Have you ever wondered why we hiccup? Hiccups are an involuntary reflex that everyone experiences at some point in their lives. They can occur unexpectedly and often catch us off guard. While other reflexes like sneezing and coughing have clear purposes, the exact reason for hiccups remains unknown.
Hiccups are typically considered a minor annoyance or inconvenience, lasting only a few minutes. However, persistent hiccups that last for more than 48 hours or occur frequently may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition. Understanding the causes and triggers of hiccups can help shed light on this curious reflex.
Key Takeaways:
- Hiccups are an involuntary reflex that everyone experiences.
- The purpose of hiccups is still unknown.
- Persistent hiccups lasting over 48 hours may indicate an underlying health issue.
- Hiccups can be triggered by various factors, including trauma, infections, and central nervous system issues.
- Home remedies and medical interventions can provide relief for persistent hiccups.
The Mechanics of Hiccups
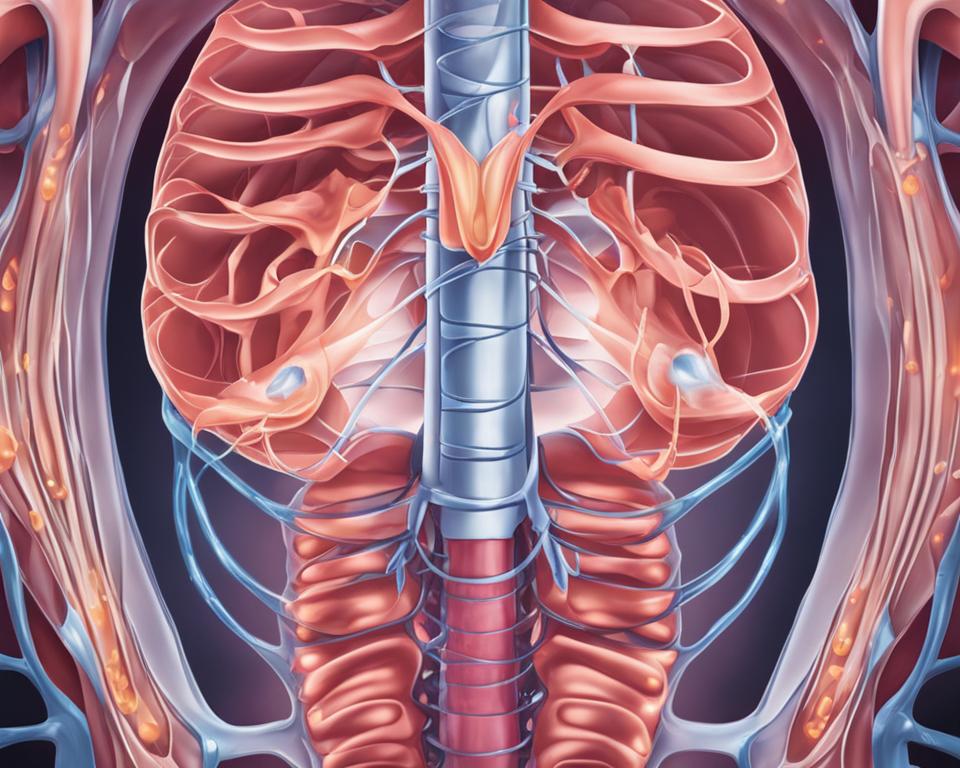
Hiccups are caused by involuntary contractions of the diaphragm muscle, which is responsible for breathing. These contractions cause a sudden intake of air, followed by the closure of the vocal cords, resulting in the characteristic “hic” sound. The exact reason why these muscle contractions occur is still unknown, but they are thought to be triggered by various factors.
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs and above the stomach. It plays a crucial role in the breathing process, contracting and relaxing to facilitate the intake and expulsion of air. During hiccups, the diaphragm contracts involuntarily, causing a brief interruption in the rhythmic breathing pattern. This sudden contraction creates a forceful inhalation, which is immediately halted by the closure of the vocal cords, resulting in the familiar “hiccup” sound.
