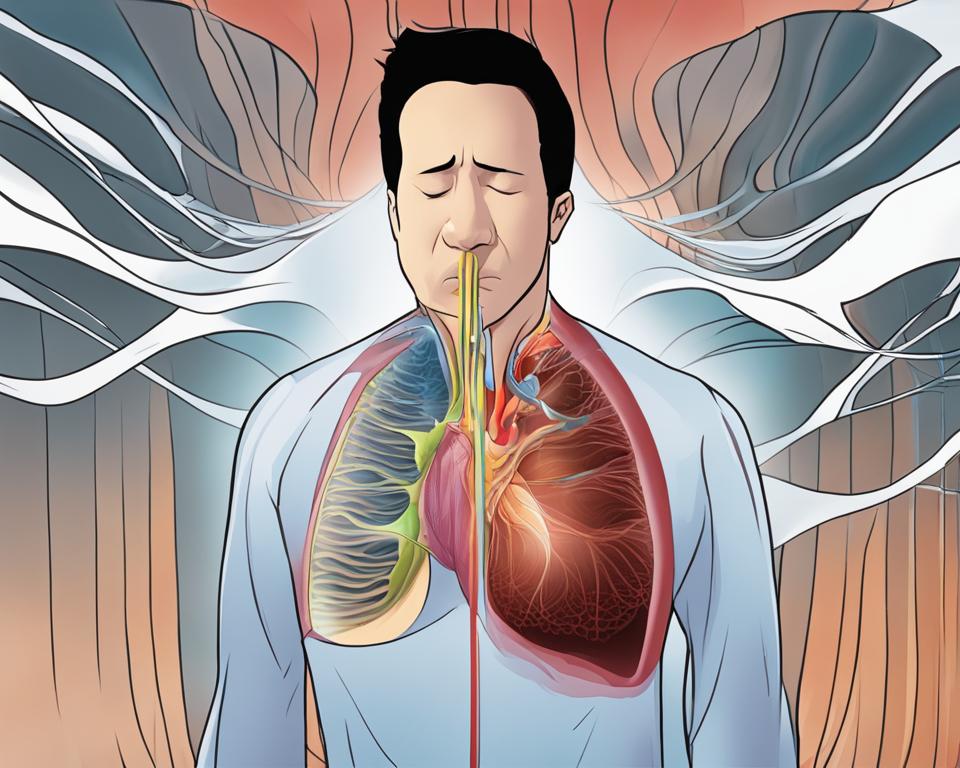
Auscultation is an important part of the respiratory examination and can help diagnose respiratory disorders. Understanding the underlying pathophysiology of lung sounds can provide insights into disease processes. The frequency, intensity, and timbre of breath sounds can help distinguish normal from abnormal sounds. Turbulent and vorticose airflow are responsible for breath sound production, while laminar flow is silent. Breath sounds can be affected by factors such as frequency, amplitude, and quality.
Key Takeaways:
- Excessive breathing noise can be a symptom of underlying respiratory disorders.
- Auscultation is a noninvasive diagnostic technique used to assess lung sounds.
- Understanding the characteristics of breath sounds can aid in the diagnosis of respiratory conditions.
- Proper auscultation technique and patient positioning are important for accurate assessment.
- Irregular breath sounds may indicate the presence of lung or airway issues that require medical attention.
The Importance of Auscultation in Respiratory Examination
Auscultation is a crucial component of the respiratory examination, allowing healthcare professionals to gain valuable insights into the health of the lungs. By listening to the breath sounds generated during auscultation, clinicians can detect and diagnose various pulmonary diseases. This cost-effective and noninvasive technique provides vital information about the trachea-bronchial tree, helping to assess airflow and identify any abnormalities.
Auscultation plays a significant role in the bedside teaching and clinical assessment of patients. Despite advancements in technology, the value of this manual examination should not be overlooked. It allows for a more personal and holistic approach to patient care, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s respiratory health.
During auscultation, different lung sounds can be detected, including normal breath sounds and adventitious sounds such as crackles, wheezing, and rhonchi. These sounds provide important clues about the underlying pathophysiology of respiratory disorders. By carefully analyzing the frequency, intensity, and quality of breath sounds, healthcare professionals can differentiate between normal and abnormal sounds, aiding in the accurate diagnosis and management of respiratory conditions.
