Maps play a crucial role in our understanding of the world around us. They provide a visual representation of geographical information, helping us explore and navigate through various locations. There are different types of maps, each serving a specific purpose and showcasing different aspects of our planet. In this article, we will explore the different types of maps, such as physical maps, political maps, topographic maps, climate maps, and thematic maps. Let’s dive in and discover the fascinating world of maps!
Key Takeaways:
- There are various types of maps, including physical maps, political maps, topographic maps, climate maps, and thematic maps.
- Physical maps showcase the natural features of a place, such as rivers, mountains, and forests.
- Political maps focus on the boundaries of countries, states, and cities.
- Topographic maps represent changes in elevation using contour lines.
- Climate maps provide information about the climate of an area, including temperature and rainfall.
Political Maps
Political maps are an essential tool for understanding the boundaries and subdivisions of a place. These maps depict the political units such as countries, states, and cities, highlighting the administrative divisions and their spatial relationships. By visually representing the political organization of an area, political maps provide valuable information for educational, research, and reference purposes.
One of the main features of political maps is the clear demarcation of boundaries between different political units. These boundaries are typically represented as solid lines, distinguishing one country or state from another. Political maps also indicate the locations of major cities, capital cities, and significant water features such as rivers and lakes.
For educational purposes, political maps play a crucial role in helping students understand the complex political subdivisions of their own country and the world. These maps facilitate the exploration and analysis of political, social, and economic systems within a geographic context.
Furthermore, political maps are an indispensable tool for travelers, as they provide valuable information about political boundaries and administrative divisions. When planning trips or navigating unfamiliar territories, political maps are helpful in understanding the different states or provinces one may be crossing and can assist in route planning and decision-making.
Physical Maps
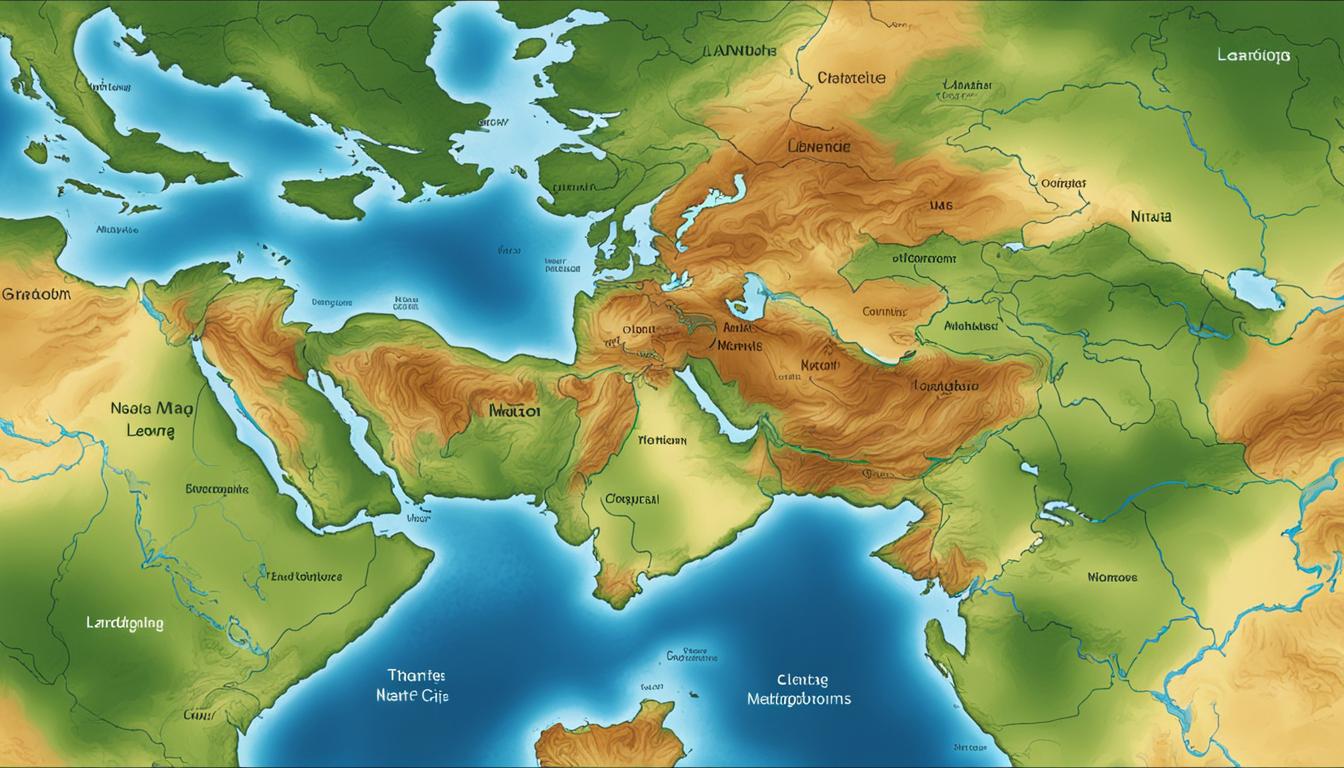
Physical maps are an essential tool for visualizing and understanding the natural features of a place. These maps provide a detailed depiction of the physical characteristics of an area, such as rivers, mountains, forests, and other landforms. Using colors to represent different elevations, physical maps offer a comprehensive view of the landscape, allowing users to explore and analyze the geographical features of a region.
