complications, including organ damage and even death.
Meningitis is a serious infection that requires immediate medical intervention. It is essential to be aware of the non-blanching rash, along with other symptoms such as high fever, pale eyelids, blueness, and poor feeding. If you suspect your baby or child has meningitis, do not hesitate to seek urgent medical care.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a common bacterial skin condition that primarily affects children. It is characterized by red, fluid-filled blisters that, when burst, form a yellow scab. This contagious infection can be spread through direct contact with the sores or blisters.
Proper hygiene is crucial in preventing the spread of impetigo. Regularly washing hands and avoiding contact with infected individuals can significantly reduce the chances of contracting the infection.
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat impetigo. Topical antibiotic creams or ointments can be applied directly to the affected areas to eliminate the bacteria and promote healing. In some cases, oral antibiotics may be necessary for more severe infections or if the impetigo is widespread.
It’s important to note that impetigo can be highly contagious, especially when the sores or blisters are present. Children with impetigo should avoid close contact with others, such as playing sports or attending school, until the infection has completely healed.
| Key Points | Treatment | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Impetigo is a bacterial skin condition. | Antibiotics, such as topical creams or oral medication, are used to treat impetigo. | Practice good hygiene and avoid close contact with infected individuals. |
| Keep the affected areas clean and dry, and apply antibiotic ointment as directed. | Regularly wash hands with soap and water or use hand sanitizer. | |
| Seek medical attention if the infection worsens or spreads. | Avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or clothing, with infected individuals. |
Baby Acne
Baby acne is a common skin condition that many infants experience. It is characterized by the presence of small pimples or whiteheads on a baby’s skin. While it may be concerning for parents, it is important to note that baby acne is harmless and typically does not cause any discomfort to the baby.
The exact cause of baby acne is unknown, but it is believed to be related to the hormones passed from the mother to the baby during pregnancy. These hormones can stimulate the baby’s oil glands, leading to the development of acne. Baby acne can appear at birth or develop within the first few weeks of life.
Most of the time, baby acne will disappear on its own without any specific treatment. It is important for parents to resist the urge to pop or squeeze the pimples, as this can lead to further irritation and potential infections. Instead, it is best to gently cleanse the baby’s face with mild, fragrance-free baby soap and water.
It is important for parents to understand that baby acne is a temporary condition. In most cases, it will resolve on its own within a few weeks or months. However, if the baby acne persists or worsens, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician for further evaluation and guidance.
Key Points:
- Baby acne is a common condition characterized by small pimples or whiteheads on a baby’s skin.
- It is a harmless condition that does not cause any discomfort to the baby.
- The exact cause of baby acne is unknown, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes.
- Baby acne typically disappears on its own without any specific treatment.
- Gently cleansing the baby’s face with mild, fragrance-free soap and water is recommended.
- If the baby acne persists or worsens, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician for further evaluation.
Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria or nettle rash, are characterized by the appearance of red patches on the skin. These red patches, often accompanied by raised bumps, can develop suddenly and may be itchy or cause a burning sensation. Hives can vary in size and shape, ranging from small spots to larger welts.
One of the common causes of hives is allergies. Allergies to certain foods, medications, insect bites, or environmental factors can trigger an allergic reaction, leading to the development of hives. When the body releases histamine as a response to these allergens, blood vessels in the skin can become leaky, resulting in the red patches and swelling associated with hives.
In some cases, hives may be an indication of a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis, which can cause swelling of the face, lips, or throat. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical attention.
Relief for Hives
If you or your child experiences hives, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Depending on the severity and underlying cause of the hives, antihistamine medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation. Antihistamines work by blocking the release of histamine, effectively reducing the redness, itchiness, and swelling associated with hives.
It is important to note that while antihistamines can provide temporary relief from hives, addressing the underlying cause of the allergic reaction is key to preventing future outbreaks. Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as specific foods or medications, can help minimize the risk of future hives episodes.
In summary, hives are characterized by the presence of red patches on the skin, often accompanied by itching and swelling. They can be triggered by various allergies and may require the use of antihistamines for symptom relief. Seeking medical attention is crucial, especially in cases of severe allergic reactions accompanied by swelling or difficulty breathing.
Fifth Disease
Fifth disease, also known as erythema infectiosum, is a mild viral illness that primarily affects children. It is characterized by a bright red facial rash followed by a lacy rash on the body. The rash typically appears after experiencing flu-like symptoms. Fifth disease is usually not serious and resolves on its own. However, pregnant women should be cautious as it can cause complications for the fetus.
If a child develops a bright red facial rash that spreads to the body in a lacy pattern, it could be a sign of fifth disease. Other symptoms may include:
- Low-grade fever
- Headache
- Sore throat
- Runny nose
The rash of fifth disease typically lasts for about one to three weeks and may come and go. It is important to note that the rash may temporarily worsen with heat, cold, or sunlight exposure.