Table: Common Breath Sounds
| Sound | Description |
|---|---|
| Tracheal sounds | Heard over the trachea, high-pitched and harsh |
| Vesicular breath sounds | Heard over most of the lung fields, low-pitched and soft |
| Bronchial breath sounds | Heard over the manubrium, higher in pitch with expiration longer than inspiration |
| Rhonchi | Low-pitched sounds caused by airflow through fluid or mucus in the larger airways |
| Crackles | High-pitched sounds caused by the movement of air through fluid-filled air sacs |
| Wheezing | High-pitched whistling sounds resulting from narrowed bronchial tubes |
| Stridor | Harsh vibratory sounds due to upper airway narrowing |
Understanding Breath Sound Characteristics
Breath sounds, a vital component of respiratory examination, can provide valuable insights into respiratory health. These sounds have three main characteristics: frequency, amplitude, and quality. Understanding these characteristics is key to distinguishing between normal and abnormal breath sounds.
Frequency: Frequency refers to the number of sound waves per second and determines the pitch of the sound. Normal breath sounds peak at frequencies below 100 Hz and are categorized into low, middle, and high frequency groups.
Amplitude: Amplitude is related to the energy of the sound waves and determines the loudness of the sound. It indicates how forcefully air is moving through the airways. Higher amplitude results in a louder sound, while lower amplitude produces a softer sound.
Quality: Quality or timbre differentiates sounds that have the same pitch and loudness. It helps identify specific characteristics of the breath sound, such as whether it is harsh, musical, or wheezing in nature.
Understanding these breath sound characteristics is essential for healthcare professionals in diagnosing respiratory conditions effectively. By analyzing the frequency, amplitude, and quality of breath sounds, medical professionals can gain valuable insights into patients’ respiratory health and identify any abnormalities that may require further investigation or treatment.
Performing Auscultation Properly
Auscultation is a fundamental technique used in respiratory examination to assess lung sounds and detect abnormalities. To ensure accurate results, it is important to perform auscultation properly. Here are some methods and techniques to consider:
1. Preparation:
Before starting the auscultation, ensure that you are in a quiet room with minimal background noise. It is ideal to have the patient in a sitting position, as this allows for better access to all areas of the chest.
2. Warm-Up and Placement:
Prior to use, warm up the stethoscope by rubbing the earpieces between your hands. This helps to prevent any discomfort for the patient. Place the stethoscope directly on the skin, avoiding any clothing or barriers that may interfere with sound transmission.
3. Patient Instructions:
Ask the patient to take deep breaths through their open mouth, as this allows for better airflow and clearer sounds. Instruct them to breathe slowly and deeply to fully evaluate the breath sounds in different areas of the chest.
4. Auscultation Technique:
Start the auscultation at the apices of the lungs and move downward on both the front and back of the chest. Compare symmetrical points on both sides of the chest to identify any differences. Pay close attention to the quality, intensity, and presence of adventitious sounds such as crackles or wheezes.
By following these methods and techniques, you can ensure that auscultation is performed accurately and efficiently, providing valuable insights into the respiratory health of your patients.
Normal and Abnormal Breath Sounds
Proper auscultation of breath sounds is essential in diagnosing respiratory conditions. By understanding the characteristics of normal and abnormal breath sounds, healthcare professionals can identify potential issues and provide appropriate treatment. Here, we explore different types of breath sounds and what they may indicate.
Vesicular Breath Sounds
Vesicular breath sounds are heard over most of the lung fields and are considered normal. These sounds are characterized by a soft, low-pitched rustling sound, similar to the sound of wind blowing through leaves. Vesicular breath sounds are a result of air moving through the smaller airways and air sacs in the lungs. They can be heard during both inhalation and exhalation.
Bronchial Breath Sounds
Bronchial breath sounds are normal over the trachea, but abnormal when heard in other areas of the lungs. These sounds are louder and higher-pitched than vesicular breath sounds and resemble air passing through a hollow tube. Bronchial breath sounds are caused by air flowing through the larger airways closer to the trachea, such as the bronchi. They are heard primarily during inspiration.
Abnormal Breath Sounds
Abnormal breath sounds can be indicative of underlying respiratory conditions. Some examples of abnormal breath sounds include:
- Rhonchi: Low-pitched sounds caused by fluid or mucus in the bronchial tubes.
- Crackles: High-pitched sounds caused by the movement of air through fluid-filled air sacs.
- Wheezing: High-pitched whistling sounds resulting from narrowed bronchial tubes.
- Stridor: Harsh vibratory sounds due to upper airway narrowing.