One of the key benefits of physical maps is their ability to showcase the diversity and beauty of the Earth’s surface. By highlighting rivers, users can trace their paths and understand their importance in shaping the landscape. Mountain ranges are depicted with varying shades of brown, representing different elevations and allowing viewers to appreciate the towering peaks and rugged terrain. Forests, portrayed in lush greens, give insights into the extent and distribution of vegetation across the area.
Physical maps provide a visual understanding of the physical characteristics of an area.
These maps are particularly useful for outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, and adventurers who rely on accurate geographical information. By studying physical maps, they can plan their routes, identify potential challenges or natural barriers, and discover scenic spots along the way. Additionally, physical maps are valuable tools for educational purposes, allowing students to learn about the Earth’s diverse landscapes and the forces that have shaped them over time.
The Importance of Physical Maps in Geography Education
Physical maps play a pivotal role in geography education. They enable students to develop spatial awareness, understand the relationship between physical features and human activities, and explore patterns and connections between different regions. By analyzing physical maps, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and develop critical thinking skills by interpreting the information presented.
| Key Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Rivers | Highlighted using blue lines, representing the flow of water across the landscape. |
| Mountains | Depicted with varying shades of brown, allowing users to distinguish between different elevations and steepness. |
| Forests | Portrayed in vibrant green, illustrating the extent and distribution of vegetation in a region. |
By studying physical maps, students can also explore the impact of physical features on climate, settlement patterns, and economic activities. For example, they can analyze how mountains influence weather patterns, how rivers have shaped civilizations, or how forests contribute to biodiversity and natural resource availability.
In conclusion, physical maps are invaluable tools for understanding the physical characteristics of a place. By visually representing rivers, mountains, forests, and other natural features, these maps provide a comprehensive and engaging way to explore the Earth’s diverse landscapes. Whether for outdoor adventures or educational purposes, physical maps offer a wealth of information and insights into the wonders of our planet.
Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are a type of map that provides detailed information about the elevation changes in a particular area. These maps are commonly used by hikers, geologists, and other outdoor enthusiasts to navigate and understand the terrain. Unlike physical maps that use colors to represent different elevations, topographic maps use contour lines.
Contour lines are curved lines that connect points of the same elevation. They help visualize the shape and characteristics of the land, indicating steep slopes, valleys, and flat areas. Closer contour lines indicate steeper terrain, while wider spaces between lines represent flatter terrain.
By studying topographic maps, individuals can plan their routes, identify potential obstacles, and gain a better understanding of the land’s features. These maps are invaluable tools for hikers and mountaineers, allowing them to assess the difficulty of a trail or expedition and make informed decisions based on the terrain.
| Symbol | Representation |
|---|---|
| Contour Lines | Indicate changes in elevation |
| Rivers/Lakes | Blue lines/show water bodies |
| Forests | Green color/depict vegetation |
| Mountains | Brown color/represent high elevations |
Symbols on Topographic Maps
Topographic maps also use symbols to represent various land features. For example, blue lines depict rivers and lakes, while green color indicates forests and vegetation. Mountains are represented by brown color, highlighting their high elevations. These symbols help users quickly identify and interpret different elements on the map, enhancing their understanding of the terrain.