While the exact triggers for hiccups are not fully understood, it is believed that certain factors can stimulate the diaphragm and initiate the reflexive contractions. These triggers can include both internal and external stimuli, such as swallowing air, eating too quickly, consuming carbonated beverages, sudden changes in temperature, or excitement or stress. The diaphragm’s sensitivity to these triggers can vary from person to person, which may explain why some individuals are more prone to experiencing hiccups than others.
| Common Triggers of Hiccups | Less Common Triggers of Hiccups |
|---|---|
|
|
While hiccups are generally harmless and short-lived, persistent or chronic hiccups that last for extended periods of time can be indicative of an underlying medical condition. In such cases, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Triggers of Hiccups
Hiccups can be triggered by various factors, including trauma, infections, abdominal distention, and central nervous system issues. Understanding the potential triggers of hiccups can help shed light on why they occur and how to manage them.
Trauma
Physical trauma, such as head injuries, can stimulate the nerves that control the diaphragm and lead to hiccups. The impact or injury disrupts the normal functioning of the diaphragm muscle, causing it to contract involuntarily and resulting in hiccups.
Infections
Certain infections, like meningitis, can irritate the nerves involved in the hiccup reflex, leading to persistent hiccups. Inflammation in the brain and spinal cord can disrupt the normal communication between the diaphragm and the brain, triggering uncontrollable contractions of the diaphragm muscle.
Abdominal Distention
When the stomach or intestines become distended or bloated, it can irritate the diaphragm muscle and cause hiccups. Conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), overeating, or swallowing air can lead to increased abdominal pressure and subsequently trigger hiccups.
Central Nervous System Issues
Problems with the central nervous system, such as tumors or lesions affecting the brain or spinal cord, can disrupt the normal coordination between the diaphragm and the brain. This disruption can result in abnormal contractions of the diaphragm muscle, leading to hiccups.
| Trigger | Description |
|---|---|
| Trauma | Physical injuries or impacts that stimulate the nerves controlling the diaphragm, causing involuntary contractions and hiccups. |
| Infections | Certain infections like meningitis can irritate the nerves involved in the hiccup reflex, leading to persistent hiccups. |
| Abdominal Distention | Conditions like GERD, overeating, or swallowing air can increase abdominal pressure and irritate the diaphragm, triggering hiccups. |
| Central Nervous System Issues | Tumors or lesions affecting the brain or spinal cord can disrupt the coordination between the diaphragm and the brain, resulting in hiccups. |
While these are common triggers of hiccups, it’s important to note that each individual may have unique triggering factors. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause of hiccups can be crucial in managing and finding relief from this involuntary reflex.
The Duration of Hiccups
Hiccups are usually a temporary and harmless reflex that lasts only a few minutes. However, there are cases where hiccups can persist for an extended period of time, raising concerns about underlying health issues. Persistent hiccups, which last for more than 48 hours, can be a sign of an underlying problem and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
In rare cases, hiccups can last for months, causing weight loss and extreme tiredness. These long-lasting hiccups, known as intractable hiccups, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. If hiccups are interfering with eating, sleeping, or breathing, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
While most hiccups resolve on their own without medical intervention, persistent hiccups may require a thorough evaluation to identify any underlying health issues. By addressing the underlying cause, healthcare professionals can provide targeted treatment options to alleviate the symptoms and improve the patient’s overall well-being.
Unusual Cases of Hiccups
While hiccups are a common occurrence, there have been rare and extreme cases that stand out due to their duration or unusual triggers. These cases shed light on the unpredictable nature of hiccups and the potential variability in their causes and manifestations.
Hiccups with Extreme Durations
One notable case is that of Charles Osborne, who holds the Guinness World Record for the longest bout of hiccups. Osborne experienced hiccups for a staggering 68 years, starting in 1922 and ending in 1990. Another extraordinary case is that of Christopher Sands, who endured 10 million hiccups over a period of 27 months. These extreme durations of hiccups highlight the significant impact they can have on an individual’s life and well-being.
Unusual Triggers for Hiccups
In addition to their duration, hiccups can also be triggered by unusual factors. For example, there have been reported cases where a single strand of hair brushing against the tympanic membrane, or eardrum, triggered hiccups. In another instance, a brain tumor pressing on the phrenic nerve, which controls the diaphragm muscle involved in hiccups, caused persistent hiccups. These cases highlight the complexity of the hiccup reflex and the diverse range of triggers that can set it off.
Table: Unusual Cases of Hiccups
| Case | Duration of Hiccups | Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| Charles Osborne | 68 years | N/A |
| Christopher Sands | 27 months | N/A |
| Unknown Case 1 | 2 weeks | Hair brushing against tympanic membrane |
| Unknown Case 2 | 3 months | Brain tumor pressing on phrenic nerve |
These unusual cases of hiccups serve as a reminder of the complexity of the human body and the mysteries that still surround certain aspects of our physiological functions. While these extreme cases are rare, they offer valuable insights into the variability of hiccups and the need for further research to better understand and treat this involuntary reflex.