These abnormal breath sounds can suggest various respiratory conditions, such as pneumonia, asthma, or bronchitis. If you experience any abnormal breath sounds, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and appropriate treatment.
| Type of Breath Sound | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Vesicular | Soft, low-pitched rustling sound heard over most of the lung fields | Normal |
| Bronchial | Louder and higher-pitched sound resembling air passing through a hollow tube | Normal over the trachea, abnormal in other areas of the lungs |
| Rhonchi | Low-pitched sounds caused by fluid or mucus in the bronchial tubes | Pneumonia, bronchitis, COPD |
| Crackles | High-pitched sounds caused by air passing through fluid-filled air sacs | Pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis, heart failure |
| Wheezing | High-pitched whistling sounds resulting from narrowed bronchial tubes | Asthma, bronchitis, COPD |
| Stridor | Harsh vibratory sounds due to upper airway narrowing | Croup, foreign body obstruction, epiglottitis |
Causes of Irregular Breath Sounds
Irregular breath sounds can be indicative of various underlying respiratory issues. Some common causes include pneumonia, COVID-19 infection, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, bronchitis, and foreign body or obstruction in the lungs or airways. Let’s take a closer look at each of these conditions:
- Pneumonia: This is an infection that causes inflammation of the air sacs in the lungs. It can lead to the accumulation of fluid and pus, resulting in abnormal breath sounds like crackles or rhonchi.
- COVID-19 infection: The respiratory symptoms associated with COVID-19, such as cough and shortness of breath, can also cause irregular breath sounds. In severe cases, pneumonia may develop, leading to further abnormalities in lung sounds.
- Heart failure: When the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, fluid can accumulate in the lungs, causing breath sounds like crackles. This accumulation of fluid, known as pulmonary edema, can lead to breathing difficulties.
- COPD: This chronic lung disease, which includes conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema, can result in wheezing and diminished breath sounds due to airway obstruction and inflammation.
- Asthma: Asthma is characterized by recurrent episodes of wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can cause irregular breath sounds.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs, can lead to breath sounds like wheezing or crackles.
- Foreign body or obstruction: If there is an object or blockage in the airways, it can cause irregular breath sounds, particularly stridor, which is a harsh vibrating sound.
It’s important to note that these are just some of the potential causes of irregular breath sounds. Each condition may have its own unique set of symptoms and diagnostic criteria. If you are experiencing abnormal breath sounds or respiratory symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
If you experience breathing difficulty, it is important to understand when it may require immediate medical attention. Breathing difficulty can be a symptom of various respiratory conditions and may indicate a medical emergency in certain cases. One such alarming sign is cyanosis, which refers to a bluish coloration of the skin and mucous membranes.
Other signs that may indicate a need for emergency medical attention include nasal flaring, abdominal breathing, accessory muscle use, and stridor, which is a harsh vibratory sound resulting from upper airway narrowing. These signs suggest that there may be an obstruction in the upper airway or a lack of sufficient oxygen supply. If you or someone around you experiences sudden, severe breathing difficulty accompanied by cyanosis or any of these other signs, it is crucial to seek immediate medical help.
Medical professionals will be able to assess the severity of the situation, provide appropriate interventions, and determine the underlying cause of the irregular breathing sounds. Prompt medical attention can help prevent further complications and ensure that the necessary treatments are administered in a timely manner.
Remember, if you are unsure whether your breathing difficulty requires emergency attention, it is always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical help. Your health and well-being are of utmost importance, and healthcare professionals are there to provide the necessary care and support in times of medical emergencies.
Real-Life Example
“I suddenly found it extremely difficult to breathe, and my skin started turning blue. I was terrified and immediately called for an ambulance. It turned out that I had a severe upper airway obstruction, and prompt medical attention saved my life. Don’t hesitate to seek emergency help if you experience breathing difficulty accompanied by cyanosis or other alarming signs.”
Diagnosing Irregular Breath Sounds: Understanding the Importance of Medical History and Tests
When it comes to identifying the underlying causes of irregular breath sounds, medical professionals rely on a combination of patients’ medical history and diagnostic tests. A thorough review of the individual’s medical background is crucial in providing valuable insights into potential risk factors, previous conditions, and medications that may contribute to respiratory issues. Additionally, a range of tests can be conducted to further investigate and diagnose the root cause of irregular breath sounds.
Understanding a patient’s medical history plays a pivotal role in diagnosing irregular breath sounds. By assessing past and current health conditions, as well as the medications being taken, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into potential triggers and underlying factors. This comprehensive review allows for a more accurate assessment and targeted approach towards resolving the respiratory issue at hand.
In addition to medical history, a variety of diagnostic tests may be ordered to provide a clearer understanding of the irregular breath sounds. Tests such as CT scans, chest X-rays, blood tests, pulmonary function tests, and sputum cultures can provide essential information on lung structure, function, and the presence of infections or inflammation. These tests help to confirm or rule out potential diagnoses and guide healthcare professionals in determining the most appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options for Irregular Breath Sounds
When it comes to treating irregular breath sounds, the approach depends on the specific diagnosis. The goal is to address the underlying cause and provide relief to the patient. Here are some common treatment options:
Medications
In cases where infections or inflammation are causing the irregular breath sounds, medications may be prescribed. Antibiotics can help clear up bacterial infections, while anti-inflammatory drugs may be used to reduce swelling in the airways. Bronchodilators are often prescribed to open up the airways and improve breathing.