Overall, topographic maps serve as invaluable tools for outdoor enthusiasts and professionals alike. Whether you’re planning a hiking trip or conducting geological research, these maps provide crucial information about elevation changes, contour lines, and the physical landscape. By understanding and utilizing topographic maps effectively, individuals can navigate the land confidently and make informed decisions based on the terrain.
Climate Maps
Climate maps are a valuable tool for understanding the climate patterns and characteristics of different regions. These maps provide visual representations of climatic zones and help us analyze temperature and rainfall variations. By using colors and symbols, climate maps depict the different climatic regions, making it easier to identify and interpret weather patterns. They are widely used in various fields, including agriculture, urban planning, and environmental research.
One of the key features of climate maps is the representation of temperature variations. Warmer regions are often depicted in shades of red or orange, while cooler regions are displayed in shades of blue or green. This color coding helps us identify areas with similar temperature ranges and understand the overall temperature distribution across a geographic area. In addition to temperature, climate maps also showcase rainfall patterns, using different shades of blue to indicate areas of high precipitation and lighter shades to represent regions with lower rainfall.
Example of a Climate Map
Let’s take a look at an example of a climate map for the United States. This map uses color coding to represent different climatic zones across the country. In the southern states, such as Florida and Texas, we can see shades of red and orange, indicating warm temperatures. As we move northward, the colors transition to shades of green and blue, signifying cooler climates. The map also shows areas with high rainfall, such as the Pacific Northwest, which is depicted in darker shades of blue, while arid regions like the southwestern states are shown in lighter shades. Overall, this climate map provides a clear visual representation of the temperature and rainfall patterns across the United States.
| Climate Zone | Temperature Range (°F) | Rainfall (inches) |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical | 70-90 | 50-100 |
| Temperate | 50-70 | 20-50 |
| Subarctic | 20-50 | 10-40 |
| Arctic | Below 20 | Less than 10 |
This table provides further details about the different climate zones and their corresponding temperature ranges and rainfall levels. It helps us understand the specific climatic characteristics of each zone, allowing for better analysis and interpretation of the climate map. By referring to the table and the map together, researchers, planners, and individuals can gain valuable insights into the climate patterns and make informed decisions based on the climatic conditions of a particular area.
Thematic Maps: Visualizing Data on Specific Themes
Thematic maps are a valuable tool for representing data related to a specific theme or topic on a geographical map. Unlike other types of maps that focus on physical features or political boundaries, thematic maps highlight patterns and trends in relation to the chosen theme. These maps utilize various visual elements such as colors, symbols, and labels to effectively convey information.
The Power of Thematic Maps
Thematic maps allow us to explore and understand data in a geographic context. They can represent a wide range of themes, including population, resources, climate, economics, and more. By overlaying data onto a map, thematic maps provide visual insights that can enhance our understanding of the world.
“Thematic maps are a powerful tool for analyzing and communicating complex data in a simplified and visually engaging way.” – Data Analyst
For example, a thematic map displaying population density can reveal patterns of high or low population concentrations in different areas. Similarly, a thematic map showcasing natural resources can help identify regions rich in minerals, forests, or agricultural land. These maps play a crucial role in research, planning, and decision-making processes.
Creating Meaningful Thematic Maps
When creating thematic maps, it is important to carefully select and represent the data in a meaningful way. The choice of colors, symbols, and labels should be based on the theme and the intended message. The map’s design should be clear, intuitive, and visually engaging, allowing users to easily interpret and analyze the data.