Transmission of Fifth Disease
Fifth disease is spread through respiratory secretions, such as saliva or nasal mucus, when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also be contracted through blood transfusions or from an infected pregnant woman to her unborn baby.
Treatment and Prevention
There is no specific treatment for fifth disease, as it usually resolves on its own without complications. However, treatment may focus on managing symptoms such as fever and pain. It is important to ensure adequate rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers as advised by a healthcare professional.
To prevent the spread of fifth disease, practicing good respiratory hygiene, such as covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, can help reduce the risk of transmission. It is also important to avoid close contact with infected individuals, especially pregnant women.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management if fifth disease is suspected. They can provide further guidance on treatment options and any necessary precautions, particularly for pregnant women.
Conclusion
Identifying the differences between heat rash and chickenpox is vital for parents to provide appropriate care for their children. Heat rash, caused by blocked sweat glands, appears as small raised spots, while chickenpox is a viral infection that results in an itchy rash, spots, and fluid-filled blisters. By understanding and recognizing the symptoms of these conditions, parents can make informed decisions about seeking medical attention and administering the necessary treatment.
Heat rash, also known as prickly heat, is triggered by excessive sweating and can be managed by keeping the skin cool and well-hydrated. On the other hand, chickenpox is highly contagious and caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It requires proper care and measures to prevent the spread of the virus.
To differentiate between heat rash and chickenpox, it is important to pay attention to the specific symptoms exhibited by the child. Heat rash typically includes an itchy and prickly feeling, whereas chickenpox presents with a more severe itchiness and the presence of fluid-filled blisters. By closely observing these symptoms and considering the overall condition of the child, parents can effectively identify and address the issue.
FAQ
What is the difference between heat rash and chickenpox?
Heat rash occurs when sweat glands become blocked, causing small red bumps and an itchy, prickly feeling. Chickenpox, on the other hand, is a viral infection that causes an itchy rash, spots, and fluid-filled blisters.
How can I determine if further medical attention is required for my baby’s rash?
It is important to go through a checklist, which includes checking the baby’s temperature, observing if they look unwell, performing the glass test to identify signs of meningitis, ensuring they are still feeding normally, checking their urine and poo output, monitoring for signs of overheating, and evaluating if any new skincare products or washing powder have been used that could potentially irritate the baby’s skin.
What are the symptoms of chickenpox?
Chickenpox is characterized by an itchy rash, spots, and fluid-filled blisters. The rash typically appears first as red spots, which then develop into itchy blisters. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus and is highly contagious.
What is heat rash?
Heat rash, also known as prickly heat, occurs when sweat glands become blocked due to excessive sweating. It presents as small raised spots on the skin and is accompanied by an itchy and prickly feeling. It is important to keep the skin cool and well-hydrated to prevent heat rash.
What are the symptoms of measles?
Measles is characterized by a high temperature, runny/blocked nose, sneezing, coughing, red, sore, or watery eyes, and a fine red rash that starts small and becomes blotchy. It is caused by a virus in the paramyxovirus family and can be spread through infected saliva.
What is eczema?
Eczema is a common skin condition characterized by dry and cracked skin that can be itchy and sore. It is often triggered by environmental factors such as weather, dust mites, pollen, certain fabrics, and food allergies. Atopic eczema is the most common form in children, appearing as small areas of dry skin that occasionally itch.
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
Meningitis is a serious infection that affects the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. The rash associated with meningitis is a non-blanching rash, meaning it does not disappear under pressure. Other symptoms include a high fever, pale eyelids, blueness on the inside of the mouth, poor feeding, and a high-pitched cry. Immediate medical attention is crucial if meningitis is suspected.
What is impetigo?
Impetigo is a common bacterial skin condition that primarily affects children. It is characterized by red, fluid-filled blisters that, when burst, form a yellow scab. Impetigo is highly contagious and can be treated with antibiotic cream.
What is baby acne?
Baby acne is a harmless condition characterized by small pimples or whiteheads on a baby’s skin. It is a common occurrence and typically disappears on its own without treatment. Baby acne can appear at birth or develop within the first few weeks of life.
What are hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria or nettle rash, manifest as red patches on the skin. They can be triggered by various allergies, including food, medicine, and insect bites. Hives can be itchy and may indicate an allergic reaction. In severe cases, hives can be accompanied by swelling and require immediate medical attention.
What is fifth disease?
Fifth disease, also known as erythema infectiosum, is a mild viral illness that primarily affects children. It is characterized by a bright red facial rash followed by a lacy rash on the body. The rash typically appears after experiencing flu-like symptoms. Fifth disease is usually not serious and resolves on its own.