Breathing Treatments
For conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or bronchitis, breathing treatments can be effective. Inhalers are commonly used to deliver medication directly to the lungs, helping to relax the airway muscles and alleviate symptoms. These treatments can help manage and control irregular breath sounds, improving overall respiratory function.
Hospitalization
In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to address fluid buildup in the lungs or airway obstructions. This allows for more intensive treatment and monitoring to ensure the patient receives the necessary care. Medical professionals can provide oxygen support, administer intravenous medications, and closely monitor the patient’s condition.
It’s important to remember that the most appropriate treatment plan will depend on the individual’s specific situation and the underlying cause of the irregular breath sounds. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment recommendations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, accurate analysis of breathing sounds plays a crucial role in diagnosing respiratory conditions. By understanding the characteristics and causes of irregular breath sounds, individuals can take the necessary steps to seek appropriate medical attention and receive effective treatment.
It is important to remember that maintaining proper respiratory health is essential for overall well-being. Regular auscultation and monitoring of breath sounds can help identify any abnormalities and allow for prompt intervention.
Whether it’s identifying normal breath sounds or recognizing the presence of abnormal ones such as rhonchi, crackles, wheezing, or stridor, a comprehensive understanding of respiratory health is key. By prioritizing respiratory examinations and following proper auscultation techniques, healthcare professionals can provide accurate diagnoses and develop tailored treatment plans to improve the quality of life for individuals with respiratory disorders.
FAQ
Why do I breathe so loud?
Excessive breathing noise can be caused by various factors, such as respiratory disorders, narrowed airways, or abnormal lung sounds. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
What is the importance of auscultation in respiratory examination?
Auscultation is a crucial diagnostic technique used to assess airflow through the trachea-bronchial tree and detect pulmonary diseases. It provides valuable information about lung sounds, adventitious sounds, and vocal resonance, aiding in the diagnosis and management of respiratory conditions.
What are the characteristics of breath sounds?
Breath sounds have three main characteristics: frequency, amplitude, and quality. Frequency determines the pitch of the sound, amplitude determines the loudness, and quality or timbre differentiates sounds with the same pitch and loudness.
How should auscultation be performed properly?
Auscultation should be done in a quiet room, with the patient in a sitting position. The stethoscope should be warmed up before use, and auscultation should be performed directly on the skin. The patient should take deep breaths through the open mouth, and auscultation should be done starting at the apices and moving downward on both the front and back of the chest.
What are normal and abnormal breath sounds?
Normal breath sounds include tracheal sounds, vesicular breath sounds, and bronchial breath sounds. Abnormal breath sounds can manifest as rhonchi, crackles, wheezing, or stridor. These abnormal sounds can indicate underlying respiratory issues.
What causes irregular breath sounds?
Irregular breath sounds can be caused by various conditions, including pneumonia, COVID-19 infection, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, bronchitis, or foreign body obstruction in the lungs or airways.
When should I seek emergency medical attention for breath sounds?
If breathing difficulty is sudden, severe, or accompanied by cyanosis (bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes), it may be a medical emergency. Other signs of emergency include nasal flaring, abdominal breathing, accessory muscle use, and stridor. Immediate medical attention should be sought in such cases.
How can I determine the cause of irregular breath sounds?
To determine the cause of irregular breath sounds, a thorough medical history review, including current and past medical conditions and medications, is essential. Additional tests such as CT scans, chest X-rays, blood tests, pulmonary function tests, and sputum cultures may be ordered to further investigate the underlying issue.
What are the treatment options for irregular breath sounds?
Treatment options for irregular breath sounds depend on the specific diagnosis. Medications may be prescribed to clear infections or open the airways. Breathing treatments, such as inhalers, may be recommended for conditions like asthma, COPD, or bronchitis. Severe cases may require hospitalization to address fluid in the lungs or airway obstructions.
What is the importance of accurate auscultation and understanding of breath sounds?
Accurate auscultation and understanding of breath sounds are crucial in diagnosing respiratory conditions. By recognizing the characteristics and causes of irregular breath sounds, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention and receive effective treatment, contributing to their overall respiratory health.

![Ray Dalio Quotes [Principles, Life, Investment]](https://tagvault.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Screen-Shot-2023-04-19-at-7.57.49-PM.png)