By harnessing the power of thematic maps, we can gain valuable insights into the world around us, uncover patterns and trends, and make informed decisions based on the data represented. These maps provide an effective means of communicating complex information and encourage a deeper understanding of various themes and their geographic implications.
| Examples of Thematic Maps | Theme | Visual Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Population Density | Population distribution and concentration | Graduated colors or dot density |
| Climate | Temperature or rainfall variations | Color-coded climatic zones |
| Natural Resources | Availability of minerals, forests, or agricultural land | Symbols or patterns |
| Economics | Income levels or economic activity | Choropleth maps or proportional symbols |
Road Maps
Road maps are an essential tool for navigation, providing detailed information about highways, cities, and various points of interest. These maps are designed to guide travelers from one location to another, making them indispensable for both local and long-distance journeys. Whether in print or digital format, road maps offer a wealth of information to help travelers plan their routes and explore new places.
When using a road map, highways are prominently displayed, along with major roads and thoroughfares. Cities are marked with symbols such as dots or circles, allowing travelers to easily identify urban areas along their route. Additionally, road maps often highlight points of interest such as parks, campgrounds, and tourist attractions, making it convenient to plan stops and explore the surrounding areas.
One of the key features of road maps is their focus on navigation. They provide accurate and up-to-date information about the road network, including exit numbers, rest areas, and toll booths. This enables travelers to make informed decisions while on the road, ensuring a smooth and efficient journey. Road maps are particularly useful for those who prefer to navigate without relying solely on GPS devices or digital maps.
Benefits of Road Maps:
- Accurate representation of highways, roads, and cities
- Detailed information about points of interest along the route
- Useful for planning stops and exploring the surrounding areas
- Reliable navigation tool, especially for those who prefer non-digital options
In conclusion, road maps play a crucial role in helping travelers navigate their way from one place to another. With their comprehensive representation of highways, cities, and points of interest, road maps provide valuable information and guidance to ensure a smooth and enjoyable journey. Whether you prefer the traditional paper maps or digital versions, road maps are an indispensable companion for any traveler.
| Key Features of Road Maps | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Clear depiction of highways, roads, and cities | Easy identification of routes and urban areas |
| Points of interest marked on the map | Convenient planning for sightseeing and stops |
| Accurate and up-to-date road information | Reliable navigation tool for effective travel |
| Available in print and digital formats | Adaptable to different preferences and needs |
Scale of a Map
The scale of a map plays a crucial role in accurately representing distances and measurements on the Earth’s surface. It provides a reference point for understanding the relationship between the map and the actual physical dimensions of the area it represents. The scale is typically presented as a ratio or a line with units of measurement, allowing users to gauge the size and distance of different features on the map.
For example, a map with a scale of 1:10,000 means that one unit of measurement on the map represents 10,000 units in the real world. This allows users to estimate distances between points and calculate the size of features accurately. Understanding the scale is essential for navigation, planning routes, and determining the feasibility of travel or transportation.
A well-defined scale helps users interpret the map’s level of detail and precision. A small-scale map shows a larger area with less detail, while a large-scale map zooms in on a smaller area with greater detail. It’s important to note that scale can vary depending on the purpose and type of map. For example, a world map typically has a smaller scale, while a city map has a larger scale to provide more detailed information about streets, landmarks, and buildings.
Determining Distance on a Map
To measure distance on a map, users can utilize the scale to calculate the actual length of a line or path. This can be done by using a ruler or a straight edge to measure the length on the map, and then multiplying it by the scale factor to determine the real-world distance. For example, if the length of a path on a map is 4 inches and the scale is 1:50,000, the actual distance would be 200,000 inches or about 3.16 miles.
It’s important to note that the accuracy of distance measurements on a map depends on the scale and the level of detail provided. Large-scale maps provide more accurate measurements as they cover smaller areas with higher precision. Additionally, factors such as the projection used in the map can also affect the accuracy of distance measurements. Understanding the scale and its implications is essential for accurate interpretation and analysis of geographic information.
| Scale Ratio | Representation | Actual Distance |
|---|---|---|
| 1:1,000 | 1 inch | 1,000 inches or about 83.33 feet |
| 1:10,000 | 1 inch | 10,000 inches or about 833.33 feet |
| 1:100,000 | 1 inch | 100,000 inches or about 8,333.33 feet |
| 1:1,000,000 | 1 inch | 1,000,000 inches or about 83,333.33 feet |
Tables are an effective way of presenting scale ratios and their corresponding representations of actual distances on a map. The table above showcases various scale ratios and the real-world distances they represent. It demonstrates the importance of understanding the scale to accurately interpret the size and distances on a map. By utilizing the scale provided, map users can navigate, plan, and understand geographical information with confidence.