Proposed Explanations for Hiccups
Despite the common occurrence of hiccups, the exact purpose and evolutionary significance of this reflex remain largely unknown. Scientists have put forth several theories to explain why we hiccup, but none have provided a definitive answer. One proposed explanation suggests that hiccups serve as a reflex to move food along the digestive tract. When we hiccup, it may help to push food down the esophagus and prevent it from entering the airway. However, this theory does not account for why hiccups occur even when the stomach is empty.
Another theory revolves around fetal development. Some researchers believe that hiccups in the womb aid in the development of the respiratory system. By practicing the contraction of the diaphragm muscle, the fetus strengthens its breathing muscles in preparation for life outside the womb. While this theory provides some insights into the purpose of hiccups, it fails to explain why hiccups persist beyond infancy and into adulthood.
It is important to note that these proposed explanations for hiccups are not definitive and are still subject to ongoing research and debate. The exact purpose of hiccups remains an intriguing mystery in the field of evolutionary biology. Future studies may shed more light on this curious reflex and provide a clearer understanding of its underlying mechanisms and significance.
Table: Theories of Hiccup Purpose
| Theory | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reflex to move food | Hiccups help push food down the esophagus. |
| Fetal development | Hiccups strengthen respiratory muscles in the womb. |
| Other theories | Additional theories include hiccup as a byproduct of nerve signaling or a regulation mechanism for the respiratory system. |
While these theories provide some potential explanations for why we hiccup, it is important to remember that the hiccup reflex is complex and may have multiple underlying causes. The true purpose of hiccups may involve a combination of factors that have yet to be fully understood. Further research is needed to unravel the evolutionary purpose of hiccups and explore the fascinating world of this involuntary reflex.
Possible Treatments for Hiccups
If you find yourself with a case of hiccups that just won’t quit, there are several methods you can try to stop them. These treatments range from simple home remedies to more advanced medical interventions, depending on the severity and duration of your hiccups.
Home Remedies for Hiccups
When it comes to home remedies, there are a few tricks that may help stop hiccups. One popular method is to hold your breath for a short period of time, which can help reset your diaphragm and stop the hiccup reflex. Another approach is to drink a glass of water in one continuous sip, as this can help regulate your breathing and disrupt the hiccup cycle.
Other home remedies include sipping cold water, eating a spoonful of sugar, or breathing into a paper bag. These techniques aim to interrupt the hiccup reflex and restore normal breathing. While these remedies may work for some people, it’s important to note that results can vary, and what works for one person may not work for another.
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Hold your breath | Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you can, then exhale slowly. This can help regulate your breathing and stop hiccups. |
| Drink water | Take a glass of water and drink it in one continuous sip. This can help reset your diaphragm and interrupt the hiccup reflex. |
| Breathe into a paper bag | Place a small paper bag over your mouth and nose, and breathe in and out slowly. This can help regulate your breathing and potentially stop hiccups. |
Medical Interventions
If home remedies don’t provide relief or if your hiccups persist for an extended period of time, it may be necessary to seek medical interventions. Medications such as muscle relaxants or sedatives can be prescribed to help relax the diaphragm and stop hiccups. In some cases, certain procedures like acupuncture or nerve blocks may be used to alleviate persistent hiccups.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if your hiccups are interfering with your daily life or causing significant discomfort. They will be able to assess your specific situation and recommend the most appropriate treatment options for you.
Remember, hiccups are usually harmless and temporary, but persistent hiccups may be a sign of an underlying health issue. If you’re experiencing prolonged or frequent episodes of hiccups, it’s always best to seek medical advice to ensure proper evaluation and management of your condition.
Hiccups and Underlying Health Conditions
Hiccups, although usually harmless, can sometimes be a symptom of underlying health conditions. If you experience hiccups that persist for an extended period of time or are accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention. Here are some underlying health conditions that may cause hiccups:
- Ear infections: Hiccups can occur as a result of irritation or inflammation in the ear, such as in the case of an infection.
- Kidney failure: Hiccups can be a sign of kidney failure, which can disrupt the body’s electrolyte balance and lead to involuntary muscle contractions.