Symbols on Maps
Maps utilize a variety of symbols to represent different features and elements, providing users with a visual understanding of the landscape. These symbols serve as a key to deciphering the information portrayed on the map. Cities, for example, are often depicted as black dots or circles, allowing individuals to quickly identify their locations. Roads, highways, and railways are represented by different lines, enabling efficient navigation.
Natural features such as trees and forests are commonly displayed in green, providing a clear indication of their presence. Mountains, on the other hand, are depicted in brown, allowing users to easily identify areas of elevated terrain. Bodies of water, including lakes and rivers, are typically represented in blue, ensuring a distinct visual separation from the surrounding landscape. These symbols work together to create a comprehensive and accessible map for users.
“Symbols on maps are like a universal language, enabling individuals from different backgrounds to understand and interpret geographic information effectively.”
By using symbols, maps are able to efficiently convey information about various features and landmarks. They help users quickly identify and interpret different elements on the map, enabling them to navigate their surroundings with ease. Whether it’s finding the nearest city, planning a route, or exploring the natural landscape, symbols on maps play a vital role in representing key information in a visually engaging and accessible manner.
Types of Map Symbols
The symbols used on maps can vary depending on the purpose and type of map. Some common types of map symbols include:
- Point symbols: Representing features such as cities, landmarks, and points of interest.
- Line symbols: Depicting various transportation routes such as roads, highways, and railways.
- Polygon symbols: Used to represent areas such as parks, forests, and bodies of water.
- Text symbols: Providing labels and names for cities, streets, and other geographic features.
- Color symbols: Employing different colors to represent thematic data or distinguish between different types of features.
These symbols, along with their combinations and variations, help create a comprehensive visual representation of the world around us. They enable us to navigate, explore, and understand the geographic landscape and its diverse features.
| Symbol | Representation |
|---|---|
| City | Black dot or circle |
| Road | Solid line |
| Highway | Thicker solid line |
| Railway | Dashed or dotted line |
| Trees/Forests | Green color |
| Mountains | Brown color |
| Bodies of Water | Blue color |
Conclusion
In conclusion, maps play a crucial role in helping us understand and navigate the world around us. From physical maps that depict the natural features of a place to political maps that show the boundaries of countries and states, each type of map serves a specific purpose. Climate maps provide valuable insights into the climate patterns of different regions, while thematic maps highlight data related to specific themes such as population or resources.
Whether you’re planning a trip, conducting research, or simply curious about the world, understanding the different types of maps can enhance your knowledge and perspective. Road maps are essential for navigation, while topographic maps help visualize changes in elevation. Symbols on maps enable us to identify and interpret different elements, such as cities, roads, and features.
By familiarizing ourselves with various types of maps, we can gain a better understanding of the world in which we live. So next time you come across a map, take a moment to appreciate the valuable information it provides and the stories it tells. Maps are fascinating tools that allow us to explore and make sense of our planet.
FAQ
What are the different types of maps?
The different types of maps include physical maps, political maps, topographic maps, climate maps, and thematic maps.
What is the purpose of political maps?
Political maps are used to depict the boundaries between countries, states, and other political units.
What do physical maps show?
Physical maps show the physical features of a place, such as rivers, mountains, and forests.
How do topographic maps represent elevation changes?
Topographic maps use contour lines to indicate changes in elevation.
What information do climate maps provide?
Climate maps provide information about the climate of an area, including rainfall distribution and temperature variations.
What is the focus of thematic maps?
Thematic maps focus on a specific theme or topic, such as population or resources.
What is the purpose of road maps?
Road maps are designed for navigation purposes, providing detailed information about highways, roads, and major cities.
What does the scale of a map indicate?
The scale of a map indicates the relationship between distances on the map and the actual distances on the Earth’s surface.
How are different features represented on maps?
Different features are represented using symbols, such as cities shown with dots, roads depicted with lines, and bodies of water displayed in blue.

![Ray Dalio Quotes [Principles, Life, Investment]](https://tagvault.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Screen-Shot-2023-04-19-at-7.57.49-PM.png)