- Laryngitis: Inflammation of the larynx can cause hiccups, along with other symptoms like hoarseness and difficulty speaking.
- Hernia: A hiatal hernia, which occurs when the upper part of the stomach protrudes into the chest through the diaphragm, can cause hiccups.
It is important to pay attention to the frequency and duration of your hiccups, as well as any accompanying symptoms. If hiccups are causing significant discomfort or interfering with your daily life, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, perform diagnostic tests if necessary, and provide appropriate treatment options to address the underlying health condition.
When to See a Doctor
While hiccups are often harmless and resolve on their own, there are certain signs and symptoms that may indicate the need for medical attention:
- Persistent hiccups lasting for more than 48 hours
- Hiccups that are accompanied by severe or worsening pain
- Hiccups that interfere with eating, sleeping, or breathing
- Unexplained weight loss or fatigue
- Development of new or worsening symptoms along with hiccups
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek prompt medical evaluation to determine the cause of your hiccups and receive appropriate treatment.
Table: Underlying Health Conditions and Hiccups
| Underlying Health Condition | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Ear infections | Ear pain, hearing loss, fever |
| Kidney failure | Decreased urine output, swelling, fatigue |
| Laryngitis | Hoarseness, difficulty speaking, sore throat |
| Hernia | Chest pain, difficulty swallowing, reflux |
Hiccups in Different Populations
Hiccups can affect people of all ages, including infants. Newborns and babies often experience hiccups, which are considered a normal part of their development. These hiccups are thought to occur as the baby’s diaphragm and respiratory system mature. Hiccups in babies are typically short-lived and harmless, resolving on their own without any intervention. However, if your baby experiences persistent hiccups or if they interfere with feeding or sleeping, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician for further evaluation.
Hiccups can also occur in individuals after eating certain foods. Spicy or greasy meals, for example, are known to trigger hiccups in some people. The exact mechanism behind this is not fully understood, but it is believed that these foods may irritate the diaphragm or stimulate the nerves responsible for the hiccup reflex. In most cases, hiccups after eating are temporary and resolve on their own. If they become persistent or occur frequently, it may be worth exploring dietary modifications or seeking medical advice.
Stress and heightened emotions can also trigger hiccups in some individuals. When we experience stress, our body’s sympathetic nervous system becomes activated, leading to various physiological responses, including changes in breathing patterns. These changes can potentially trigger hiccups. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, may help alleviate stress-related hiccups. Additionally, addressing the underlying causes of stress can contribute to overall wellbeing and reduce the likelihood of experiencing hiccups as a result of stress.
Overall, hiccups can occur in babies, after eating certain foods, and as a result of stress. While hiccups are generally harmless and temporary in nature, it is important to monitor them and seek medical advice if they become persistent, interfere with daily activities, or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms. By understanding the triggers and behaviors associated with hiccups, we can better manage and alleviate their occurrence.
Unanswered Questions About Hiccups
Despite extensive research, there are still many unanswered questions about hiccups. Scientists and researchers continue to investigate the exact triggers and purpose of this curious reflex. Ongoing research focuses on uncovering the underlying mechanisms and evolutionary biology of hiccups, seeking to shed light on their significance in human physiology.
One of the unanswered questions is why hiccups occur in the first place. While various triggers have been identified, such as trauma, infections, and central nervous system issues, the exact reason for the diaphragm’s involuntary contractions remains unclear. Additionally, the purpose of hiccups still puzzles scientists. Proposed explanations range from clearing the esophagus to strengthening respiratory muscles during fetal development, but none have provided a fully comprehensive understanding.
Ongoing research on hiccups and evolutionary biology aims to explore the evolutionary significance of this reflex. Understanding why hiccups have persisted throughout human evolution may provide valuable insights into our physiological development and functioning. By uncovering the evolutionary purpose of hiccups, scientists hope to gain a deeper understanding of this intriguing reflex and its potential implications for human health.
| Unanswered Questions About Hiccups | Ongoing Research | Hiccups and Evolutionary Biology |
|---|---|---|
| Why do hiccups occur? | Scientists and researchers | Exploring the evolutionary significance |
| The purpose of hiccups | Proposed explanations | Uncovering the evolutionary purpose |
| Research on hiccups and evolutionary biology | Triggers of hiccups | Deeper understanding of this reflex |
Through ongoing research and scientific inquiry, we hope to unravel the mysteries surrounding hiccups. By addressing these unanswered questions, we can gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating reflex and potentially develop more effective treatments for persistent hiccups.
Home Remedies for Hiccups
When hiccups strike, it’s natural to look for quick and easy ways to stop them. Fortunately, there are several home remedies and natural techniques that may provide relief. These remedies aim to interrupt the hiccup reflex and restore normal breathing. Here are a few methods you can try:
- Holding your breath: Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you comfortably can. This helps to reset the diaphragm and stop the hiccups.
- Drinking a glass of water in one continuous sip: This technique involves drinking a full glass of water without stopping. It helps to regulate the breathing pattern and may alleviate hiccups.
- Eating a spoonful of sugar: Swallowing a spoonful of sugar can stimulate the vagus nerve and disrupt the hiccup reflex.
- Breathing into a paper bag: Breathing into a paper bag can help increase the carbon dioxide levels in your blood, which may stop hiccups.
These home remedies are simple, cost-effective, and worth a try when you’re looking for relief from hiccups. However, if your hiccups persist for an extended period of time or are accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention.
While these remedies may provide temporary relief, persistent hiccups can be a sign of an underlying health condition. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Remember:
“Sometimes, simple home remedies can be surprisingly effective in stopping hiccups. Give these techniques a try the next time you find yourself hiccuping, but don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if your hiccups persist or worsen.”
Overall, home remedies can serve as a first-line approach in managing hiccups. However, it’s essential to be aware of any underlying health conditions that may be contributing to the hiccups. If hiccups become a frequent or chronic occurrence, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hiccups are a common and intriguing reflex that occurs in people of all ages. While the exact purpose of hiccups remains unknown, they are generally harmless and temporary in nature. However, if hiccups persist for an extended period of time or are accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to rule out any underlying health conditions.
There are various home remedies and medical interventions that can provide relief for persistent hiccups. From holding your breath to trying natural techniques like breathing into a paper bag, these remedies aim to interrupt the hiccup reflex and restore normal breathing. Additionally, ongoing research is shedding light on the underlying mechanisms of hiccups, which may lead to more effective treatments in the future.
Overall, while hiccups may be a minor annoyance, understanding the hiccup reflex and exploring potential treatments is an important area of study. Further research is needed to unravel the mysteries of hiccups and their evolutionary significance. In the meantime, it is reassuring to know that most hiccups are harmless and will resolve on their own.
FAQ
Why do people hiccup?
The purpose of hiccups remains unknown, but they are caused by involuntary contractions of the diaphragm muscle.
What triggers hiccups?
Hiccups can be triggered by various factors, including trauma, infections, abdominal distention, and central nervous system issues.
How long do hiccups last?
Most hiccups only last a few minutes, but persistent hiccups that last for more than 48 hours may be a sign of an underlying health problem.
Are there any unusual cases of hiccups?
There have been rare cases of extreme hiccups, such as the Guinness World Record holder for the longest bout of hiccups and unusual triggers like a hair brushing against the ear or a brain tumor pressing on a nerve.
What are the proposed explanations for hiccups?
Several theories have been proposed, including clearing the esophagus and strengthening respiratory muscles in fetal development, but none have been proven.
How can hiccups be treated?
Home remedies like holding your breath or drinking water can be tried, and medical interventions like medication or nerve blocks may be necessary for persistent hiccups.
Can hiccups be a sign of an underlying health condition?
Yes, persistent hiccups or hiccups accompanied by other symptoms can be a symptom of underlying health conditions like ear infections, kidney failure, laryngitis, or a hernia.
Do hiccups affect people of all ages?
Yes, hiccups can affect people of all ages, including infants. They can also be triggered by certain foods and stress.
What unanswered questions remain about hiccups?
Despite extensive research, the exact trigger and purpose of hiccups are still unknown, and ongoing research aims to uncover their underlying mechanisms and evolutionary significance.
Are there any home remedies for hiccups?
Yes, home remedies like holding your breath, drinking a glass of water, eating sugar, or breathing into a paper bag can be tried to stop hiccups.
What are the final thoughts on hiccups?
Hiccups are a common and temporary reflex, but persistent hiccups should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Ongoing research is shedding light on potential treatments and the biology of hiccups.

![Ray Dalio Quotes [Principles, Life, Investment]](https://tagvault.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Screen-Shot-2023-04-19-at-7.57.49-PM.png)